Related Research Articles

BNSF Railway is one of the largest freight railroads in North America. One of seven North American Class I railroads, BNSF has 35,000 employees, 32,500 miles (52,300 km) of track in 28 states, and nearly 8,000 locomotives. It has three transcontinental routes that provide rail connections between the western and eastern United States. BNSF trains traveled over 169 million miles in 2010, more than any other North American railroad.

The Kansas City Southern Railway Company is an American Class I railroad. Founded in 1887, it operates in 10 midwestern and southeastern U.S. states: Illinois, Missouri, Kansas, Oklahoma, Arkansas, Tennessee, Alabama, Mississippi, Louisiana and Texas. KCS hauls freight for seven major government and business sectors: agriculture and minerals, military, automotive, chemical and petroleum, energy, industrial and consumer products and intermodal.

U.S. Highway 96 (US 96) is a north–south United States Numbered Highway that runs for about 117.11 miles (188.47 km) entirely in the U.S state of Texas. Its number is a violation of the standard numbering convention, as even-numbered two-digit highways are east–west routes by rule. As of 2004, the highway's southern terminus is in Port Arthur at an intersection with State Highway 87 (SH 87). Its northern terminus is in Tenaha at an intersection with US 59 /(Future I-369) and US 84.

Kansas City Southern (KCS) is a pure transportation holding company with railroad investments in the United States, Mexico, and Panama.
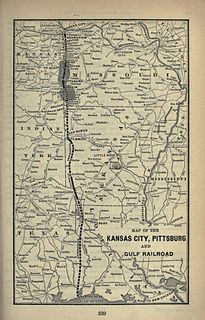
The Texarkana and Fort Smith Railway was the Texas subsidiary of the Kansas City Southern Railway, operating railroad lines in the states of Arkansas and Texas, with headquarters at Texarkana, Texas.
Watco Companies, L.L.C. (Watco) is a transportation company based in Pittsburg, Kansas, formed in 1983 by Charles R. Webb. Watco was composed of four divisions: transportation, mechanical, terminal and port services, and compliance. Watco is the owner of Watco Transportation Services, L.L.C. (WTS), which operates 41 short line railroads in the U.S. and Australia. It is one of the largest short line railroad companies in the United States. As of December 2018, it operates on 5,500 miles (8,900 km) of leased and owned track. Also under transportation is the contract switching the company provides service for 30 customers. That was the service that Watco originally offered before it branched out into other areas.

The Alabama Southern Railroad is a class III railroad that operates in the southern United States. The ABS is one of several short line railroads owned by Watco. The railroad operates an 85-mile (137 km) line leased from the Kansas City Southern Railway. It began operating in 2005.
The Arkansas Southern Railroad is a short-line railroad which started service in October 2005. ARS operates two disconnected lines consisting of Heavener, Oklahoma to Waldron, Arkansas, and Ashdown to Nashville, Arkansas, plus a switch track at Ashdown, for a total of 63 miles. The lines are leased from Kansas City Southern Railway (KCS) to ARS's owner, the Watco Companies (Watco).

The Wichita, Tillman and Jackson Railway is a shortline railroad subsidiary of the Rio Grande Pacific Corporation that operates in Oklahoma and Texas. The line for which it is named extends from Wichita Falls, Texas to just north of Altus, Oklahoma, through Wichita County, Texas, Tillman County, Oklahoma, and Jackson County, Oklahoma. It interchanges with the Union Pacific (UP) and BNSF at Wichita Falls, with Farmrail (FMRC), Stillwater Central Railroad (SLWC), and the BNSF at Altus, and with Grainbelt (GNBC) at Frederick, Oklahoma. It carries predominantly grain, chemicals and agricultural products.

The Terminal Railroad Association of St. Louis is a Class III switching and terminal railroad that handles traffic in the St. Louis, Missouri, metropolitan area. It is co-owned by five of the six Class I railroads that reach the city.
The BG&CM Railroad or Bountiful Grain and Craig Mountain Railroad is a Class III shortline railroad located in North Central Idaho.

The Kansas City Terminal Railway is a Class III terminal railroad that serves as a joint operation of the trunk railroads that serve the Kansas City metropolitan area, the United States' second largest rail hub after Chicago. It is operated by the Kaw River Railroad.

South Kansas and Oklahoma Railroad is a short line railroad which operates 511 miles (822 km) of rail lines in Kansas, Oklahoma and Missouri that used to belong to Missouri Pacific, Frisco and Santa Fe lines. SKOL is a unit of Watco. The present railroad was created in July 2000, when Watco merged one short line railroad, the Southeast Kansas Railroad (SEKR), with another short line, the South Kansas and Oklahoma Railroad. SKOL was the surviving company.

The Kaw River Railroad is a Kansas City, Missouri railroad, established in June 2004. Twelve miles of original track served the Kansas City Southern Railroad and its customers in Kansas City and Union Station. The original KAW was a Kansas City Southern Railway Company property and was the first shortline Watco began operating for KCS, serving customers in the Greater Kansas City area and interchanges with the BNSF, KCS, and Union Pacific. The April 2005 expansion was a BNSF property serving customers in Clay County, Missouri and interchanges with the BNSF at Birmingham, Missouri. The KCTL interchanges with the BNSF, ICE, KCS, Norfolk Southern and Union Pacific at Kansas City.
The Louisiana Southern Railroad (LAS) is a shortline railroad operating in the state of Louisiana. It began operations September 25, 2005 on two unconnected lines leased from the Kansas City Southern Railway (KCS). The northern branch runs south from Springhill, Louisiana through Sarepta and Cotton Valley to Minden, Louisiana, with one set of tracks continuing south to Sibley, Louisiana, and another set running west through Princeton to Shreveport, Louisiana. The south branch runs generally south-southeast from Gibsland, Louisiana through towns like Bienville, Hodge, and Winnfield, to end at Pineville, Louisiana. The total trackage is currently 195.4 miles.
The Texas and Oklahoma Railroad (TXOR), created in 1991, ran between Oklahoma and Texas on rail purchased from the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway (AT&SF). Much of the trackage has since been sold or abandoned; however, the railway continues to exist as a shortline carrier operating between Sweetwater, Texas and Maryneal, Texas.
The Arkansas Western Railway operated a 32-mile rail line between Heavener, Oklahoma and Waldron, Arkansas. It bought the assets of its predecessor in 1904, and the company was merged out of existence in 1992.
References
- 1 2 3 4 "Timber Rock Railroad leases another Texas line from BNSF". Progressive Railroading, July 2, 2004. Retrieved September 3, 2021.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 "Timber Rock Railroad (TIBR)". Watco. Retrieved September 3, 2021.
- 1 2 3 4 "Timber Rock Railroad". Railway Gazette International. Retrieved September 3, 2021.
- ↑ "Jasper and Eastern Railroad". Texas State Historical Association Handbook of Texas. Retrieved September 3, 2021.
- ↑ "Timber Rock Railroad, Inc.-Discontinuance of Service Exemption-In Burleson, Brazos, Grimes, Montgomery, Liberty, Hardin and Jefferson Counties, TX". Transportation Department and Surface Transportation Board, Federal Register, November 2, 2006. Retrieved September 3, 2021.
- 1 2 3 4 "Santa Fe rolls back into town". Mike Lout, KJAS.com, January 25, 2017. Retrieved September 3, 2021.
- 1 2 3 "TIBR: Timber Rock Railroad" (PDF). Kansas City Southern Lines. Retrieved September 3, 2021.
- ↑ "Metropolitan Transportation Plan 2045, p. 9-5" (PDF). South East Texas Regional Planning Commission Metropolitan Planning Organization (SETRPC-MPO) for the Jefferson-Orange-Hardin Regional Transportation Study (JOHRTS) Area, July 18 2019. Retrieved September 3, 2021.
- ↑ "Tenaha, TX". Google Maps. Retrieved September 3, 2021.
- ↑ "(Tencho Texas as search term)". Google Maps. Retrieved September 3, 2021.
- ↑ "(Tencho Texas as search term)". Mapquest. Retrieved September 3, 2021.