In electronics and telecommunications, modulation is the process of varying one or more properties of a periodic waveform, called the carrier signal, with a separate signal called the modulation signal that typically contains information to be transmitted. For example, the modulation signal might be an audio signal representing sound from a microphone, a video signal representing moving images from a video camera, or a digital signal representing a sequence of binary digits, a bitstream from a computer.

Ethernet over twisted-pair technologies use twisted-pair cables for the physical layer of an Ethernet computer network. They are a subset of all Ethernet physical layers.

In telecommunications and signal processing, baseband is the range of frequencies occupied by a signal that has not been modulated to higher frequencies. Baseband signals typically originate from transducers, converting some other variable into an electrical signal. For example, the electronic output of a microphone is a baseband signal that is analogous to the applied voice audio. In conventional analog radio broadcasting, the baseband audio signal is used to modulate an RF carrier signal of a much higher frequency.

Frequency-shift keying (FSK) is a frequency modulation scheme in which digital information is encoded on a carrier signal by periodically shifting the frequency of the carrier between several discrete frequencies. The technology is used for communication systems such as telemetry, weather balloon radiosondes, caller ID, garage door openers, and low frequency radio transmission in the VLF and ELF bands. The simplest FSK is binary FSK, in which the carrier is shifted between two discrete frequencies to transmit binary information.

In telecommunications, a line code is a pattern of voltage, current, or photons used to represent digital data transmitted down a communication channel or written to a storage medium. This repertoire of signals is usually called a constrained code in data storage systems. Some signals are more prone to error than others as the physics of the communication channel or storage medium constrains the repertoire of signals that can be used reliably.
In telecommunications and data storage, Manchester code is a line code in which the encoding of each data bit is either low then high, or high then low, for equal time. It is a self-clocking signal with no DC component. Consequently, electrical connections using a Manchester code are easily galvanically isolated.

In telecommunications, a non-return-to-zero (NRZ) line code is a binary code in which ones are represented by one significant condition, usually a positive voltage, while zeros are represented by some other significant condition, usually a negative voltage, with no other neutral or rest condition.
Phase-shift keying (PSK) is a digital modulation process which conveys data by changing (modulating) the phase of a constant frequency carrier wave. The modulation is accomplished by varying the sine and cosine inputs at a precise time. It is widely used for wireless LANs, RFID and Bluetooth communication.

Pulse-amplitude modulation (PAM) is a form of signal modulation where the message information is encoded in the amplitude of a series of signal pulses. It is an analog pulse modulation scheme in which the amplitudes of a train of carrier pulses are varied according to the sample value of the message signal. Demodulation is performed by detecting the amplitude level of the carrier at every single period.

In computer networking, Fast Ethernet physical layers carry traffic at the nominal rate of 100 Mbit/s. The prior Ethernet speed was 10 Mbit/s. Of the Fast Ethernet physical layers, 100BASE-TX is by far the most common.
Pulse-position modulation (PPM) is a form of signal modulation in which M message bits are encoded by transmitting a single pulse in one of possible required time shifts. This is repeated every T seconds, such that the transmitted bit rate is bits per second. It is primarily useful for optical communications systems, which tend to have little or no multipath interference.
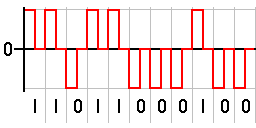
Return-to-zero describes a line code used in telecommunications signals in which the signal drops (returns) to zero between each pulse. This takes place even if a number of consecutive 0s or 1s occur in the signal. The signal is self-clocking. This means that a separate clock does not need to be sent alongside the signal, but suffers from using twice the bandwidth to achieve the same data-rate as compared to non-return-to-zero format.
Continuous phase modulation (CPM) is a method for modulation of data commonly used in wireless modems. In contrast to other coherent digital phase modulation techniques where the carrier phase abruptly resets to zero at the start of every symbol, with CPM the carrier phase is modulated in a continuous manner. For instance, with QPSK the carrier instantaneously jumps from a sine to a cosine whenever one of the two message bits of the current symbol differs from the two message bits of the previous symbol. This discontinuity requires a relatively large percentage of the power to occur outside of the intended band, leading to poor spectral efficiency. Furthermore, CPM is typically implemented as a constant-envelope waveform, i.e., the transmitted carrier power is constant. Therefore, CPM is attractive because the phase continuity yields high spectral efficiency, and the constant envelope yields excellent power efficiency. The primary drawback is the high implementation complexity required for an optimal receiver.

In telecommunications, visible light communication (VLC) is the use of visible light as a transmission medium. VLC is a subset of optical wireless communications technologies.
Autonegotiation is a signaling mechanism and procedure used by Ethernet over twisted pair by which two connected devices choose common transmission parameters, such as speed, duplex mode, and flow control. In this process, the connected devices first share their capabilities regarding these parameters and then choose the highest-performance transmission mode they both support.
4B3T, which stands for 4 (four) binary 3 (three) ternary, is a line encoding scheme used for ISDN PRI interface. 4B3T represents four binary bits using three pulses.
In a digitally modulated signal or a line code, symbol rate, modulation rate or baud rate is the number of symbol changes, waveform changes, or signaling events across the transmission medium per unit of time. The symbol rate is measured in baud (Bd) or symbols per second. In the case of a line code, the symbol rate is the pulse rate in pulses per second. Each symbol can represent or convey one or several bits of data. The symbol rate is related to the gross bit rate, expressed in bits per second.
The physical coding sublayer (PCS) is a networking protocol sublayer in the Fast Ethernet, Gigabit Ethernet, and 10 Gigabit Ethernet standards. It resides at the top of the physical layer (PHY), and provides an interface between the physical medium attachment (PMA) sublayer and the media-independent interface (MII). It is responsible for data encoding and decoding, scrambling and descrambling, alignment marker insertion and removal, block and symbol redistribution, and lane block synchronization and deskew.
In digital circuits, a logic level is one of a finite number of states that a digital signal can inhabit. Logic levels are usually represented by the voltage difference between the signal and ground, although other standards exist. The range of voltage levels that represent each state depends on the logic family being used. A logic-level shifter can be used to allow compatibility between different circuits.
In serial communication of digital data, clock recovery is the process of extracting timing information from a serial data stream itself, allowing the timing of the data in the stream to be accurately determined without separate clock information. It is widely used in data communications; the similar concept used in analog systems like color television is known as carrier recovery.








