
Mahendra Bir Bikram Shah Dev was King of Nepal from 13 March 1955 until his death in 1972, which was due to a heart attack, as told in an interview by his personal physician Dr. Mrigendra Raj Pandey. Following the 1960 coup d'état, he established the party-less Panchayat system, which governed the country for 28 years until the introduction of multi-party democracy in 1990. During his reign, Nepal experienced a period of industrial, political and economic change which opened it to the rest of the world for the first time, after the 104-year-long reign of the Rana rulers, who kept the country under an isolationist policy, came to an end in 1951.

Sir Alagappa Chettiar was an Indian businessman and philanthropist. He received the Padma Bhushan, third highest civilian award of India in 1956.
Education in Oman is provided free of charge up to end of secondary education, though attendance is not mandatory at any level. In 1970 there were only three formal schools with 900 students in the whole state. Oman's national educational program expanded rapidly during the 1970s and the 1980s, with the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia sending teachers on its own expense during that time period. In 2006–2007 about 560,000 students attended 1053 public schools. The number of students in private schools is about 65,000. There are also extensive programmes to combat adult illiteracy. Sultan Qaboos University, the only national university near Muscat, was founded in 1986, and in 2006 it had 13,500 students. The Human Development Report found the literacy rate to be 93.0% in adults, up from 54.7% in 1990. For the same period, the youth literacy rate increased from 85.6 to 97.3%. Public expenditure on education was reported to be 4.6% of GDP and 26.1% of total government spending.

Puduvayal is a town in Karaikudi taluk, Sivaganga district in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu. It is a town located in the Chettinad region of the Sivagangai district. On road, it is 12 km away from Karaikudi and 21 km away from Aranthangi. This town is famous for its rice mills. Puduvayal is the 2nd largest rice producer in Tamil Nadu. Puduvayal is an important commercial centre for trade in the Sivaganga district and part of the suburban region of Karaikudi. The town is famous for its Veerasekara Umaiyambigai Temple. Nearby Kandanur is famous for Kandanur Sivan Kovil—which is a replica of the Madurai Meenakshi Temple—built by Nagarthars.
Balugaon is a town and a Notified Area Council in Khordha district in the state of Odisha, India. It is situated very close to Chilika lake, about 90 kilometres (56 mi) from the state capital Bhubaneswar, and 76 kilometres (47 mi) from the Berhampur, Ganjam. It is a major economic centre of Khordha district because of its prawn and fish business.
Nilakkottai is a town in the Dindigul district of the Indian state of Tamil Nadu. The town was established in 1958, as 1st Grade Town Panchayat. In 1970, it was changed to Selection Grade. The Town Panchayat has been under the municipal act since 1996. In 2004, it was called Special Village Panchayat, and in 2006, Selection Grade Town Panchayat.

Palani Chettipatti is a panchayat grama in Theni district in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu. It is located on the road between Theni and Cumbum. The Mullai river flows via this village from Uthamapalayam and goes down the valley pin code is 625531.
Higher Secondary Certificate (HSC), Higher Secondary School Certificate, Higher Secondary Education Certificate (HSEC) or Intermidiate Examination is a secondary education qualification in Bangladesh, India and Pakistan. It is equivalent to the final year of high school in the United States and A level in the United Kingdom.

The importance and antiquity of education in Kerala are underscored by the state's ranking as among the most literate in the country. The educational transformation of Kerala was triggered by the efforts of both Church Mission Society missionaries like Jon Munro and clergy of Catholic church like Fr Kuriakose Elias Chavara and Fr Charles Lavigne and were the pioneers that promoted mass education in Kerala, in the early decades of the 19th century. The local dynastic precursors of modern-day Kerala, primarily the Travancore Royal Family, the Nair Service Society, Sree Narayana Dharma Paripalana Yogam, and Muslim Educational Society (MES), also made significant contributions to the progress on education in Kerala. Local schools were known by the general term kalaris, some of which taught martial arts, but other village schools run by Ezhuthachans were for imparting general education. Christian missionaries and British rule brought the modern school education system to Kerala. Ezhuthu palli was the name used in earlier times. The word was derived from the schools run by the Buddhist monasteries. For centuries, villages used to set up an ezhuthupally or ashan pallikoodam with one or two teachers. Students used to go this school from nearby areas and learn languages, literature, mathematics, grammar etc. After completing this, students may continue study about specific subjects such as ayurveda, astrology, accounting etc. Censuses during the 1800s showed that Travancore, Cochin, and Kannur areas have many such schools.
Chennai is home to many educational and research institutions. IIT Madras, located in South Chennai is considered as the premier centre of engineering education in India. Anna University and the University of Madras are the oldest state owned universities which are ranked among the best universities in India. The College of Engineering, Guindy and Madras Institute of Technology, which are the constituent college of Anna University along with Alagappa College of Technology are the pioneer institutes of engineering education in India. Some of the oldest medical colleges India, the Madras Medical College (1835) and Stanley Medical College (1938) are located in the city. Notable, liberal arts colleges in the city include Loyola College, Madras Christian College, Presidency College, Stella Maris College, Women's Christian College and Ethiraj College for Women.
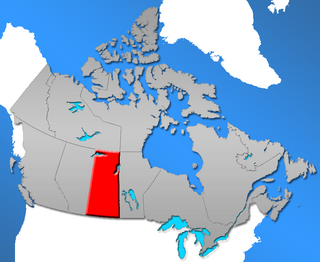
Historically, Saskatchewan's higher education system has been "significantly shaped" by demographics. In 1901, six years prior to the 1907 founding of a university in Saskatchewan, the urban population in Saskatchewan was 14,266 (16%) while the rural population was 77,013 (84%). One hundred years later, the proportions had changed significantly: urban population in 2001 was 629,036 (64%) while the rural population was 349,897 (36%). Over time the province's higher education system has changed significantly in response both to this demographic shift and to provincial politics.
Vembadithalam is a small village in Salem district of Tamil Nadu, India. The village comes under the Veerapandi Union. Vembadithalam means Land of Neem. Vembu is nothing but neem tree. Other nicknames of this village are Vembai and Vems City. Salem is nearest city (15 km) for Vembai and well connected with NH47. Every half an hour public buses and private buses help to commute the people between Vembai and Salem. Vembadithalam is located 6.8 km from its Taluk Main Town Veerapandi. It is located 19.9 km from its District Main City Salem.
Tiruppur Angappa Ramalingam Chettiar was an Indian lawyer, politician, member of parliament and businessman from the Indian state of Tamil Nadu.

Tiruppur Subrahmanya Avinashilingam Chettiar was an Indian lawyer, politician, freedom fighter and Gandhian. He served as the Education Minister of Madras Presidency from 1946 to 1949 and was responsible for introducing Tamil as the medium of instruction. He is also credited with having commissioned the creation of the first Tamil encyclopedia.
Periyapattinam is a large village located in the eastern part of Ramanathapuram district, Tamil Nadu, India. The inhabitants of this village are primarily Tamil Muslim.
Annamalai Chidambaram Muthiah is an Indian industrialist and cricket administrator. He served as the Chairman of Southern Petrochemical Industries Limited (SPIC) and is the chairman of Sri Venkateswara College of Engineering (SVCE), Sriperumbudur near Chennai. He served as the President of the Board of Control for Cricket in India from 1999 to 2001. Muthiah is the only son of M. A. Chidambaram and the grandson of Sir Annamalai Chettiar.
Chengalvaraya Naicker (1825-1874) was a philanthropist also known as Sri P.T.Lee Chengalvaraya Naicker

The West Bengal Board of Madrasah Education is the state government administered autonomous examining authority for affiliated and recognized madrasahs in West Bengal, India. Perhaps among the oldest post-secondary boards in India, it is the only madrasah board that is recognized by the Government of India. It is one of the parastatal organization of the Minority Affairs and Madrasah Education Department. The West Bengal Board of Madrasah Education is the West Bengal state government administered autonomous examining authority for the High Madrasah examination of West Bengal, India. It has come into force by the West Bengal Board of Madrasah Education Act-1994.









