
National Security Space Launch (NSSL) is a program of the United States Space Force (USSF) intended to assure access to space for United States Department of Defense and other United States government payloads. The program is managed by the Assured Access to Space Directorate (SSC/AA) of the Space Force's Space Systems Command (SSC), in partnership with the National Reconnaissance Office.

The Boeing X-37, also known as the Orbital Test Vehicle (OTV), is a reusable robotic spacecraft. It is boosted into space by a launch vehicle, then re-enters Earth's atmosphere and lands as a spaceplane. The X-37 is operated by the Department of the Air Force Rapid Capabilities Office, in collaboration with United States Space Force, for orbital spaceflight missions intended to demonstrate reusable space technologies. It is a 120-percent-scaled derivative of the earlier Boeing X-40. The X-37 began as a NASA project in 1999, before being transferred to the United States Department of Defense in 2004. Until 2019, the program was managed by Air Force Space Command.

Falcon 9 is a partially reusable, human-rated, two-stage-to-orbit, medium-lift launch vehicle designed and manufactured in the United States by SpaceX. The first Falcon 9 launch was on 4 June 2010, and the first commercial resupply mission to the International Space Station (ISS) launched on 8 October 2012. In 2020, it became the first commercial rocket to launch humans to orbit. The Falcon 9 has an exceptional safety record, with 382 successful launches, two in-flight failures, one partial failure and one pre-flight destruction. It is the most-launched American rocket in history.
The Space Test Program (STP) is the primary provider of spaceflight for the United States Department of Defense (DoD) space science and technology community. STP is managed by a group within the Advanced Systems and Development Directorate, a directorate of the Space and Missile Systems Center of the United States Space Force. STP provides spaceflight via the International Space Station (ISS), piggybacks, secondary payloads and dedicated launch services.

Space Launch Complex 4 (SLC-4) is a launch and landing site at Vandenberg Space Force Base, California, U.S. It has two pads, both of which are used by SpaceX for Falcon 9, one for launch operations, and the other as Landing Zone 4 (LZ-4) for SpaceX landings.

Falcon Heavy is a super heavy-lift launch vehicle with partial reusability that can carry cargo into Earth orbit, and beyond. It is designed, manufactured and launched by American aerospace company SpaceX.

Several new rockets and spaceports began operations in 2016.
The EELV Secondary Payload Adapter (ESPA) is an adapter for launching secondary payloads on orbital launch vehicles.

This article documents notable spaceflight events during the year 2019.

This article documents notable spaceflight events during the year 2018. For the first time since 1990, more than 100 orbital launches were performed globally.

The following is a timeline of important events in the history of private spaceflight, including important technical as well as legislative and political advances. Though the industry has its origins in the early 1960s, soon after the beginning of the Space Age, private companies did not begin conducting launches into space until the 1980s, and it was not until the 21st century that multiple companies began privately developing and operating launch vehicles and spacecraft in earnest.
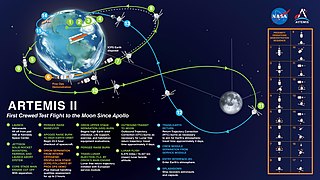
Spaceflight in 2025 promises to follow the 2020s trend of record breaking orbital launches and increased developments in lunar, Mars and low-earth orbit exploration.

USA-299, also referred to as USSF-7 and Orbital Test Vehicle 6 (OTV-6), is the third flight of the first Boeing X-37B, an American unmanned vertical-takeoff, horizontal-landing spaceplane. It was launched to low Earth orbit aboard an Atlas V launch vehicle from SLC-41 on 17 May 2020. Its mission designation is part of the USA series.

Orbital Test Vehicle 7 (OTV-7), also referred to as United States Space Force-52 (USSF-52) or USA-349, is the fourth flight of the second Boeing X-37B, an American unmanned vertical-takeoff, horizontal-landing spaceplane. It was launched to a highly elliptical high Earth orbit aboard a Falcon Heavy rocket from LC-39A on 28 December 2023.












