
The Carolina mantis is a species of praying mantis of the subfamily Stagmomantinae.

Giant cockroaches, or blaberids, are the second-largest cockroach family by number of species. Mostly distributed in warmer climates worldwide, this family is based on the American genus Blaberus, but much of the diversity is also found in Africa and Asia.

Mantidae is one of the largest families in the order of praying mantises, based on the type species Mantis religiosa; however, most genera are tropical or subtropical. Historically, this was the only family in the order, and many references still use the term "mantid" to refer to any mantis. Technically, however, "mantid" refers only to members of the family Mantidae, and not the numerous remaining families of mantises. Some of the most recent classifications have promoted a number of the mantid subfamilies to the rank of family, e.g. Iridopterygidae, Sibyllidae, Tarachodidae, Thespidae, and Toxoderidae, while other classifications have reduced the number of subfamilies without elevating them to higher rank.

Ectobiidae is a family of the order Blattodea (cockroaches). This family contains many of the smaller common household pest cockroaches, among others. They are sometimes called wood cockroaches. A few notable species include:

Conocephalus is a genus of bush crickets, known as coneheads. It was described by Carl Peter Thunberg in 1815.

The Romaleidae or lubber grasshoppers are a family of grasshoppers, based on the type genus Romalea. The species in this family can be found in the Americas. It is known to be polyphagous, but there is not much else known regarding its diet.
Oligonicella scudderi, common name Scudder's mantis or slender prairie mantid, is a species of praying mantis native to the southern United States. It is a small brown insect; the males can fly but the females are wingless.

Acanthops is a genus of mantises in the family Acanthopidae, containing 20 species that can be found in Central and South America.
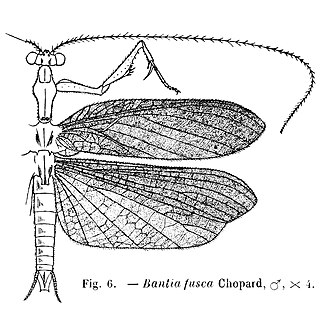
Thespidae is a family of insects in the order Mantodea. Following a major revision of this order in 2019, the old-world subfamilies Haaniinae and Hoplocoryphinae, previously placed here, have been upgraded to family level. Thespidae are mostly Neotropical and few species have reached the Nearctic realm.

The Phaneropterinae, the sickle-bearing bush crickets or leaf katydids, are a subfamily of insects within the family Tettigoniidae. They are also known as false katydids or round-headed katydids.

Panchlora is a genus of cockroaches in the subfamily Panchlorinae, erected by Hermann Burmeister in 1838. Species are mostly found in the Americas and Africa. Most species in this genus are green in colour, but some are cream or grey.
Lobocneme is a genus consisting of 3 species of mantises in the tribe Oxyopsidini.

Pseudocreobotra ocellata, known as the African flower mantis or with other species as the spiny flower mantis, is a flower mantis native to Africa, ranging from Angola and South Africa in the south to Uganda in the east and Senegal in the west. It was described by the French naturalist Palisot de Beauvois in 1805.

Gryllotalpa africana, also known as the African mole cricket, is a relatively small mole cricket species, native to Africa, but local populations exist in Asia, and southern Europe.

Conocephalinae, meaning "conical head", is an Orthopteran subfamily in the family Tettigoniidae.

Paratettix is a genus of ground-hoppers or pygmy grasshoppers, with more than 60 described species found worldwide.

Chorisoneura is a genus of cockroach in the family Ectobiidae. There are at least 90 described species in Chorisoneura.

Pseudovates is a genus of praying mantis in the family Mantidae. There are more than 20 described species in the genus Pseudovates, and are found in North, Central, and South America.

Liturgusa is the type genus of praying mantises of the family Liturgusidae. The genus consists of more than twenty species with a Neotropical distribution.


















