
Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) are a class of drugs that inhibit the activity of one or both monoamine oxidase enzymes: monoamine oxidase A (MAO-A) and monoamine oxidase B (MAO-B). They are best known as effective antidepressants, especially for treatment-resistant depression and atypical depression. They are also used to treat panic disorder, social anxiety disorder, Parkinson's disease, and several other disorders.

A transferase is any one of a class of enzymes that catalyse the transfer of specific functional groups from one molecule to another. They are involved in hundreds of different biochemical pathways throughout biology, and are integral to some of life's most important processes.

Tyramine, also known under several other names, is a naturally occurring trace amine derived from the amino acid tyrosine. Tyramine acts as a catecholamine releasing agent. Notably, it is unable to cross the blood-brain barrier, resulting in only non-psychoactive peripheral sympathomimetic effects following ingestion. A hypertensive crisis can result, however, from ingestion of tyramine-rich foods in conjunction with the use of monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs).
In enzymology, a caffeoyl-CoA O-methyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a tyramine N-methyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a propionate CoA-transferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a trans-feruloyl-CoA hydratase (EC 4.2.1.101) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 2-ethylmalate synthase (EC 2.3.3.6) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 3-ethylmalate synthase (EC 2.3.3.7) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 3-propylmalate synthase (EC 2.3.3.12) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a dihydrolipoyllysine-residue (2-methylpropanoyl)transferase (EC 2.3.1.168) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a galactarate O-hydroxycinnamoyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a homocitrate synthase (EC 2.3.3.14) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a putrescine N-hydroxycinnamoyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a quinate O-hydroxycinnamoyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, an UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 1-carboxyvinyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the first committed step in peptidoglycan biosynthesis of bacteria:
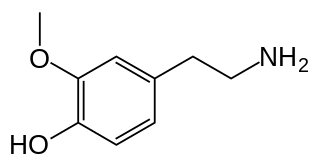
3-Methoxytyramine (3-MT), also known as 3-methoxy-4-hydroxyphenethylamine, is a human trace amine that occurs as a metabolite of the neurotransmitter dopamine. It is formed by the introduction of a methyl group to dopamine by the enzyme catechol-O-methyl transferase (COMT). 3-MT can be further metabolized by the enzyme monoamine oxidase (MAO) to form homovanillic acid (HVA), which is then typically excreted in the urine.
Omega-hydroxypalmitate O-feruloyl transferase is an enzyme with systematic name feruloyl-CoA:16-hydroxypalmitate feruloyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction

N-Feruloylserotonin an alkaloid and polyphenol found in safflower seed. Chemically, it is an amide formed between serotonin and ferulic acid. It has in vitro anti-atherogenic activity.








