
Modern Standard Hindi, commonly referred to as Hindi, is an Indo-Aryan language spoken chiefly in North India, and serves as the lingua franca of the Hindi Belt region encompassing parts of northern, central, eastern, and western India. Hindi has been described as a standardised and Sanskritised register of the Hindustani language, which itself is based primarily on the Khariboli dialect of Delhi and neighbouring areas of North India. Hindi, written in the Devanagari script, is one of the two official languages of the Government of India, along with English. It is an official language in nine states and three union territories and an additional official language in three other states. Hindi is also one of the 22 scheduled languages of the Republic of India.

Gujarati is an Indo-Aryan language native to the Indian state of Gujarat and spoken predominantly by the Gujarati people. Gujarati is descended from Old Gujarati. In India, it is one of the 22 scheduled languages of the Union. It is also the official language in the state of Gujarat, as well as an official language in the union territory of Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu. As of 2011, Gujarati is the 6th most widely spoken language in India by number of native speakers, spoken by 55.5 million speakers which amounts to about 4.5% of the total Indian population. It is the 26th most widely spoken language in the world by number of native speakers as of 2007.

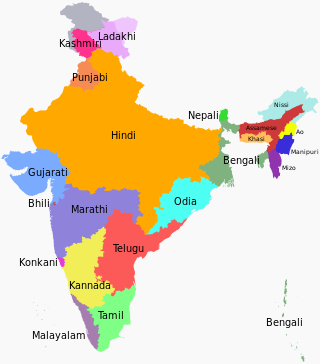
Languages spoken in the Republic of India belong to several language families, the major ones being the Indo-Aryan languages spoken by 78.05% of Indians and the Dravidian languages spoken by 19.64% of Indians; both families together are sometimes known as Indic languages. Languages spoken by the remaining 2.31% of the population belong to the Austroasiatic, Sino–Tibetan, Tai–Kadai, and a few other minor language families and isolates. According to the People's Linguistic Survey of India, India has the second highest number of languages (780), after Papua New Guinea (840). Ethnologue lists a lower number of 456.

Kashmiri or Koshur is an Indo-Aryan language spoken by around 7 million Kashmiris of the Kashmir region, primarily in the Indian union territory of Jammu and Kashmir. Kashmiri has split ergativity and the unusual verb-second word order. After Hindi, Kashmiri is the second fastest growing language of India, followed by Meitei (Manipuri) as well as Gujarati in the third place, and Bengali in the fourth place, according to the 2011 census of India.
There is no national language in the Republic of India. However, article 343(1) of the Indian constitution specifically mentions that "The official language of the Union shall be Hindi in Devanagari script. The form of numerals to be used for the official purposes of the Union shall be the international form of Indian numerals," while article 343(2) allowed for the continuation of English as an official language for another 15 years and 343(3) gave the parliament the power to provide for the use of English language after this period. The clause 3 of the Official Languages Act, 1963 allows for the continued use of English language for official purposes of the Union government and for parliamentary business. Hence Indian English and Modern Standard Hindi are the Official Languages of the Government of India.

Meitei, officially known as Manipuri, is a Tibeto-Burman language of northeast India. It is the official language and the lingua franca of Manipur, as well as one of the 22 official languages of the Indian Republic, included in the 8th Schedule to the Indian Constitution. It is one of the advanced literary languages, recognised by Sahitya Akademi, India's National Academy of Letters. It serves as one of the recognised educational and literary languages in Assam and Tripura. Native to the Meitei people, it is used as L1 by around 1.8 million people, predominantly in the state of Manipur, and as L2 by different ethnic groups, in different parts of India, Myanmar and Bangladesh. It was used as a court language in the historic Manipur Kingdom, in accordance to the Manipur State Constitution Act 1947.

Silvassa is a city and municipality in western India, and the headquarters of the Dadra and Nagar Haveli district. It was a part of the Daman district of the former Portuguese India, and is today the largest city in Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu. Many large companies have established their manufacturing units there. The city has a large number of factories providing significant government revenue, which allows the city to maintain a low level of taxation. The city was chosen as one of the hundred Indian cities in Government of India's flagship Smart Cities Mission.

The Hindi Belt, also known as the Hindi Heartland, is a linguistic region encompassing parts of northern, central and eastern India where various Northern, Western, Eastern and Central Indo-Aryan languages subsumed under the term 'Hindi' are spoken. The term “Hindi belt” is sometimes also used to refer to the nine Indian states whose official language is Modern Standard Hindi, namely Bihar, Chhattisgarh, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Jharkhand, Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh and Uttarakhand, as well as to the union territory of Chandigarh and the National Capital Territory of Delhi. It is also sometimes broadly referred to as the Hindi–Urdu Belt or Hindustani Belt.

Indo-Canadians are Canadians who have ancestry from India. The term East Indian is sometimes used to avoid confusion with the Indigenous peoples of Canada. Categorically, Indo-Canadians comprise a subgroup of South Asian Canadians which is a further subgroup of Asian Canadians. According to Statistics Canada, Indians are one of the fastest growing communities in Canada, and one of the largest non-European ethnic groups.
Kashmiri language is the official language as well as the predominantly spoken language of Jammu and Kashmir, besides being one of the scheduled languages of India.

South Asia is home to several hundred languages, spanning the countries of Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka. It is home to the third most spoken language in the world, Hindi–Urdu; and the sixth most spoken language, Bengali. The languages in the region mostly comprise Indo-Iranic and Dravidian languages, and further members of other language families like Austroasiatic, and Tibeto-Burman languages.
This is a list of States and Union Territories of India by Bengali speakers at the time of the 2011 Census.

The 2011 census of India or the 15th Indian census was conducted in two phases, house listing and population enumeration. The House listing phase began on 1 April 2010 and involved the collection of information about all buildings. Information for National Population Register (NPR) was also collected in the first phase, which will be used to issue a 12-digit unique identification number to all registered Indian residents by Unique Identification Authority of India. The second population enumeration phase was conducted between 9 and 28 February 2011. Census has been conducted in India since 1872 and 2011 marks the first time biometric information was collected. According to the provisional reports released on 31 March 2011, the Indian population increased to 1.21 billion with a decadal growth of 17.70%. Adult literacy rate increased to 74.04% with a decadal growth of 9.21%. The motto of the census was Our Census, Our Future.

Chiru (Naga) is a Southern Naga language spoken mostly in Manipur. The Chiru population numbers approximately 8,599. It is an endangered spoken in three districts of Manipur: Senapati, Noney district of Manipur and Cachar district of Assam. Chiru has been recognized as a Scheduled Tribe of Manipur by the government of India since 1956 under "The Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes Orders (Amendment) Act, Act No. 63 of 1956" Dated 25 September 1956. The total population of the native speakers of Chiru is only 8599. The native speakers have high proficiency in Meitei language. The language is neither used in schools nor in radio or mass media. Older people read and write in Meitei language. The younger generation of Chiru speakers prefers Roman script. The speakers of this language use Meitei language as their second language (L2) according to the Ethnologue.
IndoWordNet is a linked lexical knowledge base of wordnets of 18 scheduled languages of India, viz., Assamese, Bangla, Bodo, Gujarati, Hindi, Kannada, Kashmiri, Konkani, Malayalam, Meitei (Manipuri), Marathi, Nepali, Odia, Punjabi, Sanskrit, Tamil, Telugu and Urdu.

The Eighth Schedule to the Constitution of India lists the official languages of the Republic of India. At the time when the Constitution was enacted, inclusion in this list meant that the language was entitled to representation on the Official Languages Commission, and that the language would be one of the bases that would be drawn upon to enrich Hindi and English, the official languages of the Union. The list has since, however, acquired further significance. The Government of India is now under an obligation to take measures for the development of these languages, such that "they grow rapidly in richness and become effective means of communicating modern knowledge." In addition, candidates sitting for an examination conducted for public service are entitled to use any of these languages as a medium to answer the paper.
Punjabi Australians are Australians who are of Punjabi descent. According to the 2016 census, Punjabi is one of the fastest-growing languages in Australia, with 132,499 individuals identifying as Punjabi-speakers. This is an increase from 71,230 individuals in 2011 and 26,000 individuals in 2006, representing a five-fold growth in 10 years.

The official scripts of the 22 official languages of the Republic of India include abugidas (pseudo-alphabets), alphabetical writing systems and abjads.
Meitei language, the sole official language and the lingua franca of Manipur, one of the scheduled languages of India, one of the recognised educational and literary languages of Assam and Tripura states, has its speakers spread across entire India.