
Ficus is a genus of about 850 species of woody trees, shrubs, vines, epiphytes and hemiepiphytes in the family Moraceae. Collectively known as fig trees or figs, they are native throughout the tropics with a few species extending into the semi-warm temperate zone. The common fig (F. carica) is a temperate species native to southwest Asia and the Mediterranean region, which has been widely cultivated from ancient times for its fruit, also referred to as figs. The fruit of most other species are also edible though they are usually of only local economic importance or eaten as bushfood. However, they are extremely important food resources for wildlife. Figs are also of considerable cultural importance throughout the tropics, both as objects of worship and for their many practical uses.

Fig wasps are wasps of the superfamily Chalcidoidea which spend their larval stage inside fig syconia. Some are pollinators but others simply feed off the plant. The non-pollinators belong to several groups within the superfamily Chalcidoidea, while the pollinators are in the family Agaonidae. Pollinating fig wasps are all gall-makers, non-pollinating fig wasps either make their own galls or usurp the galls of other fig wasps; reports of their being parasitoids are considered dubious.

Ficus macrophylla, commonly known as the Moreton Bay fig or Australian banyan, is a large evergreen banyan tree of the Mulberry Family (Moraceae) native to eastern Australia, from the Wide Bay–Burnett region in the north to the Illawarra in New South Wales, as well as Lord Howe Island where the subspecies F. m. columnaris is a banyan form covering 2.5 acres or more of ground. Its common name is derived from Moreton Bay in Queensland, Australia. It is best known for its imposing buttress roots.

Ficus rubiginosa, the rusty fig or Port Jackson fig, is a species of flowering plant native to eastern Australia in the genus Ficus. Beginning as a seedling that grows on other plants (hemiepiphyte) or rocks (lithophyte), F. rubiginosa matures into a tree 30 m (100 ft) high and nearly as wide with a yellow-brown buttressed trunk. The leaves are oval and glossy green and measure from 4 to 19.3 cm long and 1.25 to 13.2 cm wide.

The family Agaonidae is a group of pollinating fig wasps. They spend their larval stage inside the fruits of figs. The pollinating wasps are the mutualistic partners of the fig trees. Extinct forms from the Eocene and Miocene are nearly identical to modern forms, suggesting that the niche has been stable over geologic time.

Ficus citrifolia, also known as the shortleaf fig, giant bearded fig, Jagüey, wild banyantree and Wimba tree, is a species of banyan native to southern Florida, the Caribbean, Mexico, Central America, and northern South America south to Paraguay. It is distinguished from the closely related Florida strangler fig mainly by the finer veining in the leaves.

Syconium is the type of fruit borne by figs, formed by an enlarged, fleshy, hollow receptacle with multiple ovaries on the inside surface. In essence, it is really a fleshy stem with a number of flowers, so it is considered both a multiple and accessory fruit.

Ficus aurea, commonly known as the Florida strangler fig, golden fig, or higuerón, is a tree in the family Moraceae that is native to the U.S. state of Florida, the northern and western Caribbean, southern Mexico and Central America south to Panama. The specific epithet aurea was applied by English botanist Thomas Nuttall who described the species in 1846.

Pegoscapus is a genus of fig wasp native to the Americas. They range from Florida and Mexico in the north to Argentina in the south. Fig wasps have an obligate mutualism with the fig species they pollinate. Pegoscapus pollinates species in section Americana of the subgenus Urostigma.
Ficus maxima is a fig tree which is native to Mexico, Central America, the Caribbean and South America south to Paraguay. Figs belong to the family Moraceae. The specific epithet maxima was coined by Scottish botanist Philip Miller in 1768; Miller's name was applied to this species in the Flora of Jamaica, but it was later determined that Miller's description was actually of the species now known as Ficus aurea. To avoid confusion, Cornelis Berg proposed that the name should be conserved for this species. Berg's proposal was accepted in 2005.
Tetrapus americanus is a species of fig wasp which is native to South and Central America. It has an obligate mutualism with Ficus maxima, the fig species it pollinates.

Ficus insipida is a common tropical tree in the fig genus of the family Moraceae growing in forest habitats along rivers. It ranges from Mexico to northern South America.

Ficus americana, commonly known as the West Indian laurel fig or Jamaican cherry fig, is a tree in the family Moraceae which is native to the Caribbean, Mexico in the north, through Central and South America south to southern Brazil. It is an introduced species in Florida, USA. The species is variable; the five recognised subspecies were previously placed in a large number of other species.

Ficus pleurocarpa, commonly known as the banana fig, karpe fig or gabi fig, is a fig that is endemic to the wet tropical rainforests of northeastern Queensland, Australia. It has characteristic ribbed orange and red cylindrical syconia. It begins life as a hemiepiphyte, later becoming a tree up to 25 m (82 ft) tall. F. pleurocarpa is one of the few figs known to be pollinated by more than one species of fig wasp.

Ficus obliqua, commonly known as the small-leaved fig, is a tree in the family Moraceae, native to eastern Australia, New Guinea, eastern Indonesia to Sulawesi and islands in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. Previously known for many years as Ficus eugenioides, it is a banyan of the genus Ficus, which contains around 750 species worldwide in warm climates, including the edible fig. Beginning life as a seedling, which grows on other plants (epiphyte) or on rocks (lithophyte), F. obliqua can grow to 60 m (200 ft) high and nearly as wide with a pale grey buttressed trunk, and glossy green leaves.

A wasp is any insect of the narrow-waisted suborder Apocrita of the order Hymenoptera which is neither a bee nor an ant; this excludes the broad-waisted sawflies (Symphyta), which look somewhat like wasps, but are in a separate suborder. The wasps do not constitute a clade, a complete natural group with a single ancestor, as bees and ants are deeply nested within the wasps, having evolved from wasp ancestors. Wasps that are members of the clade Aculeata can sting their prey.
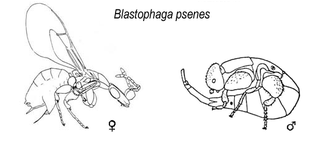
Blastophaga is a wasp genus in the family Agaonidae which pollinate figs or are otherwise associated with figs, a coevolutional relationship that has been developing for at least 80 million years. Pollinating fig wasps are specific to specific figs. The common fig Ficus carica is pollinated by Blastophaga psenes.

Blastophaga psenes is a wasp species in the genus Blastophaga. It pollinates the common fig Ficus carica and the closely related Ficus palmata. These wasps breed in figs without the need for a colony or nest, and the adults live for only a few days or weeks. They locate the fig they wish to pollinate primarily using through olfaction.

Ceratosolen is an Old World wasp genus in the family Agaonidae. They are pollinators of the monoecious fig subsections Sycomorus and Sycocarpus, and the section Neomorphe, all belonging to the subgenus Sycomorus. The genus is native to the Palearctic, Afrotropical, Indomalayan and Australasian realms.

The genus Ficus is composed of 800 species of vines, shrubs, and trees, defined by their syconiums, the fruit-like vessels that either hold female flowers or pollen on the inside. In addition to being cultivated by humans for thousands of years, Ficus is also known for its reproductive mutualism with the fig wasp.
















