
Hypoplectrus is a genus of fishes commonly known as hamlets, found mainly in coral reefs in the Caribbean Sea and the Gulf of Mexico, particularly around Florida and the Bahamas. They are a popular choice for hobbyist saltwater aquariums, and come in a variety of colors.
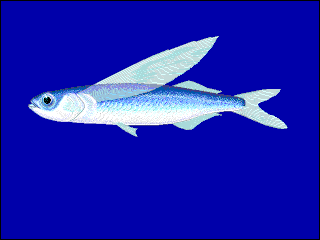
Beloniformes is an order composed of six families of freshwater and marine ray-finned fish:

Needlefish or long toms are piscivorous fishes primarily associated with very shallow marine habitats or the surface of the open sea. Some genera include species found in marine, brackish, and freshwater environments, while a few genera are confined to freshwater rivers and streams, including Belonion, Potamorrhaphis, and Xenentodon. Needlefish closely resemble North American freshwater gars in being elongated and having long, narrow jaws filled with sharp teeth, and some species of needlefishes are referred to as gars or garfish despite being only distantly related to the true gars. In fact, the name "garfish" was originally used for the needlefish Belone belone in Europe and only later applied to the North American fishes by European settlers during the 18th century.

Hemiramphus is a genus of schooling marine fish commonly called halfbeaks, garfish, or ballyhoos, and are members of the family Hemiramphidae. They inhabit the surface of warm temperate and tropical sea, and feed on algae, plankton, and smaller fish. Hemiramphus species are edible but are more important as food fish for larger predatory species including dolphinfish and billfish.

Bodianus or the hogfishes is a genus of fish in the family Labridae found in the Atlantic, Indian and Pacific Ocean. These species have many parasites.

Halichoeres, commonly called wrasses, are a genus of fish in the family Labridae found in the Atlantic, Indian and Pacific Oceans.
The keeltail needlefish, sometimes called the keeled needlefish, is a tropical fish of the family Belonidae. It was described by the French naturalist Charles Alexandre Lesueur in 1821.

Lutjanus is a genus of snappers found in the Atlantic, Indian, and Pacific Oceans. They are predatory fish usually found in tropical and subtropical reefs, and mangrove forests. This genus also includes two species that only occur in fresh and brackish waters.
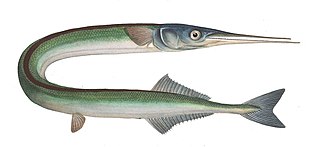
Belone is a genus of needlefish common in brackish and marine waters. It is one of ten genera in the family Belonidae.

The flat needlefish, the only known member of the genus Ablennes, is a marine fish of the family Belonidae. Flat needlefish are considered gamefish, frequently caught with the help of artificial lights, but are not often eaten because of their green-colored flesh.
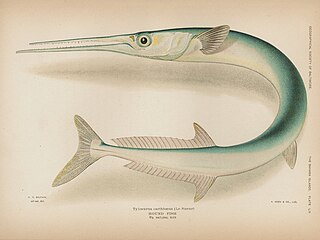
The houndfish is a game fish of the family Belonidae. It is the largest member of its family, growing up to 5 feet (1.5 m) in length and 10 pounds (4.5 kg) in weight. It is also often called the crocodile needlefish.

The Atlantic needlefish is a common demersal needlefish species common in marinas and other areas with minimal currents. Its extremely long jaw and body set this fish apart from other predators. Atlantic needlefish are found from Maine to Brazil and have been known to venture into fresh water for short periods.

Hyporhamphus is a genus of halfbeaks. The species in this genus are distributed throughout the warmer seas of the world, most species being Indo-Pacific and there are some freshwater species.
Belonion is a genus of freshwater needlefishes native to South America. It is one of 10 genera in the family Belonidae.

Tylosurus is a genus of needlefish, one of ten in the family Belonidae. They are found worldwide in tropical and warmer temperate seas and two species have been recorded as Lessepsian migrants in the eastern Mediterranean Sea.
Belonion apodion is one of two freshwater needlefish in the genus Belonion, which is in the family Belonidae. It is native to South America where it is found in the basins of the Guaporè and Madeira Rivers. This species was described by Bruce Collette in 1966 with the type locality given as Laguna 3 kilometers southwest of Costa Marques on the Rio Guapore in Bolivia at border between Brazil and Bolivia. It is the type species of the genus Belonion.

Hyporthodus is a genus of marine ray-finned fish, groupers from the subfamily Epinephelinae, part of the family Serranidae, which also includes the anthias and sea basses. It contains the following species, most of which were previously placed in Epinephelus:
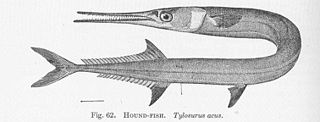
Tylosurus acus is a game fish of the family Belonidae.
Strongylura strongylura, the spottail needlefish or blackspot longtom, is a species of needlefish from the family Belonidae. It is found in the Indian and western Pacific Oceans from the Persian Gulf east to Australia and the Philippines. This species occurs in coastal waters and in mangrove-lined lagoons as well as being recorded in estuarine areas and it has even entered freshwater. Living S. strongylura have been found alive and buried in mud during low tide. It is piscivorous, feeding mainly on clupeoids. This species is oviparous and the eggs adhere to objects in the water which catch the tendrils which cover the surface of the egg. Strongylura strongylura under the synonym of Strongylura caudimaculata is the type species of the genus Strongylura. It as originally described as Belone strongylura by Johan Coenraad van Hasselt in 1823 with the type locality given as Vizagapatam, India.

Tylosurus fodiator, the Mexican needlefish, is a species of needlefish from the family Belonidae which is found only in the eastern Pacific, from the Gulf of California south to Ecuador including the Galapagos, Cocos and Malpelo Islands. It was previously considered to be a subspecies of the houndfish but is now regarded as valid species. This species is normally encountered close to the coast but can be found in offshore waters. It is a predatory species, feeding mainly on small fishes. They lay eggs which adhere to objects in the water by filaments which cover the outer layer of the eggs. This species was described in 1882 by David Starr Jordan and Charles Henry Gilbert with the type locality given as Mazatlán in Sinaloa, western Mexico.
















