
The Cortinariaceae are a large family of gilled mushrooms found worldwide, containing over 2100 species. The family takes its name from its largest genus, the varied species of the genus Cortinarius. Many genera formerly in the Cortinariaceae have been placed in various other families, including Hymenogastraceae, Inocybaceae and Bolbitiaceae.

Thaxterogaster purpurascens is a species of mushroom producing fungus in the family Cortinariaceae. It is commonly known as the bruising webcap.

Cortinarius anomalus, also known as the variable webcap, is a basidiomycete fungus of the genus Cortinarius. It produces a medium-sized mushroom with a grayish-brown cap up to 5 cm (2 in) wide, gray-violet gills and a whitish stem with pale yellow belts below. The mushroom grows solitarily or in scattered groups on the ground in deciduous and coniferous forests. It is found throughout the temperate zone of the northern hemisphere.
Cortinarius badiolaevis is a fungus in the family Cortinariaceae. The species produces mushrooms with smooth, red-brown caps up to 5 centimetres (2.0 in) in diameter, after which it is named. It has a white stem, and yellow-brown gills. It was first described in 2011, based on specimens collected in the 1990s and 2000s. C. badiolaevis is part of the subgenus Telamonia, but is not part of any known section, and does not have any close relatives within the genus. The rare species is known from Sweden and Spain, where it grows from soil in coniferous woodland.

Thaxterogaster argyrionus is a species of sequestrate (truffle-like) fungus in the family Cortinariaceae. Described as a new species in 2010, it is known only from New South Wales.

Phlegmacium basorapulum is a species of truffle-like fungus in the family Cortinariaceae. Found in New South Wales, Australia, the species was described as new to science in 2010.

Thaxterogaster caesibulga is a species of truffle-like fungus in the family Cortinariaceae. Found in New South Wales, Australia, the species was described as new to science in 2010.

Cortinarius kaputarensis is a species of truffle-like fungus in the family Cortinariaceae. Described as a new species in 2010, it is known only from New South Wales in Australia.

Cortinarius maculobulga is a species of truffle-like fungus in the family Cortinariaceae. Found only in New South Wales, Australia, it was described as new to science in 2010.

Thaxterogaster nebulobrunneus is a species of truffle-like fungus in the family Cortinariaceae. Found in New South Wales, Australia, the species was described as new to science in 2010.

Cortinarius sinapivelus is a species of truffle-like fungus in the family Cortinariaceae. Known only from New South Wales, it was described as new to science in 2010.

Cortinarius bovarius is an agaric fungus in the family Cortinariaceae. Described as new to science in 2013, it is found in western North America. The specific epithet bovarius refers to the similarity to the European lookalike Cortinarius bovinus.
Thaxterogaster melleicarneus is a species of fungus in the family Cortinariaceae.
Thaxterogaster talimultiformis is a species of mushroom producing fungus in the family Cortinariaceae. It was previously known as Cortinarius talimultiformis.
Phlegmacium boreicyanites is a species of fungus in the family Cortinariaceae

Thaxterogaster caesiolamellatus is a species of fungus in the family Cortinariaceae.
Thaxterogaster caesiophylloides is a species of fungus in family Cortinariaceae.
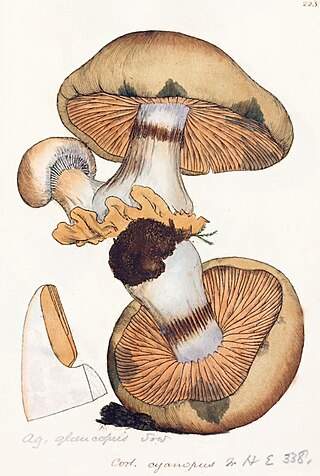
Phlegmacium glaucopus is a species of fungus in the family Cortinariaceae. It is commonly known as the blue-foot webcap.

Thaxterogaster austrovaginatus is a species of ectomycorrhizal fungus in the famlily Cortinariaceae.
Thaxterogaster is a genus of fungi in the family Cortinariaceae.








