
Eurotiomycetes is a large class of ascomycetes with cleistothecial ascocarps within the subphylum Pezizomycotina, currently containing around 3810 species according to the Catalogue of Life. It is the third largest lichenized class, with more than 1200 lichen species that are mostly bitunicate in the formation of asci. It contains most of the fungi previously known morphologically as "Plectomycetes".

The Nectriaceae comprise a family of fungi in the order Hypocreales. It was circumscribed by brothers Charles and Louis René Tulasne in 1865. In 2020, an Outline of fungi was produced and listed 70 genera and about 1,336 species.

Thielaviopsis is a small genus of fungi in the order Microascales, and family Ceratocystidaceae. The genus includes several important agricultural based pathogens. The most widespread is T. basicola, the causal agent in several root rot diseases of economically important crop species including cotton and a variety of vegetables. In cotton, Thielaviopsis causes root rot, also known as black root rot, which causes necrosis of the roots and stunting of the crop plants.
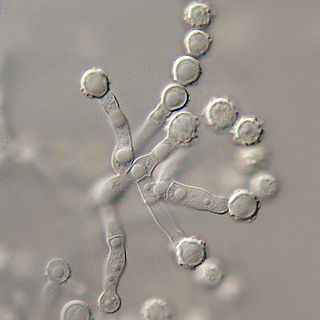
The Microascaceae are a family of fungi in the class Sordariomycetes, subclass Hypocreomycetidae. The family was published by David Malloch in 1970, an emended description based on Everet Stanley Luttrell's original 1951 publication. Family was updated in 2020.

Microascus is a genus of fungi in the family Microascaceae.
Neoscytalidium is a genus of fungi in the Botryosphaeriaceae family.

The Ophiostomataceae are a family of fungi in the Ascomycota, class Sordariomycetes. The family was circumscribed by J.A. Nannfeldt in 1932. Species in the family have a widespread distribution, and are typically found in temperate regions, as pathogens of both coniferous and deciduous trees.

Ophiostoma is a genus of fungi within the family Ophiostomataceae. It was circumscribed in 1919 by mycologists Hans Sydow and Paul Sydow.
Graphium is a genus of fungi in the family Microascaceae. Many species are known as plant pathogens. Graphium belongs to the group hyphomycetes and has about 20 species. They are found in soil, plant debris, woody substrate, manure, and polluted water. The sporulating structures of Graphium form synnema, which are a gathering of conidiophores into a sort of flower bouquet. Graphium spp. are recognized by their distinctive, erect, black synnemata, each bearing a single, terminal, ball of one-celled, hyaline conidia produced from annellides.
Lasiodiplodia is a genus of fungi in the family Botryosphaeriaceae. There were about 21 species. Lasiodiplodia, commonly referred to as black-soot disease, is a significant pathogen in tropical forestry.
The Ceratocystidaceae are a family of fungi in the class Sordariomycetes, subclass Hypocreomycetidae.
Endoconidiophora is a genus of fungi within the Ceratocystidaceae family.

The Coniochaeta are a genus of pleomorphic yeasts of the order Coniochaetales and are pathogens of trees. Some species have also been found to form endophytic associations within plants in which they live inside plant tissues but do not actually harm the organism. They can take the form of pink to brown colonies, hyphae, conidiophores or sclerotia. In 2013, the Lecythophora were merged with the Coniochaeta, following suggestions by Ziauddin Khan et al.
Raffaelea is a genus of ambrosia fungi in the family Ophiostomataceae. It was circumscribed by mycologists Josef Adolph von Arx and Grégoire L. Hennebert in 1965 with Raffaelea ambrosiae as the type species. The genus is named in honor of Italian botanist Raffaele Ciferri.
Penicillium restingae is a species of fungus in the genus Penicillium which was isolated from soil of the Guaibim sandbank in Bahia in Brazil.

The Stachybotryaceae are a family of fungi in the order Hypocreales; the genera it contains have been described as "hyper-diverse".

Rhinocladiella is a genus of fungi in the family Herpotrichiellaceae. It has 17 species. The genus was circumscribed by Swedish botanist John Axel Nannfeldt in 1934 with R. atrovirens as the type species.
Sporothrix brasiliensis is a fungus that is commonly found in soil. It is an emerging fungal pathogen that is causing disease in humans and cats mainly in Brazil and other countries in South America.
Conioscypha is a genus of terrestrial and freshwater fungi in the monotypic family Conioscyphaceae and the monotypic order Conioscyphales. They are found on decayed wood, leaves, or bamboo stems. Except for Conioscypha japonica which was isolated from dog skin fragments and hair in 2017.

Coniothyriaceae is a family of ascomycetous marine based fungi within the order of Pleosporales in the subclass Pleosporomycetidae and within the class Dothideomycetes. They are pathogenic or they can be saprobic on dead branches. They are generally a anamorphic species.










