Zygomycosis is the broadest term to refer to infections caused by bread mold fungi of the zygomycota phylum. However, because zygomycota has been identified as polyphyletic, and is not included in modern fungal classification systems, the diseases that zygomycosis can refer to are better called by their specific names: mucormycosis, phycomycosis and basidiobolomycosis. These rare yet serious and potentially life-threatening fungal infections usually affect the face or oropharyngeal cavity. Zygomycosis type infections are most often caused by common fungi found in soil and decaying vegetation. While most individuals are exposed to the fungi on a regular basis, those with immune disorders (immunocompromised) are more prone to fungal infection. These types of infections are also common after natural disasters, such as tornadoes or earthquakes, where people have open wounds that have become filled with soil or vegetative matter.

The Mucorales is the largest and best-studied order of zygomycete fungi. Members of this order are sometimes called pin molds. The term mucormycosis is now preferred for infections caused by molds belonging to the order Mucorales.

The Acura ARX-01, later known as the HPD ARX-01 is a series of Le Mans Prototype built for sports car racing, specifically in the American Le Mans Series, Le Mans Series, and at the 24 Hours of Le Mans. It is the first purpose-built race car by the Acura division of Honda Motor Company, part of their multi-year program to eventually compete in endurance race. The car debuted in 2007 in the American Le mans Series before expanding to customers in Europe. Over the years various specifications of the ARX-01 chassis have been developed, each signified by a letter suffix. In 2010 Acura withdrew their name from the program and Honda Performance Development which developed the car for Acura continued the program into 2011.

Aristaless related homeobox is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ARX gene.

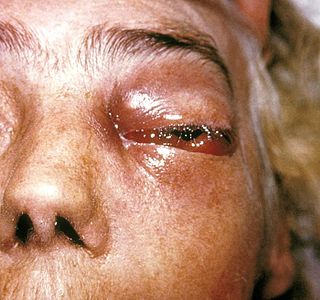
Mucormycosis, also known as black fungus, is a serious fungal infection that comes under fulminant fungal sinusitis, usually in people who are immunocompromised. It is curable only when diagnosed early. Symptoms depend on where in the body the infection occurs. It most commonly infects the nose, sinuses, eyes and brain resulting in a runny nose, one-sided facial swelling and pain, headache, fever, blurred vision, bulging or displacement of the eye (proptosis), and tissue death. Other forms of disease may infect the lungs, stomach and intestines, and skin. The fatality rate is about 54%.

The Cunninghamellaceae are a family of fungi in the order Mucorales.

The Pilobolaceae are a family of fungi in the Mucorales order. Generally, species in this family have a widespread distribution, although there are some that are restricted to tropical and subtropical regions. This family includes two genera: Pilobolus, and Utharomyces.
The Mycotyphaceae are a family of fungi in the order Mucorales. Members of this family, rarely reported, are thought to be more common in warmer climates.
The Saksenaeaceae are a family of fungi in the order Mucorales. It was circumscribed in 1974 by J.J. Ellis and Clifford Hesseltine.

The Syncephalastraceae are a family of fungi in the order Mucorales. Members of this family have a widespread distribution, but are more common in tropical and subtropical regions.

The Acura ARX-02a was a Le Mans Prototype constructed by Acura for competition in the LMP1 category of the American Le Mans Series. It was Acura's second Le Mans Prototype, following their ARX-01 which competed in the LMP2 category.

The Zoopagomycotina are a subdivision of the fungal division Zygomycota sensu lato. It contains 5 families and 20 genera. Relationships among and within subphyla of Zygomycota are poorly understood, and their monophyly remains in question, so they are sometimes referred to by the informal name zygomycetes.

MortierellalesCaval.-Sm., 1998 is a monotypic fungal order, within the phylum of Zygomycota and the monotypic, division of Mortierellomycota. It contains only 1 known family, MortierellaceaeLuerss., Handb. Syst. Bot. 1: 63. 1877, and 6 genera and around 129 species.

Mucoromycotina is a subphylum of uncertain placement in Fungi. It was considered part of the phylum Zygomycota, but recent phylogenetic studies have shown that it was polyphyletic and thus split into several groups, it is now thought to be a paraphyletic grouping. Mucoromycotina is currently composed of 3 orders, 61 genera, and 325 species. Some common characteristics seen throughout the species include: development of coenocytic mycelium, saprotrophic lifestyles, and filamentous.

The HPD ARX-03a, ARX-03b, and ARX-03c are Le Mans Prototypes race cars developed by Honda Performance Development in 2012. The 03a model utilizes a Honda V8 engine for use in the LMP1 category, while the 03b uses a turbocharged V6 engine for the LMP2 category. Three teams have already announced their use of the ARX-03 in the FIA World Endurance Championship and the American Le Mans Series, as well as at the 24 Hours of Le Mans. Muscle Milk Pickett Racing have purchased an 03a for use in the American Le Mans Series, joined by two 03bs for Level 5 Motorsports. In the 2014 FIA World Endurance Championship, Strakka Racing and JRM Racing campaigned a single 03a each, joined by a single-car 03b entry by Starworks Motorsport in LMP2.

Apophysomyces variabilis is an emerging fungal pathogen that can cause serious and sometimes fatal infection in humans. This fungus is a soil-dwelling saprobe with tropical to subtropical distribution. It is a zygomycete that causes mucormycosis, an infection in humans brought about by fungi in the order Mucorales. Infectious cases have been reported globally in locations including the Americas, Southeast Asia, India, and Australia. Apophysomyces variabilis infections are not transmissible from person to person.
Backusella is the sole genus of zygote fungi in the family Backusellaceae, which is classified in the order Mucorales. Members of this genus have been often isolated from plant litter, from locations around the world.
Lichtheimiaceae is a family of fungi in the order Mucorales. The family was circumscribed in 2013 after a molecular phylogenetic analysis helped delineate a new family structure for the Mucorales.
Umbelopsis ramanniana is a common and abundant soil fungus. Although the ecological role of this fungus in natural ecosystems is not yet known, it is a cosmopolitan saprotroph in soil, forest leaf litter, in animal dung, and on the spore-producing bodies of ascomycete fungi. Umbelopsis ramanniana has also been found growing as an endophyte within xylem tissue of both healthy and declining conifers, but its exact effect on the plant hosts is unknown. Umbelopsis ramanniana is a representative of a unique group of zygomycete fungi that is distinct from the Mucoromycotina and Mortierellomycotina and instead forms an early diverging lineage within the Mucoralean fungi. Umbelopsis ramanniana is important from a biochemistry and biotechnology perspective because it is highly tolerant to fungicides of benomyl group, and it is oleaginous. Expression of Umbelopsis ramanniana diacylglycerol O-acyltransferase 2A in seed increases oil in soybean without reduction of other important yield parameters. This increase in oil can potentially add over $1 billion to the annual value of soybean crops.















