It has been suggested that this article be merged into 1996 Atlantic hurricane season . (Discuss) Proposed since December 2024. |
Tropical storm (39–73 mph, 63–118 km/h)
Category 1 (74–95 mph, 119–153 km/h)
Category 2 (96–110 mph, 154–177 km/h)
Category 3 (111–129 mph, 178–208 km/h)
Category 4 (130–156 mph, 209–251 km/h)
Category 5 (≥157 mph, ≥252 km/h)
Unknown
On June 16, satellite imagery revealed an area of increased convection east of the Bahamas, which was believed to have been associated with a tropical wave. [2] On June 17, the convection increased in organization at the lower levels of the atmosphere. By 1800 UTC, the system had organized sufficiently to be designated as a tropical depression, making it the first of the season. Initially, the depression tracked north-northwest under the steering currents of the low-level flow around the western periphery of the Atlantic subtropical ridge. Strong wind shear due to fast upper-level winds associated with a cold-core low over the eastern Gulf of Mexico hindered further intensification for a time, but on June 18, an area of deep convection developed north of the center of circulation. Based on analysis of reconnaissance data, the tropical depression was upgraded to Tropical Storm Arthur at 1900 UTC on June 19. [3]
Further strengthening occurred, as the storm attained peak winds of 45 mph (75 km/h). [2] With time, Arthur gradually turned northeast and made landfall near Cape Lookout, North Carolina early on June 20. The center moved over the Pamlico Sound and the Cape Hatteras National Seashore and exited into the Atlantic. Although the storm contained minimal deep convection, satellite imagery indicated that Arthur had a well-defined low-level center. The tropical storm weakened to a tropical depression about 100 mi (160 km) northeast of Cape Hatteras, and accelerated towards the northeast when westerly steering currents increased. Deep convection increased once again on June 21, although the lack of symmetry indicated that the remnants of Arthur were losing tropical characteristics. Forward speed increased to 40 mph (64 km/h) and the storm subsequently lost all tropical characteristics at 1200 UTC on June 21, while centered about 350 mi (560 km) north-northeast of Bermuda. The extratropical remnants tracked northeastward for 36 hours, and were last identified about midway between Newfoundland and the Azores, where it was absorbed by a much larger extratropical cyclone over the North Atlantic. [3]
Preparations and impact

On June 18, a tropical storm warning was issued for coastal locations from Edisto Beach, South Carolina to Cape Lookout, North Carolina. Shortly thereafter, a tropical storm watch was issued north of Cape Lookout to the North Carolina/Virginia border, including Pamlico and Albemarle Sounds. The tropical storm watch was later extended from the North Carolina/Virginia border to Cape Charles, Virginia, including Virginia Beach. By late on June 19, all advisories were discontinued. [3]
One tornado touched down in Florida, causing no known fatalities or injuries. [4] As the center of Arthur passed 75 mi (121 km) east of Cape Romain, South Carolina, minor increases in surf were reported. In North Carolina, swells ranged as high as 7 ft (2.1 m). [1] Rainfall peaked at 5.85 inches (149 mm) in Georgetown, South Carolina, [5] though because it fell gradually, no significant flooding was reported, [6] other than minor ponding of water on roads. [7] In addition, Arthur also brought precipitation to Georgia and Virginia, though the amounts of rainfall recorded rarely exceeded 3 inches (76 mm). Sustained winds of 46 mph (74 km/h) were reported, and offshore, the Atlantic Huron reported a sustained wind of 48 mph (77 km/h) at 1500 UTC on June 19, while located 35 mi (56 km) southeast of Arthur's center. In addition, a C-Man station located about 34.5 mi (55.5 km) southeast of Cape Fear, North Carolina reported sustained winds of 39 mph (64 km/h) and gusts up to 45 mph (75 km/h). [3] Overall, damage caused by Arthur was minimal, totaling only $1 million (1996 USD). [1]
See also
Related Research Articles

The 2004 Atlantic hurricane season was a very deadly, destructive, and active Atlantic hurricane season, with over 3,200 deaths and more than $61 billion in damage. More than half of the 16 tropical cyclones brushed or struck the United States. Due to the development of a Modoki El Niño – a rare type of El Niño in which unfavorable conditions are produced over the eastern Pacific instead of the Atlantic basin due to warmer sea surface temperatures farther west along the equatorial Pacific – activity was above average. The season officially began on June 1 and ended on November 30, though the season's last storm, Otto, dissipated on December 3, extending the season beyond its traditional boundaries. The first storm, Alex, developed offshore of the Southeastern United States on July 31, one of the latest dates on record to see the formation of the first system in an Atlantic hurricane season. It brushed the Carolinas and the Mid-Atlantic, causing one death and $7.5 million (2004 USD) in damage. Several storms caused only minor damage, including tropical storms Bonnie, Earl, Hermine, and Matthew. In addition, hurricanes Danielle, Karl, and Lisa, Tropical Depression Ten, Subtropical Storm Nicole and Tropical Storm Otto had no effect on land while tropical cyclones. The season was the first to exceed 200 units in accumulated cyclone energy (ACE) since 1995, mostly from Hurricane Ivan, which produced the highest ACE out of any storm this season. Ivan generated the second-highest ACE in the Atlantic, only behind the 1899 San Ciriaco Hurricane.

The 2002 Atlantic hurricane season was a near-average Atlantic hurricane season. It officially started on June 1, 2002, and ended on November 30, dates which conventionally limit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones develop in the Atlantic Ocean. The season produced fourteen tropical cyclones, of which twelve developed into named storms; four became hurricanes, and two attained major hurricane status. While the season's first cyclone did not develop until July 14, activity quickly picked up: eight storms developed in the month of September. It ended early however, with no tropical storms forming after October 6—a rare occurrence caused partly by El Niño conditions. The most intense hurricane of the season was Hurricane Isidore, a Category 3 storm with a minimum central pressure of 934 mbar; however, Hurricane Lili, with a minimum pressure of 938 mbar, attained higher winds and peaked at Category 4.
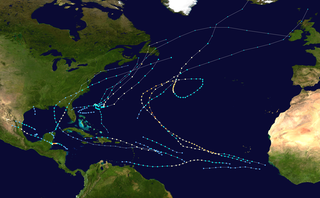
The 2000 Atlantic hurricane season was a fairly active hurricane season, but featured the latest first named storm in a hurricane season since 1992. The hurricane season officially began on June 1, and ended on November 30. It was slightly above average due to a La Niña weather pattern although most of the storms were weak. It was also the only season to have two of the storms affect Ireland. The first cyclone, Tropical Depression One, developed in the southern Gulf of Mexico on June 7 and dissipated after an uneventful duration. However, it would be almost two months before the first named storm, Alberto, formed near Cape Verde; Alberto also dissipated with no effects on land. Several other tropical cyclones—Tropical Depression Two, Tropical Depression Four, Chris, Ernesto, Nadine, and an unnamed subtropical storm—did not impact land. Five additional storms—Tropical Depression Nine, Florence, Isaac, Joyce, and Leslie—minimally affected land areas.
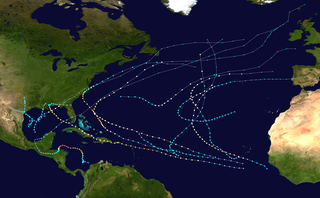
The 1998 Atlantic hurricane season was a catastrophic and deadly Atlantic hurricane season, which had the highest number of storm-related fatalities in over 218 years and some of the costliest ever at the time. The season had above average activity, due to the dissipation of an El Niño event and transition to La Niña conditions. It officially began on June 1 and ended on November 30, dates which conventionally delimit the period during which most tropical cyclones form in the Atlantic Ocean. The season had a rather slow start, with no tropical cyclones forming in June. The first tropical cyclone, Tropical Storm Alex, developed on July 27, and the season's final storm, Hurricane Nicole, became extratropical on December 1.

The 1997 Atlantic hurricane season was a below-average hurricane season. It officially began on June 1, and lasted until November 30 of that year. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the Atlantic basin. The 1997 season was fairly inactive, with only seven named storms forming, with an additional tropical depression and an unnumbered subtropical storm. It was the first time since the 1961 season that there were no active tropical cyclones in the Atlantic basin during the entire month of August—historically one of the more active months of the season—a phenomenon that would not occur again until 2022. A strong El Niño is credited with reducing activity in the Atlantic, while increasing the number of storms in the eastern and western Pacific basins to 19 and 26 storms, respectively. As is common in El Niño years, tropical cyclogenesis was suppressed in the tropical latitudes, with only two becoming tropical storms south of 25°N.

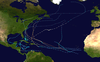
The 1996 Atlantic hurricane season had the most major hurricanes since 1950, which are Category 3 or higher on the Saffir-Simpson scale. The season was above-average, featuring a total of thirteen named storms, nine hurricanes, and six major hurricanes. The season officially began on June 1, 1996 and ended on November 30, 1996, dates which conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the Atlantic basin. The season's first tropical cyclone, Tropical Storm Arthur, developed on June 17, while the final cyclone, Hurricane Marco dissipated on November 26. The most intense hurricane, Edouard, was a powerful Cape Verde-type hurricane that affected portions of the Mid-Atlantic states and New England. The season featured nine tropical cyclone landfalls, including six hurricanes, one of which was a major hurricane. In total, six major hurricanes formed during the 1996 Atlantic hurricane season—the highest number produced in a single season since 1950.
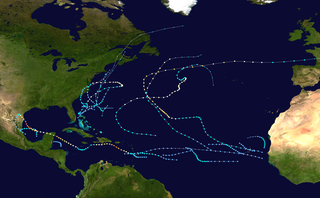
The 1967 Atlantic hurricane season was an active Atlantic hurricane season overall, producing 13 nameable storms, of which 6 strengthened into hurricanes. The season officially began on June 1, 1967, and lasted until November 30, 1967. These dates, adopted by convention, historically describe the period in each year when most tropical cyclogenesis occurs in the Atlantic Ocean. The season's first system, Tropical Depression One, formed on June 10, and the last, Tropical Storm Heidi, lost tropical characteristics on November 2.

The 1968 Atlantic hurricane season was a below average hurricane season during which only nine nameable storms developed. The season officially began on June 1 and lasted until November 30, dates which conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the Atlantic basin. Of the named storms, five strengthened into hurricanes; none however intensified into a major hurricane. Only four other seasons since the start of the satellite era—1972, 1986, 1994, and 2013—did not feature a major hurricane. The first system, Hurricane Abby, developed in the northwestern Caribbean on June 1. Abby moved northward and struck Cuba, bringing heavy rainfall and flooding to western portions of the island. Making landfall in Florida on June 4, Abby caused flooding and spawned four tornadoes, but left behind little damage. Overall, the hurricane resulted in six deaths and about $450,000 (1968 USD) in damage. In late June, Tropical Storm Candy brought minor flooding and spawned several tornadoes across portions of the Southern United States. Overall damage from the cyclone reached approximately $2.7 million. 1968 featured two simultaneously active tropical storms during the month of June, a phenomenon that would not occur again until 2023.

The 1992 Atlantic hurricane season was a significantly below average season for overall tropical or subtropical cyclones as only ten formed. Six of them became named tropical storms, and four of those became hurricanes; one hurricane became a major hurricane. The season was, however, near-average in terms of accumulated cyclone energy. The season officially started on June 1 and officially ended on November 30. However, tropical cyclogenesis is possible at any time of the year, as demonstrated by formation in April of an unnamed subtropical storm in the central Atlantic.

The 1977 Atlantic hurricane season was a very inactive Atlantic hurricane season, with only six named storms. The season officially began on Wednesday, June 1, 1977 and lasted until Wednesday, November 30, 1977. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclogenesis occurs in the Atlantic basin. The first tropical cyclone of the season developed over the western Caribbean Sea on June 13, 12 days after the start of the season. Three more organized during July and early August. Then, on August 29, the first named storm, Hurricane Anita formed and rapidly intensified to a Category 5 hurricane on September 1, before weakening slightly and striking Mexico as a high-end Category 4 hurricane on the Saffir–Simpson hurricane wind scale, bringing strong winds and heavy rainfall, causing 11 fatalities and leaving at least 25,000 people homeless.
The 1978 Atlantic hurricane season was a slightly above average hurricane season in terms of number of named storms. Eleven tropical cyclones were named in all, and five of these became hurricanes; two of the five became a major hurricane. This was also the last Atlantic hurricane season to use an all-female naming list. The season officially began on June 1, 1978, and ended on November 30, 1978. These dates, adopted by convention, denote the period in each year when most tropical cyclogenesis occurs in the Atlantic basin. However, the formation of subtropical or tropical cyclones is possible at any time of the year, as shown by the formation of an unnamed subtropical storm on January 18.

The 1980 Atlantic hurricane season featured nine hurricanes, the most since 1969. This hurricane season was fairly active, with sixteen tropical cyclones forming, eleven of which strengthened into named tropical storms. The season officially began on June 1, 1980, and lasted until November 30, 1980. It was the first time since the 1971 season that there were no active tropical cyclones in the Atlantic basin during the month of June. The season occurred during an ENSO-neutral phase, having neither an El Niño nor a La Niña.

Hurricane Isaac was a large and powerful tropical cyclone that lasted through late September and early October 2000. The thirteenth tropical cyclone, ninth named storm, and the fifth hurricane of 2000 Atlantic hurricane season, Isaac developed from a tropical wave south of Cape Verde on September 21. The depression intensified, and on the following day, it was upgraded to Tropical Storm Isaac. Due to conductive atmospheric conditions, Isaac continued to strengthen, and attained hurricane intensity on September 23. Isaac managed to become a Category 3 hurricane on September 24, before steadily weakening shortly thereafter. By September 26, the storm had deteriorated to a Category 1 hurricane. However, it again encountered favorable conditions, which caused Isaac to re-intensify.

The 2008 Atlantic hurricane season was an event in the annual tropical cyclone season in the north Atlantic Ocean. An above-average Atlantic hurricane season, it was the first on record to have a major hurricane in every month from July to November.

The 2011 Atlantic hurricane season was the second in a group of three very active Atlantic hurricane seasons, each with 19 named storms, tied with 1887, 1995, 2010, and 2012. The above-average activity was mostly due to a La Niña that persisted during the previous year. Of the season's 19 tropical storms, only seven strengthened into hurricanes, and four of those became major hurricanes: Irene, Katia, Ophelia, and Rina. The season officially began on June 1 and ended on November 30, dates which conventionally delimit the period during each year in which most tropical cyclones develop in the Atlantic Ocean. However, the first tropical storm of the season, Arlene, did not develop until nearly a month later. The final system, Tropical Storm Sean, dissipated over the open Atlantic on November 11.

The 2002 Atlantic hurricane season was an average Atlantic hurricane season in which twelve named storms formed. Although Tropical Storm Arthur formed on July 14, the season officially began on June 1 and ended on November 30, dates that conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones develop in the Atlantic basin. The season's final storm, Tropical Depression Fourteen, dissipated on October 16.

The 2012 Atlantic hurricane season was the final year in a string of three consecutive very active seasons since 2010, with 19 tropical storms. The 2012 season was also a costly one in terms of property damage, mostly due to Hurricane Sandy. The season officially began on June 1 and ended on November 30, dates that conventionally delimit the period during each year in which most tropical cyclones form in the Atlantic Ocean. However, Alberto, the first named system of the year, developed on May 19 – the earliest date of formation since Subtropical Storm Andrea in 2007. A second tropical cyclone, Beryl, developed later that month. This was the first occurrence of two pre-season named storms in the Atlantic basin since 1951. It moved ashore in North Florida on May 29 with winds of 65 mph (105 km/h), making it the strongest pre-season storm to make landfall in the Atlantic basin. This season marked the first time since 2009 where no tropical cyclones formed in July. Another record was set by Hurricane Nadine later in the season; the system became the fourth-longest-lived tropical cyclone ever recorded in the Atlantic, with a total duration of 22.25 days. The final storm to form, Tony, dissipated on October 25, and the season came to a close when Hurricane Sandy became extratropical on October 29.

The 2014 Atlantic hurricane season was a well below-average hurricane season in terms of named storms while the number of hurricanes and major hurricanes, were overall average. It produced nine tropical cyclones, eight of which became named storms; six storms became hurricanes and two intensified further into major hurricanes. The season officially began on June 1, and ended on November 30. These dates historically describe the period each year when most tropical cyclones form in the Atlantic basin. The first storm of the season, Arthur, developed on July 1, while the final storm, Hanna, dissipated on October 28, about a month prior to the end of the season.

The 2019 Atlantic hurricane season was the fourth consecutive above-average and damaging season dating back to 2016. The season featured eighteen named storms, however, many storms were weak and short-lived, especially towards the end of the season. Six of those named storms achieved hurricane status, while three intensified into major hurricanes. Two storms became Category 5 hurricanes, marking the fourth consecutive season with at least one Category 5 hurricane, and the third consecutive season to feature at least one storm making landfall at Category 5 intensity. It was also the seventh season on record to have multiple tropical cyclones reaching Category 5 strength, which would not occur again until 2024. The season officially began on June 1 and ended on November 30. These dates historically describe the period each year when most tropical cyclones form in the Atlantic basin and are adopted by convention. However, tropical cyclogenesis is possible at any time of the year, as demonstrated by the formation of Subtropical Storm Andrea on May 20, making this the fifth consecutive year in which a tropical or subtropical cyclone developed outside of the official season.
The 2021 Atlantic hurricane season was the third-most active Atlantic hurricane season on record in terms of number of tropical cyclones, although many of them were weak and short-lived. With 21 named storms forming, it became the second season in a row and third overall in which the designated 21-name list of storm names was exhausted. Seven of those storms strengthened into a hurricane, four of which reached major hurricane intensity, which is slightly above-average. The season officially began on June 1 and ended on November 30. These dates historically describe the period in each year when most Atlantic tropical cyclones form. However, subtropical or tropical cyclogenesis is possible at any time of the year, as demonstrated by the development of Tropical Storm Ana on May 22, making this the seventh consecutive year in which a storm developed outside of the official season.
References
- 1 2 3 National Climatic Data Center (1996). "Event report for Tropical Storm Arthur (2)". Archived from the original on May 20, 2011. Retrieved November 21, 2011.
- 1 2 Richard Pasch & Lixion Avila (May 1998). "Atlantic hurricane season of 1996" (PDF). National Hurricane Center. Retrieved November 21, 2011.
- 1 2 3 4 Max Mayfield (August 19, 1996). "Tropical Cyclone Report: Tropical Storm Arthur". National Hurricane Center. Retrieved November 21, 2011.
- ↑ TornadoProject. "List of Known Tropical Cyclones Which Have Spawned Tornadoes" . Retrieved November 21, 2011.
- ↑ David Roth (November 25, 2011). "Tropical Storm Arthur June 17-20, 1996". Hydrometeorological Prediction Center . Retrieved November 26, 2011.
- ↑ National Climatic Data Center (1996). "Event report for Tropical Storm Arthur". Archived from the original on May 20, 2011. Retrieved November 21, 2011.
- ↑ National Climatic Data Center (1996). "Event report for Tropical Storm Arthur (3)". Archived from the original on May 20, 2011. Retrieved November 21, 2011.
External links
 Tropical Storm Arthur at peak intensity just off the coast of North Carolina on June 19 |
Tropical cyclones of the 1996 Atlantic hurricane season | ||
|---|---|---|