Tourism in Cesar Department refers to the tourism in the Colombian Department of Cesar. Tourism developed primarily in Valledupar during the middle of the 20th century after the creation of Cesar Department, but had its precedents in religious peregrination during the holy week, Catholic church tradition with peregrines going to Valledupar to celebrate processions, religious masses, saint of Ecce Homo veneration, the Virgen del Carmen, among others, these peregrinations were also popular in Atanquez a small village enclaved in the Sierra Nevada de Santa Marta, were the local culture inherited from the Spanish and Indigenous develop the "devil dancers" (La danza de los diablos).

Tourism is travel for pleasure or business; also the theory and practice of touring, the business of attracting, accommodating, and entertaining tourists, and the business of operating tours. Tourism may be international, or within the traveller's country. The World Tourism Organization defines tourism more generally, in terms which go "beyond the common perception of tourism as being limited to holiday activity only", as people "traveling to and staying in places outside their usual environment for not more than one consecutive year for leisure and not less than 24 hours, business and other purposes".

Colombia, officially the Republic of Colombia, is a sovereign state largely situated in the northwest of South America, with territories in Central America. Colombia shares a border to the northwest with Panama, to the east with Venezuela and Brazil and to the south with Ecuador and Peru. It shares its maritime limits with Costa Rica, Nicaragua, Honduras, Jamaica, Haiti, and the Dominican Republic. Colombia is a unitary, constitutional republic comprising thirty-two departments, with the capital in Bogota.

Colombia is a unitary republic made up of thirty-two departments and a Capital District. Each department has a Governor (gobernador) and a Department Assembly, elected by popular vote for a four-year period. The governor cannot be re-elected in consecutive periods. Departments are country subdivisions and are granted a certain degree of autonomy.
Contents
With the popularization of the vallenato music, in 1968 the Vallenato Legend Festival was created to celebrate the a local legend. This festival became the major attraction for tourists in the Cesar Department and has been promoted by the local and national government as national attraction. [1]

Vallenato, along with cumbia, is a popular folk music of Colombia. It primarily comes from the Colombia's Caribbean region. Vallenato literally means "born in the valley". The valley influencing this name is located between the Sierra Nevada de Santa Marta and the Serranía de Perijá in north-east Colombia. The name also applies to the people from the city where this genre originated: Valledupar. In 2006, Vallenato and cumbia were added as a category in the Latin Grammy Awards. Colombia’s traditional Vallenato music is Intangible Cultural Heritage in Need of Urgent Safeguarding, according to UNESCO.

The Vallenato Legend Festival is one of the most important musical festivals in Colombia. The Festival features a vallenato music contests for best interpreter of accordion, caja vallenata and guacharaca, as well as piqueria and best song. It’s celebrated every year in April in the city of Valledupar, Department of Cesar.
Another touristic attraction is the Sierra Nevada de Santa Marta with its variety of flora and fauna, it is also a National Natural Parks of Colombia and it is promoted as ecotouristic destination, the most popular destinations are the towns of Pueblo Bello, La Mina, Atanquez, and Nabusimake.

The Sierra Nevada de Santa Marta is an isolated mountain range separated from the Andes chain that runs through Colombia. Reaching an altitude of 5,700 m (18,700 ft) just 42 km (26 mi) from the Caribbean coast, the Sierra Nevada is one of the world's highest coastal ranges, being 250m shorter than the Saint Elias Mountains in Canada. The Sierra Nevada encompasses about 17,000 km2 (6,600 sq mi) and serves as the source of 36 rivers. The range is in the Departments of Magdalena, Cesar and La Guajira.

Ecotourism is a form of tourism involving visiting fragile, pristine, and relatively undisturbed natural areas, intended as a low-impact and often small scale alternative to standard commercial mass tourism. It means responsible travel to natural areas, conserving the environment, and improving the well-being of the local people. Its purpose may be to educate the traveler, to provide funds for ecological conservation, to directly benefit the economic development and political empowerment of local communities, or to foster respect for different cultures and for human rights. Since the 1980s, ecotourism has been considered a critical endeavor by environmentalists, so that future generations may experience destinations relatively untouched by human intervention. Several university programs use this description as the working definition of ecotourism.
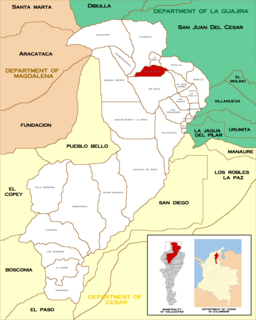
Pueblo Bello, is a village and municipality in the northern region of the Department of Cesar, Colombia. It is located in the mountains of the Sierra Nevada de Santa Marta and is home to Amerindians pertaining to the Arhuaco ethnicity, whom consider Pueblo Bello a sanctuary but by the name of Arumake in their language. Pueblo Bello is the main producer of coffee in the Caribbean Region of Colombia.
In the Sierra Nevada de Santa Marta another attraction is the Arhuaco indigenous culture with its traditions. In the corrgimiento of Valencia de Jesús there is one of the oldest churches in the Americas constructed by the Spanish. [2] as well as numerous small towns in the department still preserve the colonial architecture, constructed by the Spanish colonizers that came as part of the Spanish colonization of the Americas.

The Arhuaco are an indigenous people of Colombia. They are Chibchan-speaking people and descendants of the Tairona culture, concentrated in northern Colombia in the Sierra Nevada de Santa Marta.

Valencia de Jesús is a Colombian town and corregimiento of Valledupar in the Department of Cesar. The village is known for preserving one of the oldest churches in the Americas.

The Americas comprise the totality of the continents of North and South America. Together, they make up most of the land in Earth's western hemisphere and comprise the New World.