
Lycoptera is an extinct genus of fish that lived from Lower Cretaceous, Barremian to Aptian in present-day China, North Korea, Mongolia and Siberia. Although there is record from Jurassic Formation in Siberia, its age remains questionable. It is known from abundant fossils representing sixteen species, which serve as important index fossil used to date geologic formations in China. Along with the genus Peipiaosteus, Lycoptera has been considered a defining member of the Jehol Biota, a prehistoric ecosystem famous for its feathered dinosaurs, which flourished for 20 million years during the Early Cretaceous, where it occurs abundantly in often monospecific beds, where they are thought to have died in seasonal mass death events. Lycoptera is a crown group teleost belonging to an early diverging lineage of the Osteoglossomorpha, which contains living mooneyes, arapaima, arowana, elephantfish and knifefish/featherbacks.
Helgolandichthys is an extinct genus of prehistoric bony fish that lived during the Aptian stage of the Early Cretaceous epoch.

Vinctifer is an extinct genus of prehistoric bony fish erected by David Starr Jordan in 1919.

Dastilbe is an extinct genus of prehistoric marine & freshwater ray-finned fish from the Early Cretaceous of Brazil. It was a relative of modern milkfish.
Chanopsis is an extinct genus of prehistoric freshwater bonytongue relative that lived from the late Aptian to the Albian stage of the Early Cretaceous epoch. It contains a single species, C. lombardi from the Democratic Republic of the Congo.

Araripichthys is an extinct genus of marine ray-finned fish that lived from the Aptian to Coniacian stages of the Cretaceous period. The genus is named after the Araripe Basin, where it was found in the Crato and Santana Formations. Other fossils of the genus have been found at Goulmima in Morocco, the Tlayua Formation of Mexico and the Apón Formation of Venezuela.
Oshunia is an extinct genus of prehistoric bony fish that lived during the Albian. Fossils of the genus were found in the Romualdo Formation of the Araripe Basin, northeastern Brazil. Other authors assign a Cenomanian age to the fish.
Flindersichthys is an extinct genus of prehistoric bony fish that lived during the Albian stage of the Early Cretaceous epoch.
Luisiella is an extinct genus of prehistoric bony fish that lived during the Kimmeridgian stage of the Late Jurassic epoch. Fossils of the genus have been found in either the Cañadón Calcáreo Formation or Cañadón Asfalto Formation in Chubut Province, Argentina.
Broughia is an extinct genus of marine holostean ray-finned fish that lived during the Induan age of the Early Triassic epoch in what is now Greenland. Fossils were found in the Wordie Creek Formation. A potential concurrent record is also known from Madagascar.
Sakamenichthys is an extinct genus of prehistoric bony fish that lived during the Early Triassic epoch in what is now Madagascar. Fossils were recovered from beds of the Middle Sakamena Formation of the Beroroha basin in the southern part of the island.
Ospia is an extinct genus of neopterygian ray-finned fish that lived during the Induan age of the Early Triassic epoch in what is now Greenland. Fossils were found in the Wordie Creek Formation.
Luganoia is an extinct genus of prehistoric bony fish that lived during the Anisian and Ladinian ages of the Middle Triassic epoch. Fossils were recovered from the Besano Formation of Monte San Giorgio and Besano area and from the Zhuganpo Member of Guizhou, South China. It was also reported from the Ladinian of Spain.

Brannerion is an extinct genus of prehistoric marine bonefish. Fossils of the genus were found in the Romualdo Formation of the Santana Group, Araripe Basin, northeastern Brazil. It is considered a basal member of the Albuliformes.
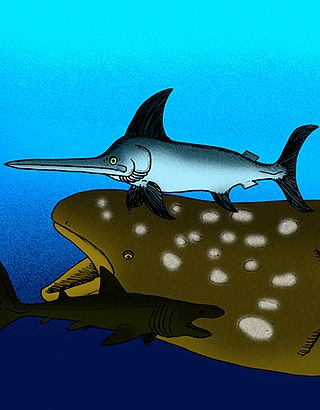
Xiphiorhynchus is an extinct genus of prehistoric swordfish that lived from the Eocene until the Oligocene. Unlike the modern swordfish, both the upper and lower jaws of Xiphiorhynchus were extended into blade-like points.
Protautoga is an extinct genus of prehistoric ray-finned fish, that lived in the Middle Miocene. Fossils have been found in the Paraná Formation of Argentina and the Calvert Formation of Virginia, USA.

Pholidorhynchodon is an extinct genus of ray-finned fish that lived in the Triassic. Its fossils have been found in Italy, in the Zorzino Limestone Formation in Cene.
Paralbula is an extinct genus of prehistoric bony fish. They can be found in the Hell Creek Formation, in Montana, United States.

Phareodus is a genus of freshwater fish from the Paleocene to the Eocene of Australia, Europe and North and South America.

Crustaceans may pass through a number of larval and immature stages between hatching from their eggs and reaching their adult form. Each of the stages is separated by a moult, in which the hard exoskeleton is shed to allow the animal to grow. The larvae of crustaceans often bear little resemblance to the adult, and there are still cases where it is not known what larvae will grow into what adults. This is especially true of crustaceans which live as benthic adults, more-so than where the larvae are planktonic, and thereby easily caught.









