
Pteranodon is a genus of pterosaur that included some of the largest known flying reptiles, with P. longiceps having a wingspan of over 6 m (20 ft). They lived during the late Cretaceous geological period of North America in present-day Kansas, Nebraska, Wyoming, South Dakota and Alabama. More fossil specimens of Pteranodon have been found than any other pterosaur, with about 1,200 specimens known to science, many of them well preserved with nearly complete skulls and articulated skeletons. It was an important part of the animal community in the Western Interior Seaway.

Plagiaulacida is a group of extinct multituberculate mammals. Multituberculates were among the most common mammals of the Mesozoic, "the age of the dinosaurs". Plagiaulacids are a paraphyletic grouping, containing all multituberculates that lie outside of the advanced group Cimolodonta. They ranged from the Middle Jurassic Period to the early Late Cretaceous of the northern hemisphere. During the Cenomanian, they were replaced by the more advanced cimolodontans.

Althaea is a genus of herbaceous perennial plants native to Europe, North Africa and western Asia. It includes Althaea officinalis, also known as the marshmallow plant, whence the fluffy confection got its name. They are found on the banks of rivers and in salt marshes, preferring moist, sandy soils. The stems grow to 1–2 m tall, and flower in mid summer. The leaves are palmately lobed with 3–7 lobes. Althaea species are used as food plants by the larvae of some Lepidoptera species including Bucculatrix quadrigemina.

Althaea officinalis, the marsh mallow or marshmallow, is a species of flowering plant indigenous to Europe, Western Asia and North Africa, which is used in herbalism and as an ornamental plant. A confection made from the root since ancient Egyptian times evolved into today's marshmallow treat, but most modern marshmallow treats no longer contain marsh-mallow root.

Hesperornis is a genus of cormorant-like Ornithuran that spanned throughout the Campanian age, and possibly even up to the early Maastrichtian age, of the Late Cretaceous period. One of the lesser-known discoveries of the paleontologist O. C. Marsh in the late 19th century Bone Wars, it was an early find in the history of avian paleontology. Locations for Hesperornis fossils include the Late Cretaceous marine limestones from Kansas and the marine shales from Canada. Nine species are recognised, eight of which have been recovered from rocks in North America and one from Russia.

Struthiomimus, meaning "ostrich-mimic", is a genus of ornithomimid dinosaurs from the late Cretaceous of North America. Ornithomimids were long-legged, bipedal, ostrich-like dinosaurs with toothless beaks. The type species, Struthiomimus altus, is one of the more common, smaller dinosaurs found in Dinosaur Provincial Park; their overall abundance—in addition to their toothless beak—suggests that these animals were mainly herbivorous or omnivorous, rather than purely carnivorous. Similar to the modern extant ostriches, emus, and rheas, ornithomimid dinosaurs likely lived as opportunistic omnivores, supplementing a largely plant-based diet with a variety of small mammals, reptiles, amphibians, insects, invertebrates, and anything else they could fit into their mouth, as they foraged.

Ornithomimus is a genus of ornithomimid theropod dinosaurs from the Campanian and Maastrichtian ages of Late Cretaceous Western North America. Ornithomimus was a swift, bipedal dinosaur which fossil evidence indicates was covered in feathers and equipped with a small toothless beak that may indicate an omnivorous diet. It is usually classified into two species: the type species, Ornithomimus velox, and a referred species, Ornithomimus edmontonicus. O. velox was named in 1890 by Othniel Charles Marsh on the basis of a foot and partial hand from the Denver Formation of Colorado. Another seventeen species have been named since then, though almost all of them have been subsequently assigned to new genera or shown to be not directly related to Ornithomimus velox. The best material of species still considered part of the genus has been found in Alberta, representing the species O. edmontonicus, known from several skeletons from the Horseshoe Canyon Formation. Additional species and specimens from other formations are sometimes classified as Ornithomimus, such as Ornithomimus samueli from the earlier Dinosaur Park Formation.
Coelurus is a genus of coelurosaurian dinosaur from the Late Jurassic period. The name means "hollow tail", referring to its hollow tail vertebrae. Although its name is linked to one of the main divisions of theropods (Coelurosauria), it has historically been poorly understood, and sometimes confused with its better-known contemporary Ornitholestes. Like many dinosaurs studied in the early years of paleontology, it has had a confusing taxonomic history, with several species being named and later transferred to other genera or abandoned. Only one species is currently recognized as valid: the type species, C. fragilis, described by Othniel Charles Marsh in 1879. It is known from one partial skeleton found in the Morrison Formation of Wyoming, United States. It was a small bipedal carnivore with elongate legs.

Epanterias is a dubious genus of theropod dinosaur from the Tithonian age Upper Jurassic upper Morrison Formation of Garden Park, Colorado. It was described by Edward Drinker Cope in 1878. The type species is Epanterias amplexus. This genus is based on what is now AMNH 5767, parts of three vertebrae, a coracoid, and a metatarsal. Although Cope thought it was a sauropod, it was later shown to be a theropod. Gregory S. Paul reassessed the material as pertaining to a large species of Allosaurus in 1988. Other authors have gone further and considered E. amplexus as simply a large individual of Allosaurus fragilis. In 2010, Gregory S. Paul and Kenneth Carpenter noted that the E. amplexus specimen comes from higher in the Morrison Formation than the type specimen of Allosaurus fragilis, and is therefore "probably a different taxon". They also considered its holotype specimen not diagnostic and classified it as a nomen dubium.

Pteranodon sternbergi is an extinct species of the pteranodontid pterodactyloid pterosaur genus Pteranodon from the Late Cretaceous geological period of North America. P. sternbergi was among the largest pterosaurs, with a wingspan of up to 6 metres (20 ft) in males. It has been argued that P. sternbergi should be classified in a separate genus, Geosternbergia, but this has not been followed by most other researchers.

Siebenrockiella is a small genus of black marsh turtles. It used to be monotypic but now has two species with the addition of the Philippine forest turtle. The genus was originally erected in 1869 by John Edward Gray under the name Bellia, commemorating Thomas Bell, but this name is a junior homonym of Bellia Milne-Edwards, 1848, a crustacean genus. The replacement name, Siebenrockiella, was published in 1929 by Wassili Adolfovitch Lindholm, and commemorates Friedrich Siebenrock.
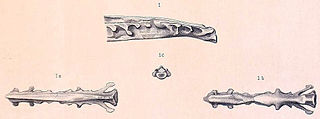
Apatornis is a genus of ornithuran dinosaurs endemic to North America during the late Cretaceous. It currently contains a single species, Apatornis celer, which lived around the Santonian-Campanian boundary, dated to about 83.5 million years ago. The remains of this species were found in the Smoky Hill Chalk of the Niobrara Formation in Kansas, United States. It is known from a single fossil specimen: a synsacrum, the fused series of vertebrae over the hips.

The corticioid fungi are a group of fungi in the Basidiomycota typically having effused, smooth basidiocarps that are formed on the undersides of dead tree trunks or branches. They are sometimes colloquially called crust fungi or patch fungi. Originally such fungi were referred to the genus Corticium and subsequently to the family Corticiaceae, but it is now known that all corticioid species are not necessarily closely related. The fact that they look similar is an example of convergent evolution. Since they are often studied as a group, it is convenient to retain the informal (non-taxonomic) name of "corticioid fungi" and this term is frequently used in research papers and other texts.

Pteranodontoidea is an extinct clade of ornithocheiroid pterosaurs from the Early to Late Cretaceous of Asia, Africa, Europe, North America and South America. It was named by Alexander Wilhelm Armin Kellner in 1996. In 2003, Kellner defined the clade as a node-based taxon consisting of the last common ancestor of Anhanguera, Pteranodon and all its descendants. The clade Ornithocheiroidea is sometimes considered to be the senior synonym of Pteranodontoidea, however it depends on its definition. Brian Andres in his analyses, converts Ornithocheiroidea using the definition of Kellner (2003) to avoid this synonymy.

Sonoma is a genus of North American rove beetles in the subfamily Pselaphinae. At least 57 species are known—the majority from the Pacific Slope, ranging from Southern California to Alaska—with other species occurring in the Appalachians and the Eastern United States.
Pselaptrichus is a genus of ant-loving beetles in the family Staphylinidae. There are more than 30 described species in Pselaptrichus.
Megarafonus is a genus of ant-loving beetles in the family Staphylinidae. There are about seven described species in Megarafonus.

Smitanosaurus is a genus of dicraeosaurid sauropod dinosaur from the Late Jurassic of Colorado. The genus contains one species, S. agilis, originally assigned to the defunct genus Morosaurus.

Sphaeropthalma is a genus of velvet ants described by C.A. Blake in 1871 within the family Mutillidae.
















