
Cape Verde is a group of arid Atlantic islands which are home to distinct communities of plants, birds, and reptiles. The islands constitute the unique Cape Verde Islands dry forests ecoregion, according to the World Wildlife Fund.

Macaronesia is a collection of four volcanic archipelagos in the North Atlantic Ocean, off the coasts of the continents of Africa and Europe. Each archipelago is made up of a number of Atlantic oceanic islands, which are formed by seamounts on the ocean floor that have peaks above the ocean's surface. Some of the Macaronesian islands belong to Portugal, some belong to Spain, and the rest belong to Cape Verde. Politically, the islands belonging to Portugal and Spain are part of the European Union. Geologically, Macaronesia is part of the African tectonic plate. Some of its islands – the Azores – are situated along the edge of that plate at the point where it abuts the Eurasian and North American plates.

The trocaz pigeon, Madeira laurel pigeon or long-toed pigeon is a pigeon which is endemic to the island of Madeira. It is a mainly grey bird with a pinkish breast; its silvery neck patch and lack of white wing markings distinguish it from its close relative and probable ancestor, the common wood pigeon. Its call is a characteristic six-note cooing, weaker and lower-pitched than that of the wood pigeon. Despite its bulky, long-tailed appearance, this pigeon has a fast, direct flight.

Dracaena draco, the Canary Islands dragon tree or drago, is a subtropical tree in the genus Dracaena, native to the Canary Islands, Cape Verde, Madeira, western Morocco, and is thought to be introduced in the Azores. Its closest living relative is the dragon blood tree of Socotra, Dracaena cinnabari.

The Cape Verde Islands dry forests is a tropical and subtropical dry broadleaf forests ecoregion in the Cape Verde Islands, which constitute the country of Cabo Verde. The islands lie off the western coast of Africa.

Sideroxylon is a genus of trees in the family Sapotaceae described as a genus by Linnaeus in 1753. They are collectively known as bully trees. The generic name is derived from the Greek words σιδηρος (sideros), meaning "iron", and ξύλον (xylon), meaning "wood."

The wildlife of Cape Verde is spread over its archipelago of ten islands and three islets, which all have parks under their jurisdiction by decree promulgated by the Cape Verde government. Located off the west coast of Africa, the total land area of the island nation is 4,564 square kilometres (1,762 sq mi). The wildlife consists of many tropical dry forest and shrub land, endemic flora and fauna, and rare breeding seabirds and plants, which are unique to this group of islands.

Prunus lusitanica, the Portuguese laurel cherry or Portugal laurel, is a species of flowering plant in the rose family Rosaceae, native to southwestern France, Spain, Portugal, Morocco, and Macaronesia.

Ilex canariensis, the small-leaved holly, is an endemic species of holly native to Macaronesian islands. It is a species of plant in the family Aquifoliaceae. It is found in the Macaronesian islands of Madeira (Portugal) and Canary Islands (Spain).

Ocotea foetens, commonly called til or stinkwood is a species of tree in the family Lauraceae. It is evergreen and grows up to 40 m tall. It is a common constituent of the laurisilva forests of Madeira and the Canary Islands. Leaf fossils of this species are known from the Mio-Pleistocene of Madeira Island.

Rhamnus glandulosa is a species of plant in the family Rhamnaceae. It is endemic to Madeira and the Canary Islands.

Globularia amygdalifolia is a flowering plant of the family Plantaginaceae. The species is endemic to Cape Verde. It is listed as an endangered species by the IUCN.

Davallia canariensis, the hare's-foot fern, is a species of fern in the family Davalliaceae. It is endemic to Macaronesia and the Iberian Peninsula. It grows well in a sunny atmosphere and amongst rocks.
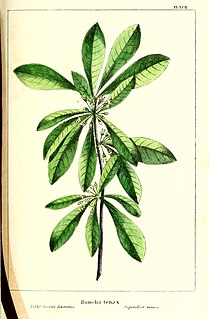
Sideroxylon tenax, called the tough bully, is a plant species native to Florida, Georgia, South Carolina and the southernmost part of North Carolina. It grows on dry, sandy soil in pine forests, pine-oak woodlands, and hummocks at elevations less than 100 m.

Monte Graciosa is a mountain in the northern part of the island of Santiago in Cape Verde. It lies 2.5 km north of the town of Tarrafal, overlooking the Baía de Tarrafal. Its elevation is 643 m. Towards the west it ends in the headland of Ponta Preta. It is part of a larger proposed natural park. The mountain is of volcanic origin, composed of phonolite and rich in feldspar and olivine.

Echium vulcanorum is a species of flowering plants of the family Boraginaceae. The species is endemic to Cape Verde. It is listed as an endangered plant by the IUCN. The species was first described in 1935 by Auguste Chevalier. Its local name is língua-de-vaca, a name that may also refer to the related species Echium hypertropicum and Echium stenosiphon. The oil of its seeds contains γ-linolenic acid, and is used for medicinal and dietary purposes.

Salix pedicellata is a species of willow. It is a shrub or small tree to about 6–8 m tall, native around the Mediterranean Sea from Portugal to Lebanon and Syria in the north and from the Canary Islands to Tunisia in the south. Salix canariensis may be treated as a subspecies of S. pedicellata.

The Madeira evergreen forests is a laurissilva ecoregion of southwestern Europe. It covers the archipelago of Madeira and some nearby islands in the Atlantic Ocean. Laurel forest, known as laurissilva, once covered the islands. Over centuries the forests were mostly cleared. Madeira's remaining forests are now protected.
Sideroxylon marginatum is a species of flowering plant in the family Sapotaceae. It is endemic to the Cape Verde Islands, where it is a mesophytic species whose habitat is now limited to steep escarpments and inaccessible places. It is threatened by continued habitat loss.

Sideroxylon canariense is a species of flowering plant in the family Sapotaceae. It It is endemic to the Canary Islands.




















