Tropical Queensland is a region of the state of Queensland, Australia that lies north of latitude 23.5 degrees South in the tropical latitude.
It contains Tropical North Queensland including Far North Queensland, North Queensland and Mackay Region as well as the Gulf Country in the west and parts of Central Queensland.
Except for the few major urban centres, such as Cairns, Townsville, Mackay and Mount Isa, these large tracts of land are largely undeveloped and have a low population density typical of remote, regional Australia. Much of the land is used for grazing; sugarcane is grown in the coastal areas where high rainfall occurs. Mining and tourism are the other significant industries in the region.
The region experiences cyclones mostly between the months of November and April. [1]

The Tropic of Capricorn is the circle of latitude that contains the subsolar point at the December solstice. It is thus the southernmost latitude where the Sun can be seen directly overhead. It also reaches 90 degrees below the horizon at solar midnight on the June Solstice. Its northern equivalent is the Tropic of Cancer.

Eungella National Park is a protected area in Queensland, Australia. It is on the Clarke Range at the end of the Pioneer Valley 80 km west of Mackay, and 858 km northwest of Brisbane. Eungella is noted for the national park which surrounds it. It is considered to be the longest continual stretch of sub-tropical rainforest in Australia. The original inhabitants are the Wirri people. The park is covered by dense rainforest and is known for its platypuses.

The Queensland tropical rain forests ecoregion covers a portion of the coast of Queensland in northeastern Australia and belongs to the Australasian realm. The forest contains the world's best living record of the major stages in the evolutionary history of the world's land plants, including most of the world's relict species of plants from the ancient supercontinent of Gondwana. The history of the evolution of marsupials and songbirds is also well represented.

Mackay is a city in the Mackay Region on the eastern or Coral Sea coast of Queensland, Australia. It is located about 970 kilometres (603 mi) north of Brisbane, on the Pioneer River. Mackay is described as being in either Central Queensland or North Queensland, as these regions are not precisely defined. More generally, the area is known as the Mackay–Whitsunday Region. Nicknames of Mackay include the Sugar capital, Alexandra and Macktown. The demonym of Mackay residents is Mackayites.

Far North Queensland (FNQ) is the northernmost part of the Australian state of Queensland. Its largest city is Cairns and it is dominated geographically by Cape York Peninsula, which stretches north to the Torres Strait, and west to the Gulf Country. The waters of Torres Strait include the only international border in the area contiguous with the Australian mainland, between Australia and Papua New Guinea.
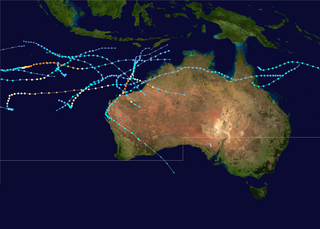
The 1999–2000 Australian region cyclone season was a slightly above average tropical cyclone season. It ran from 1 November 1999 to 30 April 2000. The regional tropical cyclone operational plan also defines a "tropical cyclone year" separately from a "tropical cyclone season", with the "tropical cyclone year" for this season lasting from 1 July 1999 to 30 June 2000.

The 1969–70 Australian region cyclone season was an above-average tropical cyclone season. It ran from 1 November 1969 to 30 April 1970. The regional tropical cyclone operational plan also defines a "tropical cyclone year" separately from a "tropical cyclone season", with the "tropical cyclone year" for this season lasting from 1 July 1969 to 30 June 1970.

Severe Tropical Cyclone Ului was one of the fastest intensifying tropical cyclones on record, strengthening from a tropical storm to a Category 5 equivalent cyclone within a 30-hour span in March 2010. Throughout Queensland, Australia, infrastructural damage from the storm amounted to A$20 million (US$18 million) and agricultural losses reached A$60 million (US$54 million).

The 1990–91 Australian region cyclone season was a slightly below average cyclone season, with ten tropical cyclones occurring within the region between 90°E and 160°E. The season officially ran from November 1, 1990, to April 30, 1991, with the first disturbance of the season forming on 10 December and the last disturbance moving out of the region during 11 May. Six people were killed by Cyclone Joy when it made landfall on Australia. During the season, tropical cyclones were monitored by the Australian Bureau of Meteorology, who ran Tropical Cyclone Warning Centers (TCWC) in Perth, Darwin, and Brisbane. The United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) and Papua New Guinea National Weather Service also monitored systems within the basin during the season. The JTWC designated systems with a number and either a S or a P suffix depending on which side of 135E. The Bureau of Meteorology and Papua New Guinea national Weather Service both used the Australian Tropical Cyclone Intensity Scale, and estimated windspeeds over a ten-minute period, while the JTWC estimated sustained winds over a one-minute period and are comparable to the Saffir–Simpson Hurricane Scale.

The 1978–79 Australian region cyclone season was the only season in which a reconnaissance aircraft flew into a tropical cyclone. Operationally, Australia's Bureau of Meteorology (BOM) tracked eleven tropical cyclones, while two additional systems were later added to the United States's Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) best track. Prior to 1985, the Australian region basin was defined as in the southern hemisphere between 80°E and 160°E, with the modern day season boundaries ranging from 1 November to 30 April of the following year. The first storm, an unnamed system, developed on 19 November 1978. The final cyclone, Kevin, dissipated by 12 May 1979. Tropical cyclones in this area were monitored by three Tropical Cyclone Warning Centres (TCWCs): the BOM in Perth, Darwin, and Brisbane.

The geography of Queensland in the north-east of Australia, is varied. It includes tropical islands, sandy beaches, flat river plains that flood after monsoon rains, tracts of rough, elevated terrain, dry deserts, rich agricultural belts and densely populated urban areas.

Severe Tropical Cyclone Rewa affected six countries and caused 22 deaths on its 28-day journey across the South Pacific Ocean in December 1993 and January 1994. Cyclone Rewa developed from a tropical disturbance on 28 December south of Nauru. After forming, Rewa moved southwest through the Solomon Islands, crossing the 160th meridian east from the South Pacific basin into the Australian region. The cyclone began to strengthen steadily and turned southward, paralleling the eastern Australian coast through 31 December. Rewa reached its initial peak intensity as a Category 4 tropical cyclone on 2 January. It maintained this intensity for about 12 hours before an increase in wind shear induced its weakening by 3 January. The cyclone turned southeastward and moved back into the South Pacific basin on 4 January, before it passed over New Caledonia between 5–6 January. After affecting New Caledonia, Rewa weakened to a tropical depression and turned northwestward before re-entering the Australian basin on 10 January.

The 2016–17 Australian region cyclone season, despite a very high number of tropical lows, was a slightly below-average season in terms of activity, with nine tropical cyclones, three of which intensified further into severe tropical cyclones; though it was much more active than the previous season. The season was the first to have a severe tropical cyclone since the 2014–15 season. It was the period of the year when most tropical cyclones form in the Southern Indian Ocean and Pacific Oceans between 90°E and 160°E. The season officially ran from 1 November 2016 to 30 April 2017, however, a tropical cyclone could form at any time between 1 July 2016 and 30 June 2017 and would count towards the season total. The first named storm, Yvette, developed during 21 December, and the final named storm, Greg, left the region on 3 May as a remnant low. This season was also the second-costliest tropical cyclone season on record in the Australian region basin, behind only the 2010–11 season, with a total of AUD$3.7 billion in damages incurred by the various storms, mostly from Cyclone Debbie.

Severe Tropical Cyclone Joy struck Australia in late 1990, causing the third highest floods on record in Rockhampton, Queensland. This cyclone began as a weak tropical low near the Solomon Islands, and initially moved westward. On 18 December, it was named Joy, becoming the 2nd named storm of the 1990–91 Australian region cyclone season. After turning southwest, Joy developed a well-defined eye and strengthened to maximum sustained winds of 165 km/h (103 mph) while approaching Cairns in Far North Queensland. Brushing the city with strong winds, the cyclone soon weakened and turned southeast. Joy later curved back southwest, making landfall near Townsville, Queensland on 26 December. It dissipated the next day; remnant moisture continued as torrential rainfall over Queensland for two weeks.

The Oil Pollution Act of 1973 or Oil Pollution Act Amendments of 1973, 33 U.S.C. Chapter 20 §§ 1001-1011, was a United States federal law which amended the United States Statute 75 Stat. 402. The Act of Congress sustained the United States commitment to control the discharge of fossil fuel pollutants from nautical vessels and to acknowledge the embargo of coastal zones in trans-boundary waters.

Severe Tropical Cyclone Debbie in 2017 was the strongest tropical cyclone to strike Queensland since Marcia in 2015, and was the costliest tropical cyclone in Australia since Yasi in 2011. Forming as a tropical low on 23 March, the low gradually intensified into a named tropical cyclone on 25 March. After steadily strengthening offshore to a Category 4 system, Debbie eventually made landfall near Airlie Beach, at 12:40 AEST on 28 March. Afterwards, Debbie rapidly weakened into a tropical low by late 28 March, but continued to travel south, causing significant damage and flooding in the populous areas of South East Queensland and Northern Rivers. In total, the storm caused A$3.5 billion (US$2.67 billion) in damage and fourteen deaths across Australia, primarily as a result of extreme flooding. This makes Debbie the deadliest cyclone to hit Australia since Fifi in 1991.

Severe Tropical Cyclone Ada was a small but intense tropical cyclone that severely impacted the Whitsunday Region of Queensland, Australia, in January 1970. It has been described as a defining event in the history of the Whitsunday Islands, and was the most damaging storm in the mainland town of Proserpine's history at the time. Forming over the far eastern Coral Sea in early January, the weather disturbance that would become Ada remained weak and disorganised for nearly two weeks as it slowly moved in a clockwise loop. Accelerating toward the southwest, the system was named Ada on 15 January. All observations of the fledgling cyclone were made remotely with weather satellite imagery until it passed over an automated weather station on 16 January. The extremely compact cyclone, with a gale radius of just 55 km (35 mi), intensified into a Category 3 severe tropical cyclone just before striking the Whitsunday Islands at 14:00 UTC on 17 January. At 18:30 UTC, Ada's eye crossed the coast at Shute Harbour. The cyclone made little inland progress before stalling northwest of Mackay and dissipating on 19 January.

Cremorne is a mixed-use locality in the Mackay Region, Queensland, Australia. In the 2021 census, Cremorne had a population of 19 people.

Tropical Cyclone Seth was a strong tropical cyclone whose main impacts came after it degenerated into a remnant low. The eighth tropical low and the fourth tropical cyclone of the 2021–22 Australian region cyclone season, Seth originated from a tropical disturbance in the Timor Sea and caused severe flooding in southeast Queensland and hazardous surf along the southeastern coast of Australia.
18°00′00.00″S143°00′00.00″E / 18.0000000°S 143.0000000°E