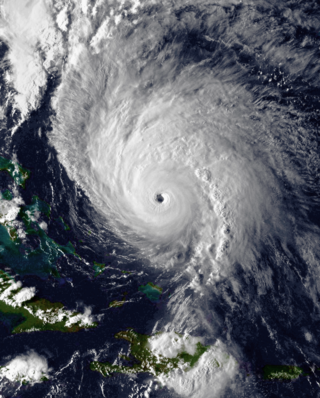
Hurricane Hortense was the first tropical cyclone to make landfall in Guadeloupe and Puerto Rico since Hurricane Hugo in 1989, and the second most intense hurricane during the 1996 Atlantic hurricane season. The eighth tropical cyclone, eighth named storm, and sixth hurricane of the season. Hortense developed on September 3 from a tropical wave in the central Atlantic Ocean. Initially a tropical depression, it headed westward without significant strengthening for four days due to unfavorable upper-level winds. While nearing the Lesser Antilles upper-level winds decreased, allowing the depression to become Tropical Storm Hortense on September 7. Hortense crossed Guadeloupe on September 8 and entered the Caribbean Sea. By on the following day, it was upgraded to a hurricane while curving northwestward. Hortense made landfall in Puerto Rico on September 9 and brushed the Dominican Republic shortly thereafter. After re-entering the Atlantic, Hortense began to substantially strengthen and peaked as a 140 mph (220 km/h) Category 4 hurricane early on September 13. Thereafter, the storm steadily weakened as it tracked rapidly north-northeastward. Early on September 15, Hortense made landfall in Nova Scotia as a minimal Category 1 hurricane. It quickly weakened further to a tropical storm before re-entering the Atlantic to the south of Newfoundland. Late on September 15, Hortense transitioned into an extratropical cyclone and subsequently merged with a frontal system about 24 hours later.

Hurricane Lenny was the strongest November Atlantic hurricane since the 1932 Cuba hurricane. It was the twelfth tropical storm, eighth hurricane, and record-breaking fifth Category 4 hurricane in the 1999 Atlantic hurricane season. Lenny formed on November 13 in the western Caribbean Sea at around 18:00 UTC and went on to form and maintain an unusual and unprecedented easterly track for its entire duration, which gave it the common nickname, "Wrong Way Lenny". It attained hurricane status south of Jamaica on November 15 and passed south of Hispaniola and Puerto Rico over the next few days. Lenny rapidly intensified over the northeastern Caribbean on November 17, attaining peak winds of 155 mph (249 km/h) about 21 mi (34 km) south of Saint Croix in the United States Virgin Islands. It gradually weakened while moving through the Leeward Islands, eventually dissipating on November 23 over the open Atlantic Ocean.

The 2003 Atlantic hurricane season was a very active season with tropical cyclogenesis occurring before and after the official bounds of the season—the first such occurrence since the 1970 season. The season produced 21 tropical cyclones, of which 16 developed into named storms; seven of those attained hurricane status, of which three reached major hurricane status. The strongest hurricane of the season was Hurricane Isabel, which reached Category 5 status on the Saffir–Simpson hurricane scale northeast of the Lesser Antilles; Isabel later struck North Carolina as a Category 2 hurricane, causing $3.6 billion in damage and a total of 51 deaths across the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States.
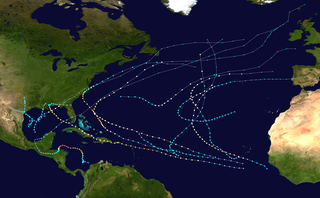
The 1998 Atlantic hurricane season was a catastrophic and deadly Atlantic hurricane season, featuring the highest number of storm-related fatalities in over 218 years and some of the costliest ever at the time. The season had above average activity, due to the dissipation of an El Niño event and transition to La Niña conditions. It officially began on June 1 and ended on November 30, dates which conventionally delimit the period during which most tropical cyclones form in the Atlantic Ocean. The season had a rather slow start, with no tropical cyclones forming in June. The first tropical cyclone, Tropical Storm Alex, developed on July 27, and the season's final storm, Hurricane Nicole, became extratropical on December 1.
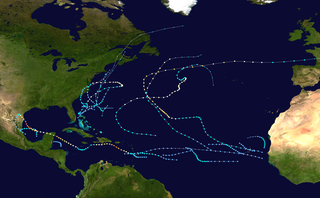
The 1967 Atlantic hurricane season was an active Atlantic hurricane season overall, producing 13 nameable storms, of which 6 strengthened into hurricanes. The season officially began on June 1, 1967, and lasted until November 30, 1967. These dates, adopted by convention, historically describe the period in each year when most tropical cyclogenesis occurs in the Atlantic Ocean. The season's first system, Tropical Depression One, formed on June 10, and the last, Tropical Storm Heidi, lost tropical characteristics on November 2.
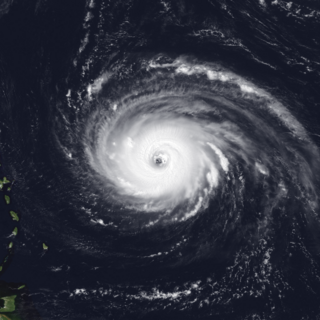
Hurricane Luis was a long lived and powerful Category 4 hurricane. It was the strongest hurricane to make landfall and the third-most intense hurricane recorded during the 1995 Atlantic hurricane season. The storm, along with Humberto, Iris, and Karen, was one of four simultaneous tropical systems in the Atlantic basin.

The 1930 Atlantic hurricane season was the second least active Atlantic hurricane season on record in terms of tropical storms formed, only behind 1914, with only three systems reaching tropical storm intensity. Of those three, two reached hurricane status, both of which also became major hurricanes, Category 3 or higher storms on the Saffir–Simpson hurricane wind scale. The first system developed in the central Atlantic Ocean on August 21. Later that month, a second storm, the Dominican Republic hurricane, formed on August 29. It peaked as a Category 4 hurricane with winds of 155 mph (250 km/h). The third and final storm dissipated on October 21.

Tropical Storm Odette was a rare off-season tropical cyclone that hit the island of Hispaniola in early December 2003. As the fifteenth named storm of the 2003 Atlantic hurricane season, Odette formed near the coast of Panama a few days after the official end of the Atlantic hurricane season ended on November 30, and ultimately made landfall on the Dominican Republic as a moderate tropical storm, before becoming extratropical on December 7, dissipating two days later.

The 2007 Atlantic hurricane season was the first season since 2003 to feature tropical activity both before and after the official bounds of the season. There were an above-average number of named storms during the season – 15, however many storms were weak and short-lived. Despite the predominance of weak systems, this was the first season on record to feature more than one Category 5 landfalling hurricane. This would not happen again until 2017. It produced 17 tropical cyclones, 15 tropical storms, six hurricanes, and two major hurricanes. It officially started on June 1 and ended on November 30, dates which conventionally delimit the period during which most tropical cyclones form in the Atlantic Ocean, although as shown by Subtropical Storm Andrea and Tropical Storm Olga in early May and early December, respectively, the formation of tropical cyclones is possible at any time of the year. The first system, Subtropical Storm Andrea, developed on May 9, while the last storm, Tropical Storm Olga, dissipated on December 13. The most intense hurricane, Dean, was, at the time, the third most intense landfalling Atlantic storm on record. It was the second on record in which an Atlantic hurricane, Felix, and an eastern Pacific hurricane, Henriette, made landfall on the same day. September had a then record-tying eight storms, until it was surpassed in 2020. However, the strengths and durations of most of the storms were low.
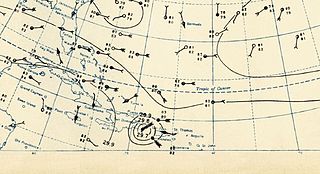
The 1930 Dominican Republic hurricane, also known as Hurricane San Zenón, was a small but intense and deadly tropical cyclone that severely impacted areas of the Greater Antilles, particularly the Dominican Republic, where an estimated 2,000 to 8,000 people died. The second of three known tropical cyclones in the 1930 Atlantic hurricane season, the system was first observed on August 29 to the east of the Lesser Antilles, and made landfall in the Dominican Republic at Category 4 strength on the modern Saffir-Simpson Scale. Later, it also struck Cuba and the U.S. states of Florida and North Carolina, with less severe effects.

Hurricane Debby caused minor damage in the Greater and Lesser Antilles in August 2000. The seventh tropical cyclone, fourth named storm, and second hurricane of the annual season, Debby developed from a tropical wave east of the Lesser Antilles on August 19. Favorable conditions allowed the depression to become Tropical Storm Debby early on August 20, and further strengthening into a hurricane occurred 24 hours later. Sustained winds peaked at 85 mph (137 km/h) on August 21. Debby made three landfalls on August 22, in Barbuda, Saint Barthélemy, and Virgin Gorda, before re-entering the Atlantic north of Puerto Rico. As Debby moved parallel to the north coast of Hispaniola late on August 23, it weakened back to a tropical storm. The storm tracked westward and weakened further, instead of approaching Florida and strengthening into a major hurricane. While south of eastern Cuba on August 24, Debby was downgraded to a tropical depression, six hours before completely dissipating.

Hurricane Iris was the first of three tropical cyclones to affect the Lesser Antilles in a three-week period, preceding the more destructive hurricanes Luis and Marilyn. The ninth named storm and fifth hurricane of the 1995 Atlantic hurricane season, Iris developed from a tropical wave to the east of the Lesser Antilles on August 22 and attained hurricane status within 30 hours. The hurricane weakened to a tropical storm before crossing the islands of the eastern Caribbean from August 26 through August 28. During that time, Iris became one of four active tropical storms in the Atlantic basin. Earlier it had interacted with Hurricane Humberto, and beginning on August 30, Iris interacted with Tropical Storm Karen. Iris re-intensified into a hurricane and attained peak sustained winds of 110 mph (175 km/h) while moving slowly across the central Atlantic. The hurricane accelerated to the north and absorbed a dissipating Karen on September 3. Iris weakened to a tropical storm and became extratropical on September 4, though its remnants re-attained hurricane-force winds, before affecting western Europe on September 7. The storm dissipated soon afterward.

Tropical Storm Cindy was a weak but unusually wet Atlantic tropical cyclone that caused disastrous floods and mudslides across Martinique in August 1993. Cindy formed east of the island and became the annual hurricane season's third named storm on August 14. Due to unfavorable atmospheric conditions, Cindy remained disorganized throughout its journey across the northeastern Caribbean Sea. After attaining maximum sustained winds of 45 mph (72 km/h), the storm began to weaken from an interaction with the high terrain of Hispaniola. It made landfall in the Dominican Republic as a tropical depression on August 16, and dissipated over the territory the following day.

The meteorological history of Hurricane Georges spanned seventeen days from September 15 to October 1, 1998. Hurricane Georges began as a tropical wave that moved off the coast of Africa during mid-September 1998. Tracking westward, the wave spawned an area of low pressure two days later, which quickly strengthened into a tropical depression. On September 16, the depression was upgraded to Tropical Storm Georges, and to Hurricane Georges the next day. Over the next few days, an eye developed and deep Atmospheric convection persisted around it. Strong outflow and warm sea surface temperatures allowed the storm to intensify as it tracked towards the west-northwest. The storm reached its peak intensity on September 20 with winds of 155 mph (250 km/h), just below Category 5 status on the Saffir–Simpson hurricane scale, and a barometric pressure of 937 mbar.

Tropical Storm Erika was a short-lived tropical cyclone that brought minor impacts to the Lesser Antilles. The fifth named storm of the 2009 Atlantic hurricane season, Erika originated out of a tropical wave on September 1 near the Lesser Antilles. Although it was a disorganized system, it was immediately declared a tropical storm, rather than a tropical depression. Later that day, the system reached its peak intensity with winds of 50 mph (85 km/h) and a barometric pressure of 1004 mbar. Increased wind shear caused the storm to weaken shortly thereafter, with Erika barely maintaining tropical storm-status by September 2. Later that day, the storm passed over the island of Guadeloupe and entered the Caribbean Sea. On September 3, Erika weakened to a tropical depression as the low pressure center became fully displaced from convective activity. Later that day, the system degenerated into a remnant low before dissipating near Puerto Rico on September 4.

The 2012 Atlantic hurricane season was the final year in a string of three consecutive very active seasons since 2010, with 19 tropical storms. The 2012 season was also a costly one in terms of property damage, mostly due to Hurricane Sandy. The season officially began on June 1 and ended on November 30, dates that conventionally delimit the period during each year in which most tropical cyclones form in the Atlantic Ocean. However, Alberto, the first named system of the year, developed on May 19 – the earliest date of formation since Subtropical Storm Andrea in 2007. A second tropical cyclone, Beryl, developed later that month. This was the first occurrence of two pre-season named storms in the Atlantic basin since 1951. It moved ashore in North Florida on May 29 with winds of 65 mph (105 km/h), making it the strongest pre-season storm to make landfall in the Atlantic basin. This season marked the first time since 2009 where no tropical cyclones formed in July. Another record was set by Hurricane Nadine later in the season; the system became the fourth-longest-lived tropical cyclone ever recorded in the Atlantic, with a total duration of 22.25 days. The final storm to form, Tony, dissipated on October 25 – however, Hurricane Sandy, which formed before Tony, became extratropical on October 29.

Tropical Storm Emily was a weak Atlantic tropical cyclone that brought torrential rains to much of the northern Caribbean in 2011. The fifth named storm of the annual hurricane season, Emily developed from a strong but poorly organized tropical wave that traversed the open Atlantic over the last week July. On August 1, it approached the Lesser Antilles and became more consolidated, producing inclement weather over many of the northern islands. Two days later, the disturbance’s wind flow became more cyclonic with a defined center of circulation, which marked the formation of Tropical Storm Emily. The storm remained fairly irregular in structure, though generating strong thunderstorms and gusty winds along its path over the Caribbean Sea. On August 4, Emily was declassified as a tropical cyclone after the mountainous areas of Hispaniola further disrupted its diffuse circulation. Upon exiting the northeastern Caribbean on August 6, its remnants briefly regenerated into a tropical storm before dissipating completely the next day.

Hurricane Ophelia was the most intense hurricane of the 2011 Atlantic hurricane season. The seventeenth tropical cyclone, sixteenth tropical storm, fifth hurricane, and third major hurricane, Ophelia originated in a tropical wave in the central Atlantic, forming approximately midway between the Cape Verde Islands and the Lesser Antilles on September 17. Tracking generally west-northwestward, Ophelia was upgraded to a tropical storm on September 21, and reached an initial peak of 65 mph (105 km/h) on September 22. As the storm entered a region of higher wind shear it began to weaken, and was subsequently downgraded to a remnant low on September 25. The following day, however, the remnants of the system began to reorganize as wind shear lessened, and on September 27, the National Hurricane Center once again began advisories on the system. Moving northward, Ophelia regained tropical storm status early on September 28, and rapidly deepened to attain its peak intensity with maximum sustained winds of 140 mph (230 km/h) several days later. The system weakened as it entered cooler sea surface temperatures and began a gradual transition to an extratropical cyclone, a process it completed by October 3.

Hurricane Danny was the first major hurricane to develop between the Lesser Antilles and Western Africa since Hurricane Julia in 2010. The fourth tropical cyclone, and first hurricane of the 2015 Atlantic hurricane season, Danny originated from a well-defined tropical wave that emerged over the Atlantic Ocean on August 14. Traveling west, the system gradually coalesced into a tropical depression by August 18. After becoming a tropical storm later that day, dry air slowed further development. On August 20–21, dry air became removed from the system, and Danny rapidly intensified into a Category 3 hurricane on the Saffir–Simpson hurricane wind scale. Its peak was short-lived as wind shear soon increased and prompted significant weakening. Degrading to a tropical storm by August 23, Danny approached the Lesser Antilles. It degenerated into a tropical wave as it traversed the archipelago on August 24 and was last noted over Hispaniola the following day.

Hurricane Maria was the tenth-most intense Atlantic hurricane on record and caused catastrophic damage in Puerto Rico in late September 2017. Originating from a tropical wave, it developed into a tropical depression on September 16 while situated to the east of the Lesser Antilles. Gradual intensification occurred over the next day or two and it strengthened into a tropical storm, which was named Maria. By late on September 17, Maria had intensified into a hurricane. As it approached the island arc, it underwent explosive intensification on September 18, with the hurricane reaching Category 5 intensity as it made landfall on the island of Dominica early on September 19. Land interaction weakened the storm somewhat, although it was able to quickly recover and later peaked that night with sustained winds of 175 mph (280 km/h) and a pressure of 908 mbar (26.8 inHg). Early the next morning it weakened to a high-end Category 4 hurricane before making landfall in Puerto Rico. Maria weakened significantly due to crossing the island, but was able to strengthen somewhat as it passed close to Hispaniola and The Bahamas on September 21–23. Structural changes in the hurricane as it moved further north and close to the Outer Banks in the United States ultimately caused Maria to weaken quickly. Turning away from the United States as a weakened tropical storm, it became extratropical on September 30, dissipating 3 days later.






















