Related Research Articles

BNSF Railway is the largest freight railroad network in North America. One of eight North American Class I railroads, BNSF has 35,000 employees, 32,500 miles (52,300 km) of track in 28 states, and nearly 8,000 locomotives. It has three transcontinental routes that provide rail connections between the western and eastern United States. BNSF trains traveled over 169 million miles in 2010, more than any other North American railroad.
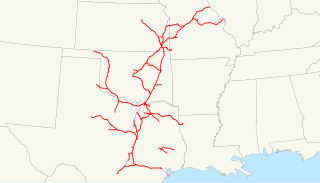
The Missouri–Kansas–Texas Railway is a former Class I railroad company in the United States, with its last headquarters in Dallas, Texas. Established in 1865 under the name Union Pacific Railway, Southern Branch, it came to serve an extensive rail network in Texas, Oklahoma, Kansas, and Missouri. In 1988, it merged with the Missouri Pacific Railroad; today, it is part of Union Pacific Railroad.

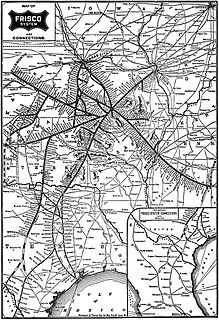
The St. Louis–San Francisco Railway, commonly known as the "Frisco", was a railroad that operated in the Midwest and South Central United States from 1876 to April 17, 1980. At the end of 1970, it operated 4,547 miles (7,318 km) of road on 6,574 miles (10,580 km) of track, not including subsidiaries Quanah, Acme and Pacific Railway and the Alabama, Tennessee and Northern Railroad; that year, it reported 12,795 million ton-miles of revenue freight and no passengers. It was purchased and absorbed into the Burlington Northern Railroad in 1980. Despite its name, it never came close to San Francisco.

Farmrail System, Inc. is an employee-owned holding company for two Class III common-carrier railroads comprising "Western Oklahoma’s Regional Railroad" based in Clinton, Oklahoma. Farmrail Corporation has acted since 1981 as a lessee-operator for Oklahoma Department of Transportation, managing an 82-mile east-west former Rock Island line between Weatherford and Erick and an additional 89 miles of former Santa Fe track, Westhorn-Elmer, acquired by the State in 1992 from the ATSF Railway. Another wholly owned affiliate, Grainbelt Corporation (GNBC), was formed in 1987 to buy 176 contiguous north-south route-miles linking Enid and Frederick.

The Missouri and Northern Arkansas Railroad, LLC is a Class III shortline railroad headquartered in Carthage, Missouri. It is not to be confused with the Missouri and North Arkansas Railroad which connected Joplin, Missouri with Helena, Arkansas from 1906 to 1946.

The Kiamichi Railroad Company is a Class III short-line railroad headquartered in Hugo, Oklahoma.

The Wichita, Tillman and Jackson Railway is a shortline railroad subsidiary of the Rio Grande Pacific Corporation that operates in Oklahoma and Texas. The line for which it is named extends from Wichita Falls, Texas to just north of Altus, Oklahoma, through Wichita County, Texas, Tillman County, Oklahoma, and Jackson County, Oklahoma. It interchanges with the Union Pacific (UP) and BNSF at Wichita Falls, with Farmrail (FMRC), Stillwater Central Railroad (SLWC), and the BNSF at Altus, and with Grainbelt (GNBC) at Frederick, Oklahoma. It carries predominately grain, chemicals and agricultural products.
The Oklahoma City – Ada – Atoka Railway (OCAA) was formed from trackage from Oklahoma City to Atoka via Shawnee, Ada, and Coalgate, Oklahoma. Atoka to Coalgate had been built between 1882 and 1886 as feeder to the old Missouri–Kansas–Texas Railroad (Katy) main line, and Coalgate-Shawnee-Oklahoma City had been constructed by Katy affiliates, and specifically the first 40 miles northwest out of Coalgate having been built by the Texas and Oklahoma Railroad in 1902, and the remaining 78 miles into Oklahoma City having been built in the 1903-1904 timeframe by that line’s successor, the Missouri, Kansas and Oklahoma Railroad Company. However, these properties were not included in the 1923 reorganization of the Katy, and were put in the OCAA instead. The OCAA ended up being sold to the Muskogee Company in 1929, becoming one of the Muskogee Roads.

The Arkansas–Oklahoma Railroad is a Class III carrier headquartered in Wilburton, OK that operates two segments of the former Chicago, Rock Island and Pacific Railroad (CRIP) Choctaw Route that originally ran between Memphis Tennessee and Tucumcari, New Mexico. AOK started operations on March 3, 1996 on 73 miles of track then owned by the U.S. state of Oklahoma between Howe and McAlester by assuming the existing lease of the Missouri Pacific, then wholly owned by the Union Pacific Railroad (UP). This lease included a purchase option which was exercised by AOK in April 2016. The line interchanges with the Kansas City Southern Railway at Howe, and with the UP at McAlester.
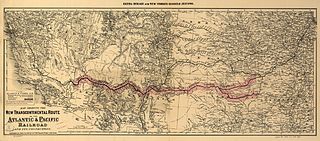
The Atlantic and Pacific Railroad was a U.S. railroad that owned or operated two disjointed segments, one connecting St. Louis, Missouri with Tulsa, Oklahoma, and the other connecting Albuquerque, New Mexico with Southern California. It was incorporated by the U.S. Congress in 1866 as a transcontinental railroad connecting Springfield, Missouri and Van Buren, Arkansas with California. The central portion was never constructed, and the two halves later became parts of the St. Louis-San Francisco Railway and Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway systems, now both merged into the BNSF Railway.

The Panhandle and Santa Fe Railway (P&SF) is a now-defunct railroad company that was a subsidiary of the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway (AT&SF), operating primarily in the Texas Panhandle.
The Arkansas Valley and Western Railway (AV&W) was built as a short line railroad operating within the U.S. state of Oklahoma. It was founded in 1902 to link the city of Tulsa with the main transcontinental line of the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway (AT&SF) at Avard. The line was built in sections, initially from AV&W Jct. to Steen (Enid) during 1902-03. In 1904 it was extended westward to the junction with AT&SF at Avard. On July 19, 1907, the railroad was purchased by the St. Louis-San Francisco Railway, who operated it until November 21, 1980, when the Frisco was acquired by Burlington Northern Railroad.

Maryneal is an unincorporated community in southern Nolan County, Texas, United States. It lies along FM 608 south of the city of Sweetwater, the county seat of Nolan County. Its elevation is 2,566 feet (782 m). Although Maryneal is unincorporated, it has a post office, with the ZIP code of 79535; the ZCTA for ZIP Code 79535 had a population of 181 at the 2000 census.
The following is a brief history of the North American rail system, mainly through major changes to Class I railroads, the largest class by operating revenue.
The Fort Worth and Rio Grande Railway, chartered under the laws of Texas on June 1, 1885, was part of a plan conceived by Buckley Burton Paddock and other Fort Worth civic leaders to create a transcontinental route linking New York, Fort Worth, and the Pacific port of Topolobampo, which they believed would stimulate the growth and development of southwest Texas in general, and the economy of Fort Worth in particular.
The Southwestern Railroad is a Class III railroad operating since 1990, and until 2017 consisted of two unconnected railroad sections in New Mexico, with no shared functions. These and a third section in the Texas panhandle and Oklahoma, now closed, all operated separately. Since January 2017, only the Whitewater Division is operated by Southwestern.
The Chillicothe Subdivision or "Chillicothe Sub" is a railway line running about 229 miles (369 km) from Chicago, Illinois to Fort Madison, Iowa in the United States of America. It is operated by BNSF Railway as part of their Southern Transcon route from Chicago to Los Angeles. The Chillicothe Subdivision is a high volume route connecting three principal yards in Chicago in the east and the Marceline Subdivision in the west which continues to Kansas City.
The Timber Rock Railroad (TIBR) is a shortline rail carrier operating in the states of Texas and Louisiana. Its single line runs from Kirbyville, Texas to DeRidder, Louisiana, about 41.5 miles. It is owned by the Watco Companies.
The Wichita Falls and Northwestern Railway, its affiliate the Northwestern Railway Company of Texas, and two subsidiaries collectively constructed a railway running from Wichita Falls, Texas through Altus, Oklahoma to Forgan, Oklahoma, with a branch running from Altus to Wellington, Texas. The network comprised 359.3 miles of track, and was collectively known as the Wichita Falls Route.
The Texas and Oklahoma Railroad (T&O) existed briefly from its incorporation in mid-1902 to its consolidation with another line at the end of 1903. Its main accomplishment was to construct 40 miles of track northwest out of Coalgate, Oklahoma.
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 "Employer Status Determination" (PDF). Railroad Retirement Board. Retrieved January 5, 2022.
- 1 2 3 4 "Chillicothe to Sweetwater, TX". AbandonedRails.com. Retrieved January 4, 2022.
- ↑ "Kansas City, Mexico & Orient Railway Company (Kans., Okla., Tex., Mex.), Public Timetable and Map Showing Route in 1906". Texas Transportation Archive. Retrieved January 4, 2022.
- 1 2 "Railroad Map of Texas, 1926". Texas-Louisiana Tariff Bureau & Texas Industrial Traffic League (accessed on Library of Congress website). Retrieved December 27, 2021.
- ↑ "Oklahoma 1989 Official State Railroad Map". Oklahoma Department of Transportation (accessed on Flickr.com). Retrieved January 4, 2022.
- ↑ "Sweetwater, TX". Bing Maps. Retrieved January 4, 2022.
- ↑ "Homepage". Farmrail. Retrieved January 4, 2022.
- 1 2 "Farmrail Corporation FMRC #280". Union Pacific. Retrieved January 4, 2022.
- ↑ "Railway freight trains BNSF at WESTHOM". RoadOnMap.com. Retrieved January 4, 2022.
- ↑ "News Archive". Farmrail. Retrieved January 4, 2022.
- ↑ "Oklahoma 2009 State Railroad Map" (PDF). Oklahoma Department of Transportation. Retrieved January 4, 2022.
- ↑ "Statewide Railroad Map, 2021" (PDF). Texas Transportation Commission. Retrieved December 27, 2021.
- ↑ "BNSF Network Map" (PDF). BNSF. Retrieved January 4, 2022.
- ↑ Railroads of Oklahoma, June 6, 1870 to April 1, 1978. State of Oklahoma Department of Transportation, Survey Division. April 1, 1978. pp. 50–53.