
A corona is the outermost layer of a star's atmosphere. It is a hot but relatively dim region of plasma populated by intermittent coronal structures known as solar prominences or filaments.

In physics, motion is when an object changes its position with respect to a reference point in a given time. Motion is mathematically described in terms of displacement, distance, velocity, acceleration, speed, and frame of reference to an observer, measuring the change in position of the body relative to that frame with a change in time. The branch of physics describing the motion of objects without reference to their cause is called kinematics, while the branch studying forces and their effect on motion is called dynamics.

The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is a massive, nearly perfect sphere of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core, radiating the energy from its surface mainly as visible light and infrared radiation with 10% at ultraviolet energies. It is by far the most important source of energy for life on Earth. The Sun has been an object of veneration in many cultures. It has been a central subject for astronomical research since antiquity.

Sunspots are temporary spots on the Sun's surface that are darker than the surrounding area. They are regions of reduced surface temperature caused by concentrations of magnetic flux that inhibit convection. Sunspots appear within active regions, usually in pairs of opposite magnetic polarity. Their number varies according to the approximately 11-year solar cycle.
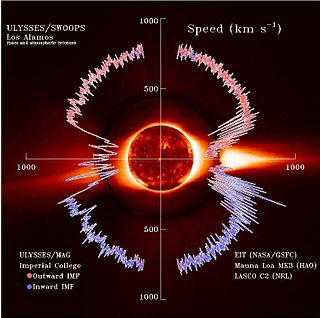
The solar wind is a stream of charged particles released from the Sun's outermost atmospheric layer, the corona. This plasma mostly consists of electrons, protons and alpha particles with kinetic energy between 0.5 and 10 keV. The composition of the solar wind plasma also includes a mixture of particle species found in the solar plasma: trace amounts of heavy ions and atomic nuclei of elements such as carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, neon, magnesium, silicon, sulfur, and iron. There are also rarer traces of some other nuclei and isotopes such as phosphorus, titanium, chromium, and nickel's isotopes 58Ni, 60Ni, and 62Ni. Superimposed with the solar-wind plasma is the interplanetary magnetic field. The solar wind varies in density, temperature and speed over time and over solar latitude and longitude. Its particles can escape the Sun's gravity because of their high energy resulting from the high temperature of the corona, which in turn is a result of the coronal magnetic field. The boundary separating the corona from the solar wind is called the Alfvén surface.

The photosphere is a star's outer shell from which light is radiated. It extends into a star's surface until the plasma becomes opaque, equivalent to an optical depth of approximately 2⁄3, or equivalently, a depth from which 50% of light will escape without being scattered.

Convection is single or multiphase fluid flow that occurs spontaneously due to the combined effects of material property heterogeneity and body forces on a fluid, most commonly density and gravity. When the cause of the convection is unspecified, convection due to the effects of thermal expansion and buoyancy can be assumed. Convection may also take place in soft solids or mixtures where particles can flow.

A chromosphere is the second layer of a star's atmosphere, located above the photosphere and below the solar transition region and corona. The term usually refers to the Sun's chromosphere, but not exclusively.
Differential rotation is seen when different parts of a rotating object move with different angular velocities at different latitudes and/or depths of the body and/or in time. This indicates that the object is not rigid. In fluid objects, such as accretion disks, this leads to shearing. Galaxies and protostars usually show differential rotation; examples in the Solar System include the Sun, Jupiter and Saturn.
Helioseismology, a term coined by Douglas Gough, is the study of the structure and dynamics of the Sun through its oscillations. These are principally caused by sound waves that are continuously driven and damped by convection near the Sun's surface. It is similar to geoseismology, or asteroseismology, which are respectively the studies of the Earth or stars through their oscillations. While the Sun's oscillations were first detected in the early 1960s, it was only in the mid-1970s that it was realized that the oscillations propagated throughout the Sun and could allow scientists to study the Sun's deep interior. The modern field is separated into global helioseismology, which studies the Sun's resonant modes directly, and local helioseismology, which studies the propagation of the component waves near the Sun's surface.

In solar physics, a spicule, also known as a fibril or mottle, is a dynamic jet of plasma in the Sun's chromosphere about 300 km in diameter. They move upwards with speeds between 15 and 110 km/s from the photosphere and last a few minutes each before falling back to the solar atmosphere. They were discovered in 1877 by Angelo Secchi, but the physical mechanism that generates them is still hotly debated.

In solar physics and observation, granules are convection cells in the Sun's photosphere. They are caused by currents of plasma in the Sun's convective zone, directly below the photosphere. The grainy appearance of the photosphere is produced by the tops of these convective cells; this pattern is referred to as granulation.
A granule is a large particle or grain. It can refer to:
The standard solar model (SSM) is a mathematical model of the Sun as a spherical ball of gas. This stellar model, technically the spherically symmetric quasi-static model of a star, has stellar structure described by several differential equations derived from basic physical principles. The model is constrained by boundary conditions, namely the luminosity, radius, age and composition of the Sun, which are well determined. The age of the Sun cannot be measured directly; one way to estimate it is from the age of the oldest meteorites, and models of the evolution of the Solar System. The composition in the photosphere of the modern-day Sun, by mass, is 74.9% hydrogen and 23.8% helium. All heavier elements, called metals in astronomy, account for less than 2 percent of the mass. The SSM is used to test the validity of stellar evolution theory. In fact, the only way to determine the two free parameters of the stellar evolution model, the helium abundance and the mixing length parameter, are to adjust the SSM to "fit" the observed Sun.

Mantle convection is the very slow creep of Earth's solid silicate mantle as convection currents carry heat from the interior to the planet's surface. Mantle convection causes tectonic plates to move around the Earth's surface.

In solar physics, a coronal loop is a well-defined arch-like structure in the Sun's atmosphere made up of relatively dense plasma confined and isolated from the surrounding medium by magnetic flux tubes. Coronal loops begin and end at two footpoints on the photosphere and project into the transition region and lower corona. They typically form and dissipate over periods of seconds to days and may span anywhere from 1 to 1,000 megametres in length.

Granulation is the process of forming grains or granules from a powdery or solid substance, producing a granular material. It is applied in several technological processes in the chemical and pharmaceutical industries. Typically, granulation involves agglomeration of fine particles into larger granules, typically of size range between 0.2 and 4.0 mm depending on their subsequent use. Less commonly, it involves shredding or grinding solid material into finer granules or pellets.

A nanoflare is a very small episodic heating event which happens in the corona, the external atmosphere of the Sun.

The atmosphere of Jupiter is the largest planetary atmosphere in the Solar System. It is mostly made of molecular hydrogen and helium in roughly solar proportions; other chemical compounds are present only in small amounts and include methane, ammonia, hydrogen sulfide, and water. Although water is thought to reside deep in the atmosphere, its directly-measured concentration is very low. The nitrogen, sulfur, and noble gas abundances in Jupiter's atmosphere exceed solar values by a factor of about three.

This glossary of meteorology is a list of terms and concepts relevant to meteorology and atmospheric science, their sub-disciplines, and related fields.
















