
The Dnepr rocket was a space launch vehicle named after the Dnieper River. It was a converted ICBM used for launching artificial satellites into orbit, operated by launch service provider ISC Kosmotras. The first launch, on April 21, 1999, successfully placed UoSAT-12, a 350 kg demonstration mini-satellite, into a 650 km circular Low Earth orbit.
The Space Test Program (STP) is the primary provider of spaceflight for the United States Department of Defense (DoD) space science and technology community. STP is managed by a group within the Advanced Systems and Development Directorate, a directorate of the Space and Missile Systems Center of the United States Space Force. STP provides spaceflight via the International Space Station (ISS), piggybacks, secondary payloads and dedicated launch services.

Gonets is a Russian civilian low Earth orbit communications satellite system. It consists of a number of satellites, derived from Strela military communications satellites. The first two satellites, which were used to test and validate the system, were launched by a Tsyklon-3 launch vehicle from the Plesetsk Cosmodrome on 13 July 1992, and were designated Gonets-D. The first operational satellites, designated Gonets-D1, were launched on 19 February 1996. After launch, the first three satellites were given military Kosmos designations, a practice which was not continued with the other satellites.
Orbcomm is a family of low Earth orbit communications satellites, operated by the United States satellite communications company Orbcomm. As of July 2014, 51 such satellites have orbited Earth, with 50 still continuing to do so.

In 2015, the maiden spaceflights of the Chinese Long March 6 and Long March 11 launch vehicles took place.

In 2014, the maiden flight of the Angara A5, Antares 120 and Antares 130 took place.

Several new rockets and spaceports began operations in 2016.

This article documents notable spaceflight events during the year 2019.

Notable spaceflight activities in 2017 included the maiden orbital flight of India's Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle Mark III on 5 June and the first suborbital test of Rocket Lab's Electron rocket, inaugurating the Mahia spaceport in New Zealand. The rocket is named for its innovative Rutherford engine which feeds propellants via battery-powered electric motors instead of the usual gas generator and turbopumps.

This article documents notable spaceflight events during the year 2018. For the first time since 1990, more than 100 orbital launches were performed globally.
SkySat is a constellation of sub-meter resolution Earth observation satellites owned by Planet Labs, providing imagery, high-definition video and analytics services. Planet acquired the satellites with their purchase of Terra Bella, a Mountain View, California-based company founded in 2009 by Dan Berkenstock, Julian Mann, John Fenwick, and Ching-Yu Hu, from Google in 2017.

Planet Labs PBC is a publicly trading American Earth imaging company based in San Francisco, California. Their goal is to image the entirety of the Earth daily to monitor changes and pinpoint trends.
Hodoyoshi-3 is a Japanese micro-satellite launched in 2014. The satellite is built in 0.5x0.5x0.65m box-shape bus, optimized for piggy-back launch. All instruments are powered by solar cells mounted on the spacecraft body and two stub wings, with estimated electrical power of 50W. For orbit-keeping, a hydrogen peroxide thruster is used. The satellite was developed under the Funding Program for World-Leading Innovation R&D on Science and Technology.

ÑuSat satellite series, is a series of Argentinean commercial Earth observation satellites. They form the Aleph-1 constellation, which is designed, built and operated by Satellogic.

This article documents notable spaceflight events during the year 2020.
Sputnix is a privately-owned satellite construction company headquartered at the Skolkovo Innovation Center. It is one of Russia's first private space companies. It was founded in 2011 by ScanEx.
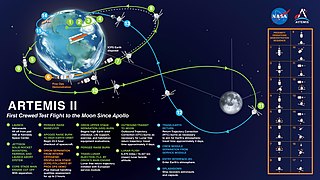
Spaceflight in 2025 promises to follow the 2020s trend of record breaking orbital launches and increased developments in lunar, Mars and low-earth orbit exploration.












