
Starlings are small to medium-sized passerine birds in the family Sturnidae, common name of Sturnid. The Sturnidae are named for the genus Sturnus, which in turn comes from the Latin word for starling, sturnus. The family contains 128 species which are divided into 36 genera. Many Asian species, particularly the larger ones, are called mynas, and many African species are known as glossy starlings because of their iridescent plumage. Starlings are native to Europe, Asia, and Africa, as well as northern Australia and the islands of the tropical Pacific. Several European and Asian species have been introduced to these areas, as well as North America, Hawaii, and New Zealand, where they generally compete for habitats with native birds and are considered to be invasive species. The starling species familiar to most people in Europe and North America is the common starling, and throughout much of Asia and the Pacific, the common myna is indeed common.

The mynas are a group of birds in the starling family (Sturnidae). This is a group of passerine birds which are native to Iran and Southern Asia, especially Afghanistan, India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Nepal and Sri Lanka. Several species have been introduced to areas like North America, Australia, South Africa, Fiji and New Zealand, especially the common myna, which is often regarded as an invasive species. It is often known as "Selarang" and "Teck Meng" in Malay and Chinese respectively in Singapore, due to their high population there.

The rosy starling is a passerine bird in the starling family, Sturnidae, also known as the rose-coloured starling or rose-coloured pastor. The species was recently placed in its own monotypic genus, Pastor, and split from Sturnus. This split is supported by recent studies, though other related species within its new genus are not yet known for certain.

The common myna or Indian myna, sometimes spelled mynah, is a bird in the family Sturnidae, native to Asia. An omnivorous open woodland bird with a strong territorial instinct, the common myna has adapted extremely well to urban environments.

The yellow-browed bulbul, or golden-browed bulbul, is a species of songbird in the bulbul family, Pycnonotidae. It is found in the forests of southern India and Sri Lanka. The yellow-browed bulbul is mainly yellow on the underside and olive above with a distinct yellow brow. They are easily located by their loud calls but tend to skulk within foliage below the forest canopy. While its taxonomic classification has changed over time, it is currently the sole species within the monotypic genus Acritillas which is closely related to Hemixos.

The yellow-billed babbler is a member of the family Leiothrichidae endemic to southern India and Sri Lanka. The yellow-billed babbler is a common resident breeding bird in Sri Lanka and southern India. Its habitat is scrub, cultivation and garden land. This species, like most babblers, is not migratory, and has short rounded wings and a weak flight and is usually seen calling and foraging in groups. It is often mistaken for the jungle babbler, whose range overlaps in parts of southern India, although it has a distinctive call and tends to be found in more vegetated habitats. Its name is also confused with Turdoides leucocephala, which is also known as white-headed babbler.

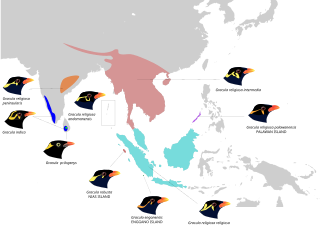
The common hill myna, sometimes spelled "mynah" and formerly simply known as the hill myna or myna bird, is the myna most commonly sighted in aviculture, where it is often simply referred to by the latter two names. It is a member of the starling family (Sturnidae), resident in hill regions of South Asia and Southeast Asia. The Sri Lanka hill myna, a former subspecies of G. religiosa, is now generally accepted as a separate species G. ptilogenys. The Enggano hill myna and Nias hill myna are also widely accepted as specifically distinct, and many authors favor treating the southern hill myna from the Nilgiris and elsewhere in the Western Ghats of India as a separate species.

The Sri Lanka hill myna or Ceylon myna is a myna, a member of the starling family. This bird is endemic to Sri Lanka.

The brahminy starling or brahminy myna is a member of the starling family of birds. It is usually seen in pairs or small flocks in open habitats on the plains of the Indian subcontinent.

The chestnut-tailed starling, also called grey-headed starling and grey-headed myna is a member of the starling family. It is a resident or partially migratory species found in wooded habitats in India and Southeast Asia. The species name is after the distribution of a former subspecies in the Malabar region. While the chestnut-tailed starling is a winter visitor to peninsular India, the closely related resident breeding population with a white head is now treated as a full species, the Malabar starling.

The grey-headed canary-flycatcher, sometimes known as the grey-headed flycatcher, is a species of small flycatcher-like bird found in tropical Asia. It has a square crest, a grey hood and yellow underparts. They are found mainly in forested habitats where they often join other birds in mixed-species foraging flocks. Pairs are often seen as they forage for insects by making flycatcher-like sallies and calling aloud. Several subspecies are recognized within their wide distribution range. In the past the genus Culicicapa was considered to be an Old World flycatcher but studies have found them to belong to a new family designated as the Stenostiridae or fairy flycatchers that include the African genera Stenostira and Elminia.

The crested myna, also known as the Chinese starling, is a species of starling in the genus Acridotheres native to southeastern China and Indochina. It is named after the tuft of feathers on its forehead that resembles a crest.
Gracula is a genus of mynas, tropical members of the starling family of birds found in southern Asia and introduced to Florida in the United States.

Acridotheres is a genus of starlings, the "typical" mynas, which are tropical members of the family Sturnidae.

The bank myna is a myna found in the northern parts of South Asia. It is smaller but similar in colouration to the common myna, only differing in having brick-red naked skin behind the eyes instead of yellow. It is greyer on the underside and in this and in the presence of a slight tuft of feathers bears some resemblance to the jungle myna. They are found in flocks on the plains of northern and central India, often within towns and cities. Their range appears to be extending southwards into India. The name is derived from their habit of nesting almost exclusively in the earthen banks of rivers, where they excavate burrows and breed in large colonies.

The wattled starling is a nomadic resident bird in eastern and southern Africa. It is a species of grassland, open woodland, and cultivation.

The greater blue-eared starling or greater blue-eared glossy-starling is a bird that breeds from Senegal east to Ethiopia and south through eastern Africa to northeastern South Africa and Angola. It is a very common species of open woodland bird, and undertakes some seasonal migration.

The yellow-faced myna is a species of starling in the family Sturnidae. It is found in New Guinea and nearby smaller islands, where its natural habitat is subtropical or tropical moist lowland forests. The long-tailed myna was formerly included as a subspecies. One of the largest species of starling, this species attains 23 to 26 cm in length and weighs around 217 g (7.7 oz). They have dark plumage with a metallic lustre and bright orange facial markings and beak. These birds are social and omnivorous. Their diet consists of fruit and insects for which they forage high in the canopy. They are common birds with a wide range, and the International Union for Conservation of Nature has assessed their conservation status as being of "least concern". It was named after Charles Dumont.

The black-collared starling is a species of starling in the family Sturnidae. Its plumage is black and white, with a black collar. It is found in southern China and most of mainland Southeast Asia, and has been introduced to Taiwan, Malaysia and Singapore. Its habitats include grassland, dry forest and human settlements. The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) has assessed it as being of least concern.

The Nias hill myna or Nias myna is a member of the starling family. It is an endemic resident of Nias and other nearby islands off western Sumatra. Clements lumps this species with the common hill myna.





















