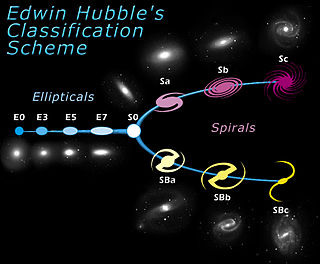
The Hubble sequence is a morphological classification scheme for galaxies invented by Edwin Hubble in 1926. It is often known colloquially as the Hubble tuning fork diagram because of the shape in which it is traditionally represented. In June 2019, however, citizen scientists through Galaxy Zoo reported that the usual Hubble classification, particularly concerning spiral galaxies, may not be supported, and may need updating.

A lenticular galaxy is a type of galaxy intermediate between an elliptical and a spiral galaxy in galaxy morphological classification schemes. It contains a large-scale disc but does not have large-scale spiral arms. Lenticular galaxies are disc galaxies that have used up or lost most of their interstellar matter and therefore have very little ongoing star formation. They may, however, retain significant dust in their disks. As a result, they consist mainly of aging stars. Despite the morphological differences, lenticular and elliptical galaxies share common properties like spectral features and scaling relations. Both can be considered early-type galaxies that are passively evolving, at least in the local part of the Universe. Connecting the E galaxies with the S0 galaxies are the ES galaxies with intermediate-scale discs.

Galaxy morphological classification is a system used by astronomers to divide galaxies into groups based on their visual appearance. There are several schemes in use by which galaxies can be classified according to their morphologies, the most famous being the Hubble sequence, devised by Edwin Hubble and later expanded by Gérard de Vaucouleurs and Allan Sandage. However, galaxy classification and morphology are now largely done using computational methods and physical morphology.

A disc galaxy is a galaxy characterized by a disc, a flattened circular volume of stars. These galaxies may or may not include a central non-disc-like region.

NGC 7331 is an unbarred spiral galaxy about 40 million light-years (12 Mpc) away in the constellation Pegasus. It was discovered by William Herschel in 1784. NGC 7331 is the brightest member of the NGC 7331 Group of galaxies. The other members of the group are the lenticular or unbarred spirals NGC 7335 and 7336, the barred spiral galaxy NGC 7337 and the elliptical galaxy NGC 7340. These galaxies lie at distances of approximately 332, 365, 348 and 294 million light years, respectively. In both visible light and infrared photos of the NGC 7331, the core of the galaxy appears to be slightly off-center, with one side of the disk appearing to extend further away from the core than the opposite side.

AM 0644-741, also known as the Lindsay-Shapley Ring, is an unbarred lenticular galaxy, and a ring galaxy, which is 300 million light-years away in the southern constellation Volans. The yellowish nucleus was once the center of a normal spiral galaxy, and the ring which currently surrounds the center is 150,000 light years in diameter. The ring is theorized to have formed by a collision with another galaxy, which triggered a gravitational disruption that caused dust in the galaxy to condense and form stars, which forced it to then expand away from the galaxy and create a ring. The ring is a region of rampant star formation dominated by young, massive, hot blue stars. The pink regions along the ring are rarefied clouds of glowing hydrogen gas that is fluorescing as it is bombarded with strong ultraviolet light from the blue stars. Galactic simulation models suggest that the ring of AM 0644-741 will continue to expand for about another 300 million years, after which it will begin to disintegrate.

NGC 7217 is an unbarred spiral galaxy in the constellation Pegasus.

An intermediate spiral galaxy is a galaxy that is in between the classifications of a barred spiral galaxy and an unbarred spiral galaxy. It is designated as SAB in the galaxy morphological classification system devised by Gerard de Vaucouleurs. Subtypes are labeled as SAB0, SABa, SABb, or SABc, following a sequence analogous to the Hubble sequence for barred and unbarred spirals. The subtype is based on the relative prominence of the central bulge and how tightly wound the spiral arms are.

An unbarred spiral galaxy is a type of spiral galaxy without a central bar, or one that is not a barred spiral galaxy. It is designated with an SA in the galaxy morphological classification scheme.

NGC 2535 is an unbarred spiral galaxy exhibiting a weak inner ring structure around the nucleus in the constellation Cancer that is interacting with NGC 2536. The interaction has warped the disk and spiral arms of NGC 2535, producing an elongated structure, visible at ultraviolet wavelengths, that contain many bright, recently formed blue star clusters in addition to enhanced star forming regions around the galaxy center. The two galaxies are listed together in the Atlas of Peculiar Galaxies as an example of a spiral galaxy with a high surface brightness companion.
NGC 5890 is an unbarred lenticular galaxy in the constellation Libra. It was discovered in April 1785 by Ormond Stone.

The Eridanus Cluster is a galaxy cluster roughly 23 Mpc (75 Mly) from Earth, containing about 73 main galaxies and about 200 total galaxies. About 30% have Hubble classifications of elliptical or S0 and the remaining 70% are spiral or irregular. These galaxies reside in smaller groups which are all loosely gravitationally bound to each other, suggesting that the system is still condensing from the Hubble flow and may eventually form a cluster of about 1014M☉. A low velocity dispersion compared to that of, for example, the Coma cluster, supports this hypothesis. The Eridanus Cluster is located in the constellation Eridanus near the Fornax Cluster, and is sometimes called the "Fornax II Cluster".

NGC 7499 is an unbarred lenticular galaxy within the constellation Pisces.

NGC 296 is a low surface brightness unbarred spiral galaxy in the constellation of Pisces. The designation NGC 295 is sometimes mistakenly used for NGC 296.

NGC 4452 is an edge-on lenticular galaxy that is part of the Virgo Cluster. NGC 4452 is located approximately 60 million light-years distant and is 35,000 light-years in width. This galaxy was first seen by William Herschel in 1784 with his 47 cm telescope.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to galaxies:
Abell 2152 is a bimodal galaxy cluster and one of three clusters comprising the Hercules Supercluster. It contains 3 BCGs; the S0 lenticular UGC 10204, the pair UGC 10187, and the SA0 unbarred lenticular CGCG 108-083. In total there are 41 galaxies which are confirmed to be members of the cluster. The cluster is classified as a Bautz-Morgan type III and Rood-Sastry class F cluster, indicating morphological irregularity and perhaps dynamical youth. It is receding from the Milky Way galaxy with a velocity of 12385 km/s.

NGC 966 is an unbarred lenticular galaxy approximately 440 million light-years away from Earth in the constellation of Cetus. It was discovered by American astronomer Francis Preserved Leavenworth in 1886.

NGC 1375 is barred lenticular galaxy in constellation Fornax discovered by John Herschel on November 29, 1837. It is a member of Fornax Cluster.

NGC 1460 is a barred lenticular galaxy in the constellation Eridanus. It was discovered by John Herschel on November 28, 1837. It is moving away from the Milky Way 1341 km/s.
















