Related Research Articles

Asimina is a genus of small trees or shrubs described as a genus in 1763. Asimina is the only temperate genus in the tropical and subtropical flowering plant family Annonaceae. Asimina have large, simple leaves and large fruit. It is native to eastern North America and collectively referred to as pawpaw. The genus includes the widespread common pawpaw Asimina triloba, which bears the largest edible fruit indigenous to the United States. Pawpaws are native to 26 states of the U.S. and to Ontario in Canada. The common pawpaw is a patch-forming (clonal) understory tree found in well-drained, deep, fertile bottomland and hilly upland habitat. Pawpaws are in the same plant family (Annonaceae) as the custard apple, cherimoya, sweetsop, soursop, and ylang-ylang; the genus is the only member of that family not confined to the tropics.
Family is one of the eight major hierarchical taxonomic ranks in Linnaean taxonomy. It is classified between order and genus. A family may be divided into subfamilies, which are intermediate ranks between the ranks of family and genus. The official family names are Latin in origin; however, popular names are often used: for example, walnut trees and hickory trees belong to the family Juglandaceae, but that family is commonly referred to as the "walnut family".
Order is one of the eight major hierarchical taxonomic ranks in Linnaean taxonomy. It is classified between family and class. In biological classification, the order is a taxonomic rank used in the classification of organisms and recognized by the nomenclature codes. An immediately higher rank, superorder, is sometimes added directly above order, with suborder directly beneath order. An order can also be defined as a group of related families.

Retama is a genus of flowering bushes in the legume family, Fabaceae. It belongs to the broom tribe, Genisteae. Retama broom bushes are found natively in North Africa, the Levant and some parts of southern Europe. Retama raetam and Retama monosperma have white flowers, while Retama sphaerocarpa has yellow flowers. It remains an open question in taxonomy whether the members of the genus Retama should be incorporated into the genus Genista.

Michel Adanson was an 18th-century French botanist and naturalist who traveled to Senegal to study flora and fauna. He proposed a "natural system" of taxonomy distinct from the binomial system forwarded by Linnaeus.

Fallopia is a genus of about 12 species of flowering plants in the buckwheat family, often included in a wider treatment of the related genus Polygonum in the past, and previously including Reynoutria. The genus is native to temperate and subtropical regions of the Northern Hemisphere, but species have been introduced elsewhere. The genus includes species forming vines and shrubs.

Asterophora is a genus of fungi that grow as parasites on mushrooms. The genus contains four species, which have a widespread distribution, especially in temperate areas. The most recently described species, A. salvaterrensis, was found in Pinus pinaster forests in Galicia. Asterophora species are characterized by the massive production of chlamydospores in their fruit bodies and by the production of carminophilous lysosomes in their basidia. A frequently used but synonymous genus name is Nyctalis. The chlamydospores have been classified in the genus Ugola, which is an anamorphic name.
An early system of plant taxonomy developed by Antoine Laurent de Jussieu, the de Jussieu System' (1789), is of great importance as a starting point of botanical nomenclature at the rank of family, together with Michel Adanson's Familles naturelles des plantes (1763). While Adanson introduced the concept of families, Jussieu arranged them hierarchically into Divisions, Classes and Orders, in his seminal Genera plantarum.

Liabum is a genus of South American flowering plants in tribe Liabeae of the family Asteraceae.

Apera is a small genus of annual grasses, known commonly as silkybent grass or windgrass. They are native to Europe, North Africa and parts of Asia but have been introduced and naturalized in much of North and South America.

Grangea is a genus of flowering plants in the family Asteraceae.
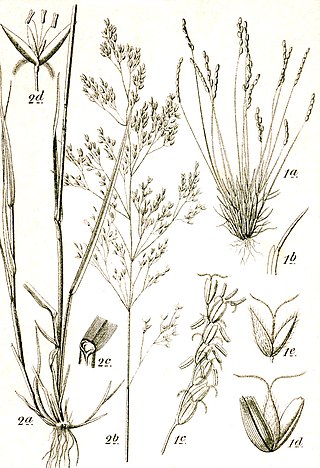
Mibora, or sandgrass, is a genus of European and North African plants in the grass family.

Tolpis is a genus of flowering plants in the tribe Cichorieae within the family Asteraceae. It is native to Africa, Southern Europe, the Middle East and Macaronesia. Many species are limited to the Canary Islands.

Limbarda is a genus of succulent, xerophytic plants in the daisy family.

Picnomon is a genus of flowering plants in the tribe Cardueae within the family Asteraceae.

Borrichia is a genus of flowering plants in the family Asteraceae. It is named for Danish physician Ole Borch (1628–1690). Members of the genus are commonly known as seaside tansies. They are native to North and South America.

Asterophora mirabilis is a species of fungus that grows as a parasite on mushrooms. It was originally described as Nyctalis mirabilis by Australian mycologist Tom May in 1995, and later transferred to the genus Asterophora in 2001. The fungus grows in temperate rainforests of Australia on decaying fruit bodies of species in the genera Russula and Lactarius.

Benkara is a genus of flowering plants in the family Rubiaceae. It is found in tropical and subtropical Asia from India east to China and the Ryukyu Islands, south to Java and the Philippines. It was described by Michel Adanson in 1763.
The Adanson system, published by French botanist Michel Adanson as the Familles des plantes in two volumes in 1763, was an important step in botanical nomenclature by establishing the ordering of genera into families.

Condea is a genus of flowering plants in the family Lamiaceae.
References
- ↑ Adanson M. (1763). Familles des plantes (in French). Vol. 2. Paris, France: Vincent. p. 5.
- ↑ Kirk PM, Cannon PF, Minter DW, Stalpers JA (2008). Dictionary of the Fungi (10th ed.). Wallingford, UK: CABI. p. 711. ISBN 978-0-85199-826-8.
- ↑ Redhead SA, Seifert KA (2001). "Asterophora Ditmar ex Link 1809 versus Nyctalis Fries 1825, and the status of Ugola Adanson 1763". Taxon. 50 (1): 243–68. doi:10.2307/1224526. JSTOR 1224526.(subscription required)