
Enterobacterales is an order of Gram-negative, non-spore forming, facultatively anaerobic, rod-shaped bacteria with the class Gammaproteobacteria. The type genus of this order is Enterobacter.

The tectofilosids are a group of filose amoebae with shells. These are composed of organic materials and sometimes collected debris, in contrast to the euglyphids, which produce shells from siliceous scales. The shell usually has a single opening, but in Amphitrema and a few other genera it has two on opposite ends. The cell itself occupies most of the shell. They are most often found on marsh plants such as Sphagnum.

Gymnothorax is a genus of fish in the family Muraenidae found in Atlantic, Indian, and Pacific Oceans. With more than 120 species, it the most speciose genus of moray eels.

Trichopezinae are a subfamily of empidoid flies. They are mainly predatory flies like most of their relatives, and generally small to medium-sized, long-legged and large-eyed.

The Bionectriaceae are a family of fungi in the order Hypocreales. A 2008 estimate places 35 genera and 281 species in the family. Species in the family tend to grow on plant material, including woody debris, while some species associate with algae, bryophytes, or other fungi.

Brachystomatinae is a subfamily of flies belonging to the family Empididae.

The Diplectanidae are a family of monopisthocotylean monogeneans. They are all parasitic on the gills of fish. Diplectanids are small animals, generally around 1 mm in length. As parasites, they can be extremely numerous, up to several thousand on an individual fish.

Neurigoninae is a subfamily of flies in the family Dolichopodidae.

Sclerorhynchoidei is an extinct suborder of rajiform rays that had long rostra with large denticles similar to sawfishes and sawsharks. This feature was convergently evolved, recently proposed as 'pristification', and their closest living relatives are actually skates. While they are often called "sawfishes", sawskates is a more accurate common name proposed in 2021 for sclerorhynchoids, which has been subsequently used by other researchers.
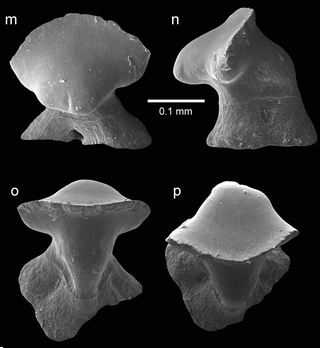
Antiquaobatis is an extinct genus of ray from the Early Jurassic of Europe, containing the single species A. grimmenensis. It is the oldest known described member of the Rajiformes, and is based on a single tooth from Pliensbachian of Northern Germany. It was recovered from the Grimmen Clay Pit, on Spinatum strata that belongs in the region to the Komorowo Formation. The holotype is a single antero-lateral tooth, very small and slightly asymmetrical, measuring 0.25 mm in maximum height and 0.26 mm in maximum width, that has an overall morphology, that suggests a consistent referral to Batoidea, encompassing all skates and rays. The tooth has an overall rather gracile crown morphology, different from any other know jurassic batomorphs, indicating closest affinities to the monotypic genus Engaibatis schultzei from the Kimmeridgian-Tithonian of Tanzania.

Rangomaramidae is a family of flies in the infraorder Bibionomorpha. The family, members of which are known as long-winged fungus gnats, was erected in 2002 by Jaschhof and Didham to include five new species of flies in the genus Rangomarama from New Zealand. The family was then expanded to include several other genera from across the world which were formerly classified as Sciaroidea incertae sedis, but preliminary studies show that the broad family is non-monophyletic.
This paleoentomology list records new fossil insect taxa that are to be described during the year 2022, as well as notes other significant paleoentomology discoveries and events which occurred during that year.
This list of fossil fish research presented in 2022 is a list of new fossil taxa of jawless vertebrates, placoderms, cartilaginous fishes, bony fishes, and other fishes that were described during the year, as well as other significant discoveries and events related to paleoichthyology that occurred in 2022.
Toarcibatidae is a family of extinct rays that lived in the Early Jurassic in what would become Europe and North America. The family includes two genera, Cristabatis and Toarcibatis, and was originally named "Archaeobatidae", but that name did not conform to the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature and was replaced. Doliobatis was originally included in this family as well, but it has since been reassigned to the Rhinobatidae.
Cristabatis is an extinct genus of rays that lived during the Early Jurassic. It contains two valid species, C. exundans and C. crescentiformis, which have been found in Belgium and France. It was originally referred to the family "Archaeobatidae", but was later reassigned to the family Toarcibatidae.
Doliobatis is an extinct genus of guitarfish that lived during the Early Jurassic. It contains one valid species, D. weisi, which has been found in Luxembourg. It was originally referred to the family Archaeobatidae, but was later reassigned to the family Rhinobatidae.
This list of 2023 in paleoentomology records new fossil insect taxa that are to be described during the year, as well as documents significant paleoentomology discoveries and events which occurred during that year.










