
Taharqa, also spelled Taharka or Taharqo, was a pharaoh of the Twenty-fifth Dynasty of Egypt and qore (king) of the Kingdom of Kush, from 690 to 664 BC. He was one of the "Black Pharaohs" who ruled over Egypt for nearly a century.

Aspelta was a ruler of the kingdom of Kush. More is known about him and his reign than most of the rulers of Kush. He left several stelae carved with accounts of his reign.

Jebel Barkal or Gebel Barkal is a mesa or large rock outcrop located 400 km north of Khartoum, next to Karima in Northern State in Sudan, on the Nile River, in the region that is sometimes called Nubia. The jebel is 104 m tall, has a flat top, and came to have religious significance for both ancient Kush and ancient Egyptian occupiers. In 2003, the mountain, together with the extensive archaeological site at its base, were named as the center of a World Heritage Site by UNESCO. The Jebel Barkal area houses the Jebel Barkal Museum.

Alara was a King of Kush, who is generally regarded as the founder of the Napatan royal dynasty by his 25th Dynasty Kushite successors and was the first recorded prince of Kush. He unified all of Upper Nubia from Meroë to the Third Cataract and is possibly attested at the Temple of Amun at Kawa. Alara also established Napata as the religious capital of Kush. Alara himself was not a 25th dynasty Kushite king since he never controlled any region of Egypt during his reign compared to his two immediate successors: Kashta and Piye respectively. Nubian literature credits him with a substantial reign since future Nubian kings requested that they might enjoy a reign as long as Alara's. His memory was also central to the origin myth of the Kushite kingdom, which was embellished with new elements over time. Alara was a deeply revered figure in Nubian culture and the first Kushite king whose name came down to scholars.

Amanishakheto was a Kandake of Kush. She seems to have reigned from 10 BC to 1 AD, although most dates of Kushite history before the Middle Ages are very uncertain.

The Department of Ancient Egypt is a department forming an historic part of the British Museum, with Its more than 100,000 pieces making it the largest and most comprehensive collection of Egyptian antiquities outside the Egyptian Museum in Cairo.

The National Museum of Sudan or Sudan National Museum, abbreviated SNM, is a two-story building, constructed in 1955 and established as national museum in 1971.

Anlamani was a king of the Kingdom of Kush in Nubia, who ruled from 620 BC and died around 600 BC.

Atlanersa was a Kushite ruler of the Napatan kingdom of Nubia, reigning for about a decade in the mid-7th century BC. He was the successor of Tantamani, the last ruler of the 25th Dynasty of Egypt, and possibly a son of Taharqa or less likely of Tantamani, while his mother was a queen whose name is only partially preserved. Atlanersa's reign immediately followed the collapse of Nubian control over Egypt, which witnessed the Assyrian conquest of Egypt and then the beginning of the Late Period under Psamtik I. The same period also saw the progressive cultural integration of Egyptian beliefs by the Kushite civilization.

Nubian architecture is diverse and ancient. Permanent villages have been found in Nubia, which date from 6000 BC. These villages were roughly contemporary with the walled town of Jericho in Palestine.

Nubia is a region along the Nile river encompassing the area between the first cataract of the Nile and the confluence of the Blue and White Niles, or more strictly, Al Dabbah. It was the seat of one of the earliest civilizations of ancient Africa, the Kerma culture, which lasted from around 2500 BC until its conquest by the New Kingdom of Egypt under Pharaoh Thutmose I around 1500 BC, whose heirs ruled most of Nubia for the next 400 years. Nubia was home to several empires, most prominently the Kingdom of Kush, which conquered Egypt in the eighth century BC during the reign of Piye and ruled the country as its 25th Dynasty.

The Kingdom of Kush, also known as the Kushite Empire, or simply Kush, was an ancient kingdom in Nubia, centered along the Nile Valley in what is now northern Sudan and southern Egypt.

Kawa is a site in Sudan, located between the Third and Fourth Cataracts of the Nile on the east bank of the river, across from Dongola. In ancient times it was the site of several temples to the Egyptian god Amun, built by the Egyptian rulers Amenhotep III and Tutankhamun, and by Taharqa and other Kushite kings.

The Sphinx of Taharqo is a granite gneiss statue of a sphinx with the face of Taharqo. He was a Nubian king, who was one of the 25th Egyptian Dynasty rulers of the Kingdom of Kush. It is now in the British Museum in London.
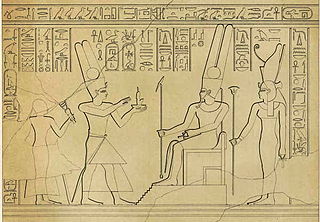
Abar was a Nubian queen of the Kingdom of Kush dated to the Twenty-fifth Dynasty of Egypt. She is known from a series of stela found in Sudan and Egypt. Her appearances mark her as the niece of King Alara of Nubia, married to King Piye and the mother of King Taharqa.

The Twenty-fifth Dynasty of Egypt, also known as the Nubian Dynasty, the Kushite Empire, the Black Pharaohs, or the Napatans, after their capital Napata, was the last dynasty of the Third Intermediate Period of Egypt that occurred after the Nubian invasion.

The Temple of Amun is an archaeological site at Jebel Barkal in Northern State, Sudan. It is situated about 400 kilometres (250 mi) north of Khartoum near Karima. The temple stands near a large bend of the Nile River, in the region that was called Nubia in ancient times. The Temple of Amun, one of the largest temples at Jebel Barkal, is considered sacred to the local population. Not only was the Amun temple a main centre of what at one time was considered to be an almost universal religion, but, along with the other archaeological sites at Jebel Barkal, it was representative of the revival of Egyptian religious values. Up to the middle of the 19th century, the temple was subjected to vandalism, destruction, and indiscriminate plundering, before it came under state protection.

The Temple of Mut, also named Temple B300, is a temple at Jebel Barkal in Northern State, Sudan. It is situated about 400 km north of Khartoum near Karima and stands near a large bend of the Nile River, in the region that was called Nubia in ancient times. The partially rock-cut temple was built on the west side base of the Jebel Barkal pinnacle, from which angle it assumed the shape of an Uraeus wearing the White Crown of Upper Egypt. Dedicated to the goddess Mut, the wife of Amun, the Temple of Mut was erected by pharaoh Taharqa in the 680s BCE, at a time when he ruled Upper and Lower Egypt.

Nubia is a region along the Nile river encompassing the area between the first cataract of the Nile as well as the confluence of the blue and white Niles or, more strictly, Al Dabbah. Nubia was the seat of several civilizations of ancient Africa, including the Kerma culture, the kingdom of Kush, Nobatia, Makuria and Alodia.






















