
Chlorine is a chemical element; it has symbol Cl and atomic number 17. The second-lightest of the halogens, it appears between fluorine and bromine in the periodic table and its properties are mostly intermediate between them. Chlorine is a yellow-green gas at room temperature. It is an extremely reactive element and a strong oxidising agent: among the elements, it has the highest electron affinity and the third-highest electronegativity on the revised Pauling scale, behind only oxygen and fluorine.

Sodium hydroxide, also known as lye and caustic soda, is an inorganic compound with the formula NaOH. It is a white solid ionic compound consisting of sodium cations Na+ and hydroxide anions OH−.

Sodium chloride, commonly known as edible salt, is an ionic compound with the chemical formula NaCl, representing a 1:1 ratio of sodium and chlorine ions. It is transparent or translucent, brittle, hygroscopic, and occurs as the mineral halite. In its edible form, it is commonly used as a condiment and food preservative. Large quantities of sodium chloride are used in many industrial processes, and it is a major source of sodium and chlorine compounds used as feedstocks for further chemical syntheses. Another major application of sodium chloride is deicing of roadways in sub-freezing weather.
A period 3 element is one of the chemical elements in the third row of the periodic table of the chemical elements. The periodic table is laid out in rows to illustrate recurring (periodic) trends in the chemical behavior of the elements as their atomic number increases: a new row is begun when chemical behavior begins to repeat, meaning that elements with similar behavior fall into the same vertical columns. The third period contains eight elements: sodium, magnesium, aluminium, silicon, phosphorus, sulfur, chlorine and argon. The first two, sodium and magnesium, are members of the s-block of the periodic table, while the others are members of the p-block. All of the period 3 elements occur in nature and have at least one stable isotope.
The Bayer process is the principal industrial means of refining bauxite to produce alumina (aluminium oxide) and was developed by Carl Josef Bayer. Bauxite, the most important ore of aluminium, contains only 30–60% aluminium oxide (Al2O3), the rest being a mixture of silica, various iron oxides, and titanium dioxide. The aluminium oxide must be further purified before it can be refined into aluminium.

Mercury(II) chloride (or mercury bichloride, mercury dichloride), historically also known as sulema or corrosive sublimate, is the inorganic chemical compound of mercury and chlorine with the formula HgCl2, used as a laboratory reagent. It is a white crystalline solid and a molecular compound that is very toxic to humans. Once used as a treatment for syphilis, it is no longer used for medicinal purposes because of mercury toxicity and the availability of superior treatments.

Lithium aluminium hydride, commonly abbreviated to LAH, is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Li[AlH4] or LiAlH4. It is a white solid, discovered by Finholt, Bond and Schlesinger in 1947. This compound is used as a reducing agent in organic synthesis, especially for the reduction of esters, carboxylic acids, and amides. The solid is dangerously reactive toward water, releasing gaseous hydrogen (H2). Some related derivatives have been discussed for hydrogen storage.

Aluminium chloride, also known as aluminium trichloride, is an inorganic compound with the formula AlCl3. It forms a hexahydrate with the formula [Al(H2O)6]Cl3, containing six water molecules of hydration. Both the anhydrous form and the hexahydrate are colourless crystals, but samples are often contaminated with iron(III) chloride, giving them a yellow colour.

Thionyl chloride is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula SOCl2. It is a moderately volatile, colourless liquid with an unpleasant acrid odour. Thionyl chloride is primarily used as a chlorinating reagent, with approximately 45,000 tonnes per year being produced during the early 1990s, but is occasionally also used as a solvent. It is toxic, reacts with water, and is also listed under the Chemical Weapons Convention as it may be used for the production of chemical weapons.
In chemistry, an aluminate is a compound containing an oxyanion of aluminium, such as sodium aluminate. In the naming of inorganic compounds, it is a suffix that indicates a polyatomic anion with a central aluminium atom.

Aluminium hydride refers to a collection of inorganic compounds with the formula AlH3. As a gas, alane is a planar molecule. When generated in ether solutions, it exists as an ether adduct. Solutions of alane polymerizes to a solid, which exists in several crystallograhically distinguishable forms.

Tetrachloroaluminate [AlCl4]− is an anion formed from aluminium and chlorine. The anion has a tetrahedral shape and is isoelectronic with silicon tetrachloride. Some tetrachloroaluminates are soluble in organic solvents, creating an ionic non-aqueous solution, making them suitable as component of electrolytes for batteries. For example, lithium tetrachloroaluminate is used in some lithium batteries.

Sodium aluminium hydride or sodium alanate is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula NaAlH4. It is a white pyrophoric solid that dissolves in tetrahydrofuran (THF), but not in diethyl ether or hydrocarbons. It has been evaluated as an agent for the reversible storage of hydrogen and it is used as a reagent for the chemical synthesis of organic compounds. Similar to lithium aluminium hydride, it is a salt consisting of separated sodium cations and tetrahedral AlH−
4 anions.
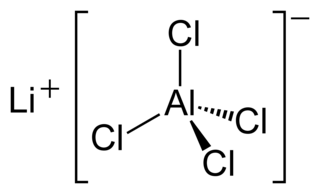
Lithium tetrachloroaluminate is an inorganic compound with the formula Li[AlCl4]. It consists of lithium cations Li+ and tetrahedral tetrachloroaluminate anions [AlCl4]−.
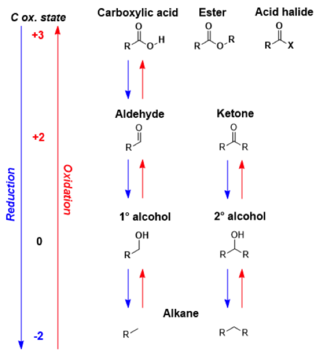
In organic chemistry, carbonyl reduction is the conversion of any carbonyl group, usually to an alcohol. It is a common transformation that is practiced in many ways. Ketones, aldehydes, carboxylic acids, esters, amides, and acid halides - some of the most pervasive functional groups, -comprise carbonyl compounds. Carboxylic acids, esters, and acid halides can be reduced to either aldehydes or a step further to primary alcohols, depending on the strength of the reducing agent. Aldehydes and ketones can be reduced respectively to primary and secondary alcohols. In deoxygenation, the alcohol group can be further reduced and removed altogether by replacement with H.

Ethylaluminium sesquichloride, also called EASC, is an industrially important organoaluminium compound used primarily as a precursor to triethylaluminium and as a catalyst component in Ziegler–Natta type systems for olefin and diene polymerizations. Other applications include use in alkylation reactions and as a catalyst component in linear oligomerization and cyclization of unsaturated hydrocarbons. EASC is a colourless liquid, spontaneously combustible in air and reacts violently when in contact with water and many other compounds.

Metal halides are compounds between metals and halogens. Some, such as sodium chloride are ionic, while others are covalently bonded. A few metal halides are discrete molecules, such as uranium hexafluoride, but most adopt polymeric structures, such as palladium chloride.
Aluminium triacetate, formally named aluminium acetate, is a chemical compound with composition Al(CH
3CO
2)
3. Under standard conditions it appears as a white, water-soluble solid that decomposes on heating at around 200 °C. The triacetate hydrolyses to a mixture of basic hydroxide / acetate salts, and multiple species co-exist in chemical equilibrium, particularly in aqueous solutions of the acetate ion; the name aluminium acetate is commonly used for this mixed system.
Aluminium cyanide is a metallic cyanide with a chemical formula of Al(CN)3. It is a white solid that undergoes hydrolysis to produce aluminium hydroxide and hydrogen cyanide.















