
A midge is any small fly, including species in several families of non-mosquito nematoceran Diptera. Midges are found on practically every land area outside permanently arid deserts and the frigid zones. Some midges, such as many Phlebotominae and Simuliidae, are vectors of various diseases. Many others play useful roles as prey for insectivores, such as various frogs and swallows. Others are important as detritivores, and form part of various nutrient cycles. The habits of midges vary greatly from species to species, though within any particular family, midges commonly have similar ecological roles.

The Chironomidae comprise a family of nematoceran flies with a global distribution. They are closely related to the Ceratopogonidae, Simuliidae, and Thaumaleidae. Many species superficially resemble mosquitoes, but they lack the wing scales and elongated mouthparts of the Culicidae.
Alotanypus is a genus of non-biting midges of the bloodworm family Chironomidae.
Clunio is a genus of non-biting midges in the subfamily Orthocladiinae of the bloodworm family (Chironomidae). All species in the genus are marine. They are found in the intertidal zone of many coasts worldwide. The species Clunio marinus is a long-standing model system in Chronobiology and its genome has been sequenced. Clunio species can be dispersed widely by hitch-hiking on sea-turtles, feeding on algae growing on their carapace.
Corynoneura is a speciose genus of non-biting midges in the subfamily Orthocladiinae of the bloodworm family Chironomidae. With a world-wide distribution, these small midges are found in both flowing and standing freshwater of various thermal regimes.
Paratanytarsus is a genus of European non-biting midges in the subfamily Chironominae of the bloodworm family Chironomidae.
Labrundinia is a genus of non-biting midges in the subfamily Tanypodinae of the bloodworm family Chironomidae.
Telmatogetoninae is a subfamily of midges in the non-biting midge family (Chironomidae).

Telmatogeton is a genus of midges in the non-biting midge family (Chironomidae).
Diamesini is a tribe of midges in the non-biting midge family (Chironomidae).
Diamesa is a genus of non-biting midges in the subfamily Diamesinae of the bloodworm family Chironomidae.
Syndiamesa is a genus of non-biting midges in the subfamily Diamesinae of the bloodworm family Chironomidae.
Sympotthastia is a genus of non-biting midges in the subfamily Diamesinae of the bloodworm family Chironomidae.
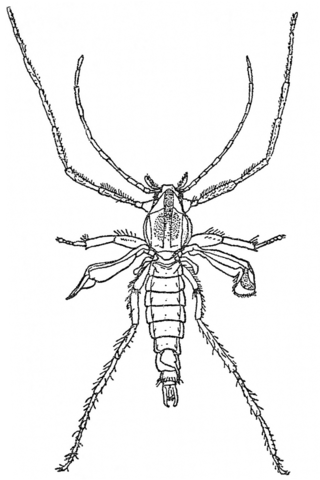
Pontomyia is a genus of flightless marine midges belonging to the subfamily Chironominae in the Chironomidae family. Insects in marine environments are extremely rare while flightlessness, extreme sexual dimorphism, and an extremely short adult life span contribute to making these midges unusual among insects. They are known from the shores of islands in the Indian, Atlantic and Pacific Oceans.
Thalassomya bureni is a species of midges in the family Chironomidae.

Goeldichironomus is a genus of midges in the family Chironomidae. There are about 14 described species in Goeldichironomus. Most species are found in tropical America, with G. carus ranging north to the southern United States.
Mallochohelea is a genus of biting midges in the family Ceratopogonidae. There are at least 40 described species in Mallochohelea.
Nilobezzia is a genus of biting midges in the family Ceratopogonidae. There are more than 70 described species in Nilobezzia.




