Siorapaluk Hiurapaluk | |
|---|---|
 Siorapaluk | |
| Coordinates: 77°47′08″N70°38′00″W / 77.78556°N 70.63333°W | |
| State | |
| Constituent country | |
| Municipality | Avannaata |
| Population (2025) | |
• Total | 34 |
| Time zone | UTC−02:00 (Western Greenland Time) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−01:00 (Western Greenland Summer Time) |
| Postal code | 3971 Qaanaaq |
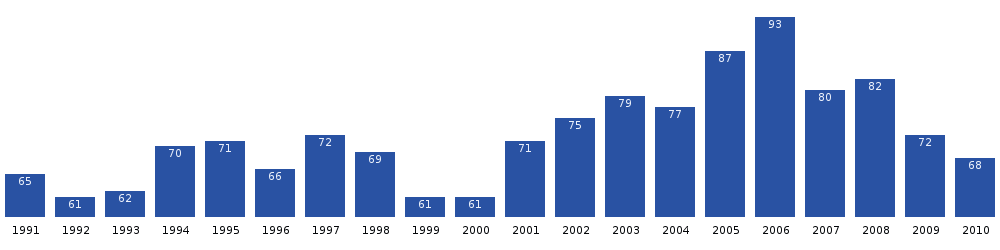
Siorapaluk (West Greenlandic) or Hiurapaluk (Polar Inuit) is a settlement in the Qaanaaq area of the Avannaata municipality in northern Greenland. The settlement is located in the northern shore of the Siorapaluup Kangerlua (Robertson Fjord). [1] It has a population of 43 [2] who speak the Inuktun language of the Polar Inuit as well as the Kalaallisut dialect of Greenlandic. Many of the inhabitants are direct descendants of the last migration of Inuit from Canada in the 20th century. [3]
Contents
Siorapaluk is the northernmost inhabited public settlement in Greenland, and one of the northernmost such settlements in the world, surpassed only by a few villages and Longyearbyen in Svalbard. It is also the world's northernmost place inhabited by natives.