In biological classification, a subfamily is an auxiliary (intermediate) taxonomic rank, next below family but more inclusive than genus. Standard nomenclature rules end subfamily botanical names with "-oideae", and zoological names with "-inae".

In biology, a subgenus is a taxonomic rank directly below genus.
Monascus is a genus of mold. Among the known species of this genus, the red-pigmented Monascus purpureus is among the most important because of its use in the production of certain fermented foods in East Asia, particularly China and Japan.

Pieter Willem Korthals was a Dutch botanist. Korthals was the official botanist with the Dutch East India Service from 1831 to 1836. Among his many discoveries was the medicinal plant Kratom . Korthals wrote the first monograph on the tropical pitcher plants, "Over het geslacht Nepenthes", published in 1839.

Philippe Édouard Léon Van Tieghem was a French botanist born in Baillleul in the département of Nord. He was one of the best known French botanists of the latter nineteenth century.
Hyphochytrids are eukaryotic organisms in the group of Stramenopiles (Heterokonta).

Coemansia is a genus of fungi in the family Kickxellaceae. It was circumscribed in 1873.

The Icacinaceae are a family of flowering plants, consisting of trees, shrubs, and lianas, primarily of the tropics.
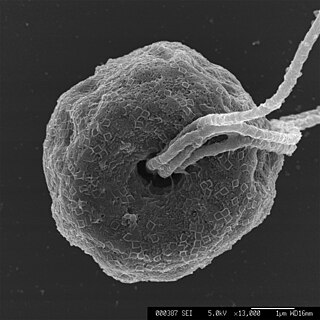
Pyramimonadales are an order of green algae in the Chlorophyta.
David Van Tieghem is an American composer, musician, percussionist, drummer, keyboard player, performance artist, video artist and actor, notorious for his philosophy of utilizing any available object as a percussion instrument and his collaborations with the experimental rock artists Laurie Anderson, Brian Eno and David Byrne.

Mucoromycotina is a subphylum of uncertain placement in Fungi. It was considered part of the phylum Zygomycota, but recent phylogenetic studies have shown that it was polyphyletic and thus split into several groups, it is now thought to be a paraphyletic grouping. Mucoromycotina is currently composed of 3 orders, 61 genera, and 325 species. Some common characteristics seen throughout the species include: development of coenocytic mycelium, saprotrophic lifestyles, and filamentous.

Mycena leptocephala, commonly known as the nitrous bonnet, is a species of fungus in the Mycenaceae family. The mushrooms have conical grayish caps that reach up to 3 cm (1.2 in) in diameter, and thin fragile stems up to 5 cm (2.0 in) long. The gills are gray and distantly spaced. The spores are elliptical, typically measure 7–10 by 4–6 μm, and are white in deposit. When viewed under a light microscope, the gills have abundant spindle-shaped cystidia on the gill edges, but few on the gill faces. The mushroom is found in North America and Asia, where it grows singly or in groups on conifer needles, cones and sticks on the forest floor. It has a distinctive odor of bleach; the edibility is unknown. Similar species include Mycena alcalina, M. austera, and M. brevipes.

Paul Auguste Hariot, the son of Louis Hariot, was a French pharmacist and noted phycologist, best known for his 1900 publication Atlas Colorié des Plantes Médicinales Indigènes.
Olpidiaceae is a fungal plant pathogen families that was placed in the order Chytridiales.

Lichtheimia corymbifera is a thermophilic fungus in the phylum Zygomycota. It normally lives as a saprotrophic mold, but can also be an opportunistic pathogen known to cause pulmonary, CNS, rhinocerebral, or cutaneous infections in animals and humans with impaired immunity.

Muellerina is a genus of parasitic arial shrubs in the family Loranthaceae.
Ascodesmis is a genus of fungi in the family Ascodesmidaceae. It was described by French botanist Philippe Édouard Léon Van Tieghem in 1876. Species in the genus are coprophilous, and are characterized by the absence of an exipulum.

Muellerina eucalyptoides is a hemiparasitic arial shrub in the family Loranthaceae. The species is endemic to Australia. M. eucalyptoides is pendulous in habit, unlike other Muellerina species, but has the long epicortical runners of all Muellerina species.













