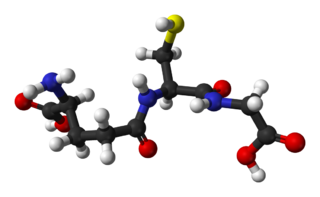
Glutathione is an antioxidant in plants, animals, fungi, and some bacteria and archaea. Glutathione is capable of preventing damage to important cellular components caused by sources such as reactive oxygen species, free radicals, peroxides, lipid peroxides, and heavy metals. It is a tripeptide with a gamma peptide linkage between the carboxyl group of the glutamate side chain and cysteine. The carboxyl group of the cysteine residue is attached by normal peptide linkage to glycine.

In organic chemistry, a thiol, or thiol derivative, is any organosulfur compound of the form R−SH, where R represents an alkyl or other organic substituent. The −SH functional group itself is referred to as either a thiol group or a sulfhydryl group, or a sulfanyl group. Thiols are the sulfur analogue of alcohols, and the word is a blend of "thio-" with "alcohol".

Trypanothione is an unusual form of glutathione containing two molecules of glutathione joined by a spermidine (polyamine) linker. It is found in parasitic protozoa such as leishmania and trypanosomes. These protozoal parasites are the cause of leishmaniasis, sleeping sickness and Chagas' disease. Trypanothione was discovered by Alan Fairlamb. Its structure was proven by chemical synthesis. It is present mainly in the Kinetoplastida but can be found in other parasitic protozoa such as Entamoeba histolytica. Since this thiol is absent from humans and is essential for the survival of the parasites, the enzymes that make and use this molecule are targets for the development of new drugs to treat these diseases.

Glutathione disulfide (GSSG) is a disulfide derived from two glutathione molecules.

Glutathione reductase (GR) also known as glutathione-disulfide reductase (GSR) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the GSR gene. Glutathione reductase catalyzes the reduction of glutathione disulfide (GSSG) to the sulfhydryl form glutathione (GSH), which is a critical molecule in resisting oxidative stress and maintaining the reducing environment of the cell. Glutathione reductase functions as dimeric disulfide oxidoreductase and utilizes an FAD prosthetic group and NADPH to reduce one molar equivalent of GSSG to two molar equivalents of GSH:

Thiosulfate is an oxyanion of sulfur with the chemical formula S2O2−3. Thiosulfate also refers to the compounds containing this anion, which are the salts of thiosulfuric acid, e.g. sodium thiosulfate Na2S2O3. Thiosulfate also refers to the esters of thiosulfuric acid. The prefix thio- indicates that the thiosulfate is a sulfate with one oxygen replaced by sulfur. Thiosulfate is tetrahedral at the central S atom. Thiosulfate salts occur naturally. Thiosulfate ion has C3v symmetry, and is produced by certain biochemical processes. It rapidly dechlorinates water and is notable for its use to halt bleaching in the paper-making industry. Thiosulfate salts are mainly used in dying in textiles and the bleaching of natural substances.

Sulfur assimilation is the process by which living organisms incorporate sulfur into their biological molecules. In plants, sulfate is absorbed by the roots and then be transported to the chloroplasts by the transipration stream where the sulfur are reduced to sulfide with the help of a series of enzymatic reactions. Furthermore, the reduced sulfur is incorporated into cysteine, an amino acid that is a precursor to many other sulfur-containing compounds. In animals, sulfur assimilation occurs primarily through the diet, as animals cannot produce sulfur-containing compounds directly. Sulfur is incorporated into amino acids such as cysteine and methionine, which are used to build proteins and other important molecules. Besides, With the rapid development of economy, the increase emission of sulfur results in environmental issues, such as acid rain and hydrogen sulfilde.

Rhodanese is a mitochondrial enzyme that detoxifies cyanide (CN−) by converting it to thiocyanate. In enzymatology, the common name is listed as thiosulfate sulfurtransferase. The diagram on the right shows the crystallographically-determined structure of rhodanese.
Peroxiredoxins are a ubiquitous family of antioxidant enzymes that also control cytokine-induced peroxide levels and thereby mediate signal transduction in mammalian cells. The family members in humans are PRDX1, PRDX2, PRDX3, PRDX4, PRDX5, and PRDX6. The physiological importance of peroxiredoxins is indicated by their relative abundance. Their function is the reduction of peroxides, specifically hydrogen peroxide, alkyl hydroperoxides, and peroxynitrite.

In enzymology, a sulfur oxygenase/reductase (EC 1.13.11.55) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
Adenylyl-sulfate reductase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction of the reduction of adenylyl-sulfate/adenosine-5'-phosphosulfate (APS) to sulfite through the use of an electron donor cofactor. The products of the reaction are AMP and sulfite, as well as an oxidized electron donor cofactor.
Adenylyl-sulfate reductase (glutathione) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
Adenylyl-sulfate reductase (thioredoxin) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a CoA-glutathione reductase (EC 1.8.1.10) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a protein-disulfide reductase (glutathione) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a 3-mercaptopyruvate sulfurtransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reactions of 3-mercaptopyruvate. This enzyme belongs to the family of transferases, specifically the sulfurtransferases. This enzyme participates in cysteine metabolism. It is encoded by the MPST gene.
In enzymology, a thiosulfate-dithiol sulfurtransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
Sulfur is metabolized by all organisms, from bacteria and archaea to plants and animals. Sulfur can have an oxidation state from -2 to +6 and is reduced or oxidized by a diverse range of organisms. The element is present in proteins, sulfate esters of polysaccharides, steroids, phenols, and sulfur-containing coenzymes.
Sulfur dioxygenase (EC 1.13.11.18, sulfur oxygenase, sulfur:oxygen oxidoreductase) is an enzyme with systematic name S-sulfanylglutathione:oxygen oxidoreductase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Dissimilatory sulfite reductase is an enzyme that participates in sulfur metabolism in dissimilatory sulfate reduction.












