
The Republic of Colombia is situated largely in the north-west of South America, with some territories falling within the boundaries of Central America. It is bordered to the north-west by Panama; to the east by Brazil and Venezuela; to the south by Ecuador and Peru; and it shares maritime limits with Costa Rica, Nicaragua, Honduras, Jamaica, the Dominican Republic, and Haiti.

Cesar Department or simply Cesar is a department of Colombia located in the north of the country in the Caribbean region, bordering to the north with the Department of La Guajira, to the west with the Department of Magdalena and Department of Bolivar, to the south with Department of Santander, to the east with the Department of North Santander, and further to the east with the country of Venezuela. The department capital city is Valledupar.

The Sierra Nevada de Santa Marta is an isolated mountain range in northern Colombia, separate from the Andes range that runs through the north of the country. Reaching an elevation of 5,700 m (18,700 ft) just 42 km (26 mi) from the Caribbean coast, the Sierra Nevada is the highest coastal range in the tropics, and one of the highest coastal ranges in the world, being 250 metres (820 ft) shorter than the Saint Elias Mountains in Canada. The Sierra Nevada encompasses about 17,000 km2 (6,600 sq mi) and serves as the source of 36 rivers. The range is in the Departments of Magdalena, Cesar and La Guajira.

The Guajira Peninsula is a peninsula in northern Colombia and northwestern Venezuela in the Caribbean. It is the northernmost peninsula in South America and has an area of 25,000 km2 (9,700 sq mi) extending from the Manaure Bay (Colombia) to the Calabozo Ensenada in the Gulf of Venezuela (Venezuela), and from the Caribbean to the Serranía del Perijá mountains range.
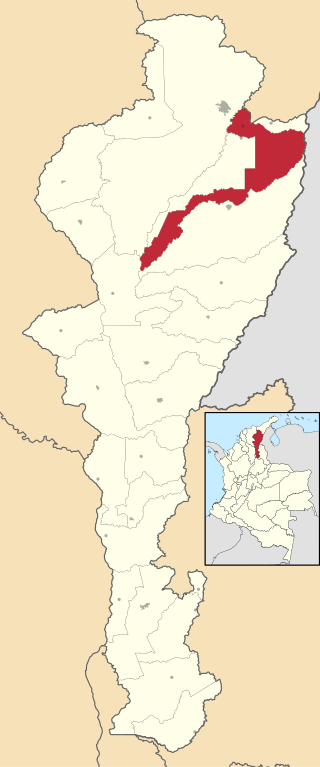
Los Robles La Paz or simply La Paz is a municipality and a town in the Department of Cesar, Colombia. The town is close to the Capital city of the Department of Cesar; Valledupar. The municipality of La Paz borders to the north with La Guajira Department, to the northeast with the municipality of Manaure. To the east with the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela sharing the Serranía del Perijá mountain range. To the south with the municipality of Codazzi, southwest with the municipality of El Paso, Cesar. To the west with the municipality of San Diego and to the northwest with the municipality of Valledupar.

The Serranía del Perijá, Cordillera de Perijá or Sierra de Perijá is a mountain range, an extension of the eastern Andean branch, in northern South America, between Colombia and Venezuela, ending further north in the Guajira Desert, a total distance of about 310 kilometres (190 mi). It separates the Maracaibo Basin from the Cesar-Ranchería Basin. Some of the area has been considered as a Flora and Fauna Sanctuary.

The Cordillera Central is the highest of the three branches of the Colombian Andes. The range extends from south to north dividing from the Colombian Massif in Cauca Department to the Serranía de San Lucas in Bolivar Departments. The highest peak is Nevado del Huila at 5,364 m (17,598 ft).

The Cordillera Occidental is the lowest in elevation of the three branches of the Colombian Andes. The average altitude is 2,000 m (6,600 ft) and the highest peak is Cerro Tatamá at 4,100 m (13,500 ft). The range extends from south to north dividing from the Colombian Massif in Nariño Department, passes north through Cauca, Valle del Cauca, Risaralda, Chocó, and Caldas Departments to the Paramillo Massif in Antioquia and Córdoba Departments. The cordillera is paralleled on the east by the Cauca river. From this massif the range divides further to form the Serranías de Ayapel, San Jerónimo and Abibe. Only to recede into the Caribbean plain and the Sinú River valley.

The Cordillera Oriental is the widest of the three branches of the Colombian Andes. The range extends from south to north dividing from the Colombian Massif in Huila Department to Norte de Santander Department where it splits into the Serranía del Perijá and the Cordillera de Mérida in Venezuelan Andes. The highest peak is Ritacuba Blanco at 5,410 m (17,750 ft) in the Sierra Nevada del Cocuy.

La Guajira is a department of Colombia. It occupies most of the Guajira Peninsula in the northeast region of the country, on the Caribbean Sea and bordering Venezuela, at the northernmost tip of South America. The capital city of the department is Riohacha.

Villanueva is a town and municipality located in the northern Department of La Guajira, Colombia. Villanueva is known in Colombia for being the cradle of many vallenato singers and composers. The economy of the town relies heavily on agriculture and farming.
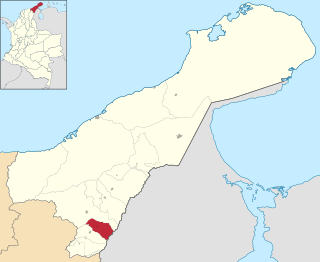
El Molino is a town and municipality located in the Colombian Department of La Guajira.

The Venezuelan Coastal Range, also known as Venezuelan Caribbean Mountain System, is a mountain range system and one of the eight natural regions of Venezuela, that runs along the central and eastern portions of Venezuela's northern coast. The range is a northeastern extension of the Andes, and is also known as the Maritime Andes. It covers around 48,866 km2, being the 4th largest natural region in Venezuela.

Because of its natural structure, Colombia can be divided into six distinct natural regions. These consist of the Andean Region, covering the three branches of the Andes mountains found in Colombia; the Caribbean Region, covering the area adjacent to the Caribbean Sea; the Pacific Region adjacent to the Pacific Ocean; the Orinoquía Region, part of the Llanos plains mainly in the Orinoco river basin along the border with Venezuela; the Amazon Region, part of the Amazon rainforest; and finally the Insular Region, comprising the islands in both the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans. Colombia is located in South America.

Geology of Colombia refers to the geological composition of the Republic of Colombia that determines its geography. Most of the emerged territory of Colombia covers vast areas within the South American plate, whereas much submerged territory lies within the Caribbean plate and the Nazca plate.
The Serranía del Pinche are part of the Western Ranges of the Colombian Andes. The mountains consist of several high peaks with small patches of isolated páramo and provide a corridor between the Pacific and Andean biogeographic regions. It is located municipality of Argelia in the Department of Cauca. This area is under consideration for protection as a Flora and Fauna Sanctuary by the Colombian government. This area is important for its incredible biodiversity and high percentage of primary forest. An endemic hummingbird - the gorgeted puffleg - is only found here and the population is considered to be critically endangered.

The Chimilas or Ette Ennaka are an indigenous people in the Andes of north-eastern Colombia. Their Chimila language is part of the Chibcha language family, of which there were estimated to be around 1000 speakers in 1998. At the time of the Spanish Conquest the Ariguaní River valley was the strategic centre of their territory. On the Serranía del Perijá mountains the Yukpas were also part of the Chimila confederation of tribes.
The Paramillo Massif is a mountain range of the Tropical Andes System, located at the northern end of the Cordillera Occidental range in Colombia.
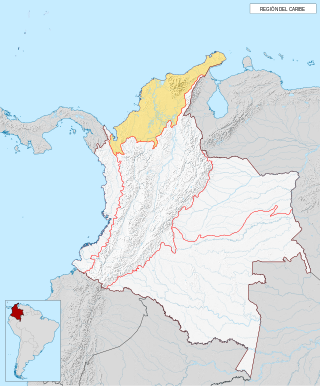
The Caribbean region is mostly lowland plains extending from the northern reaches of the Colombian Andes to the Caribbean Sea that are characterized by a variety of ecosystems including: humid forests, dry forests, savannas, wetlands and desert. The Sierra Nevada de Santa Marta rise from the plains to snow-capped peaks, separated from the Andes as an isolated area of high biodiversity and endemism. It contains one of the largest marshes in Colombia, the Ciénaga Grande de Santa Marta. The main river is the Magdalena which is fully navigable in the region and a major path for the flow of shipments to and from inland Colombia.

The Magdalena–Urabá moist forests (NT0137) is an ecoregion in the north of Colombia. The terrain is largely flat or undulating, but includes mountainous areas in the south. It contains moist forests and large wetlands that are important to resident and migratory birds. The ecoregion forms a bridge between the Pacific coast ecoregions of Colombia and Central America, and the ecoregions of the Andes and Amazon. It is surrounded by the more populated parts of Colombia and is threatened by farming, ranching, logging, oil exploitation and water pollution in the main rivers.


















