
The Kingdom of Ormus was located in the eastern side of the Persian Gulf and extended as far as Bahrain in the west at its zenith. The Kingdom was established in 11th century initially as a dependency of the Kerman Seljuk Sultanate, and later as an autonomous tributary of the Salghurids and the Ilkhanate of Iran. In its last phase Ormus became a client state of the Portuguese Empire in the East. Most of its territory was eventually annexed by the Safavid Empire in the 17th century.

Hormuz Island, also spelled Ormus, is an Iranian island in the Persian Gulf. Located in the Strait of Hormuz, 8 km (5 mi) off the Iranian coast, the island is part of Hormozgan Province. It is sparsely inhabited, but some development has taken place since the late 20th century.

The Dutch–Portuguese War was a global armed conflict involving Dutch forces, in the form of the Dutch East India Company, the Dutch West India Company, and their allies, against the Iberian Union, and after 1640, the Portuguese Empire. Beginning in 1598, the conflict primarily involved the Dutch companies and fleet invading Portuguese colonies in the Americas, Africa, and the East Indies. The war can be thought of as an extension of the Eighty Years' War being fought in Europe at the time between Spain and the Netherlands, as Portugal was in a dynastic union with Spain after the War of the Portuguese Succession, for most of the conflict.

The Ottoman Navy or The Imperial Navy, also known as the Ottoman Fleet, was the naval warfare arm of the Ottoman Empire. It was established after the Ottomans first reached the sea in 1323 by capturing Praenetos, the site of the first Ottoman naval shipyard and the nucleus of the future navy.
The Ottoman–Portuguese or the Turco-Portuguese confrontations refers to a series of different military encounters between the Portuguese Empire and the Ottoman Empire, or between other European powers and the Ottoman Empire in which relevant Portuguese military forces participated. Some of these conflicts were brief, while others lasted for many years. Most of these conflicts took place in the Indian Ocean, in the process of the expansion of the Portuguese Empire, but also in the Red Sea. These conflicts also involved regional powers, after 1538 the Adal Sultanate, with the aid of the Ottoman Empire, fought against the Ethiopian Empire, which was supported by the Portuguese, under the command of Cristóvão da Gama, the son of the famous explorer Vasco da Gama. This war is known as the Ethiopian–Adal war.

The Ottoman-Portuguese conflicts were a period of conflict during the Ottoman–Portuguese confrontations and series of armed military encounters between the Portuguese Empire and the Ottoman Empire along with regional allies in and along the Indian Ocean, Persian Gulf, and Red Sea.

The Ottoman–Portuguese Conflicts (1586–1589) were armed military engagements which took place between the Portuguese Empire and the Ottoman Empire along the coast of eastern Africa.

The Capture of Hormuz was a combined Anglo-Persian expedition that successfully captured the Portuguese garrison at Hormuz Island after a ten-week siege, thus opening up Persian trade with England in the Persian Gulf. Before the capture of Hormuz, the Portuguese had held the Castle of Hormuz for more than a century, since 1507 when Afonso de Albuquerque established it in the capture of Hormuz, giving them full control of the trade between India and Europe through the Persian Gulf. According to Stephen Neill, the capture of Hormuz entirely changed the balance of power and trade.

The capture of Aden of 1548 was accomplished when Ottomans under Piri Reis managed to take the harbour of Aden in Yemen from the Portuguese on 26 February 1548.
The Ottoman expedition to Aceh started from around 1565 when the Ottoman Empire endeavoured to support the Aceh Sultanate in its fight against the Portuguese Empire in Malacca. The expedition followed an envoy sent by the Acehnese Sultan Alauddin Riayat Syah al-Kahhar (1539–71) to Suleiman the Magnificent in 1564, and possibly as early as 1562, requesting Ottoman support against the Portuguese.

The siege of Diu occurred when an army of the Sultanate of Gujarat under Khadjar Safar, aided by forces of the Ottoman Empire, attempted to capture the city of Diu in 1538, then held by the Portuguese. The Portuguese successfully resisted the four months long siege. It is part of the Ottoman-Portuguese war.

The Portuguese–Safavid wars were a series of wars between the Portuguese Empire and Safavid Iran from 1507 to 1625. The Portuguese were also supported by Kingdom of Hormuz, its vassal, and Safavids had the help of the Kingdom of England on the other side.

The third siege of Diu was a siege of the Portuguese Indian city of Diu by the Gujarat Sultanate in 1546. It ended with a major Portuguese victory.

The capture of Muscat occurred in 1552, when an Ottoman fleet under Piri Reis attacked Old Muscat, in modern Oman, and plundered the town from the Portuguese. These events followed the important Ottoman defeat in the third siege of Diu in 1546, which put a stop to their attempts in India, but also the successful capture of Aden in 1548, which allowed the Ottomans to resist the Portuguese in the northwestern part of the Indian Ocean.

The Ottoman campaign against Hormuz took place in 1552–1554. An Ottoman fleet led by Admiral Piri Reis and Seydi Ali Reis was dispatched from the Ottoman harbour of Suez to eliminate the Portuguese presence from the northwestern part of the Indian Ocean, and especially their fortress at Hormuz Island.
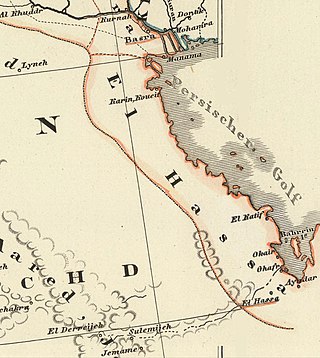
Lahsa Eyalet was an eyalet of the Ottoman Empire. The territory of the former eyalet is now part of Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, and Qatar. Al-Ahsa and Qatif were the main cities of the eyalet, and it was named after the former.
Sefer Reis was an Ottoman admiral and privateer who was active against the Portuguese in the Indian Ocean in the 16th century.

The siege of Bahrain of 1559 occurred when forces of the Ottoman Empire, commanded by the governor of the Lahsa eyalet Mustafa Pasha, attempted to seize Bahrain, and thus wrest control of the island and its famed pearl trade from the Portuguese Empire. The siege was unsuccessful, and the Portuguese defeated the Turks when reinforcements were dispatched by sea from the fortress of Hormuz.
The siege of Qatif was a military confrontation between the Portuguese Empire and the Ottoman Empire at Qatif in 1551. The Portuguese, together with their Hormuzi vassals successfully sieged, captured and demolished the fort captured from the Ottomans.













