
Huntsman spiders, members of the family Sparassidae, are known by this name because of their speed and mode of hunting. They are also called giant crab spiders because of their size and appearance. Larger species sometimes are referred to as wood spiders, because of their preference for woody places. In southern Africa the genus Palystes are known as rain spiders or lizard-eating spiders. Commonly, they are confused with baboon spiders from the Mygalomorphae infraorder, which are not closely related.

Corythalia is a genus of jumping spiders that was first described by Carl Ludwig Koch in 1850. The genus is distributed throughout most of the Western Hemisphere. Species of this genus are found in The Americas.
Eustiromastix is a genus of jumping spiders that was first described by Eugène Louis Simon in 1902.

Pachomius is a genus of jumping spiders that was first described by George and Elizabeth Peckham in 1896. Uspachia was merged into genus Romitia in 2007, and all nine species were merged into Pachomius in 2015. The name is derived from Pachomius, the founder of cenobitic monasticism.

Micrathena, known as spiny orbweavers, is a genus of orb-weaver spiders first described by Carl Jakob Sundevall in 1833. Micrathena contains more than a hundred species, most of them Neotropical woodland-dwelling species. The name is derived from the Greek "micro", meaning "small", and the goddess Athena.

Olios is the largest genus of huntsman spiders, containing 166 species. They are found throughout the world, with most species occurring in hot countries. The genus was first described by Charles Athanase Walckenaer in 1837.

Corinna is a genus of corinnid sac spiders first described by Carl Ludwig Koch in 1841. They are found in Mexico and south to Brazil, and with selected species found in Africa.
Synotaxus is a genus of araneomorph spiders in the family Synotaxidae that was first described by Eugène Louis Simon in 1895. Originally placed with the tangle web spiders, it was moved to the family Synotaxidae in 2017.

Anaptomecus is a genus of huntsman spiders that was first described by Eugène Louis Simon in 1903.
Guadana is a genus of South American huntsman spiders that was first described by C. A. Rheims in 2010.
Pseudosparianthis is a genus of huntsman spiders that was first described by Eugène Louis Simon in 1887.
Sampaiosia is a monotypic genus of Brazilian huntsman spiders containing the single species, Sampaiosia crulsi. It was first described by Cândido Firmino de Mello-Leitão in 1930, and is found in Brazil.
Sparianthina is a genus of huntsman spiders that was first described by Nathan Banks in 1929.
Uaiuara is a genus of huntsman spiders that was first described by C. Rheims in 2013.
Vindullus is a genus of huntsman spiders that was first described by Eugène Louis Simon in 1880. Though often considered a synonym of Olios, it has been validated as its own genus.
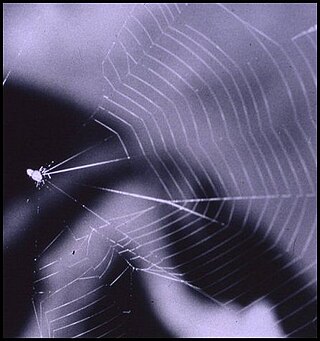
Naatlo is a genus of ray spiders that was first described by Jonathan A. Coddington in 1986.

Epicadinus is a genus of crab spiders that was first described by Eugène Louis Simon in 1895.

Epicadus is a genus of crab spiders that was first described by Eugène Louis Simon in 1895. It is considered a senior synonym of Tobias.
Macrinus is a genus of huntsman spiders that was first described by Eugène Louis Simon in 1887.

Alpaida is a genus of South American orb-weaver spiders first described by Octavius Pickard-Cambridge in 1889.










