Brush Traction was a manufacturer and maintainer of railway locomotives in Loughborough, England whose operations have now been merged into the Wabtec company's Doncaster UK operations.
Dick, Kerr and Company was a locomotive and tramcar manufacturer based in Kilmarnock, Scotland and Preston, England.

A double-decker tram or double-deck tram is a tram that has two levels or decks. Some double-decker trams have open tops. Double-deck trams were once popular in some European cities, like Berlin and London, throughout the British Empire countries in the early half of the 20th century including Auckland, Christchurch and Wellington in New Zealand; Hobart, Tasmania in Australia, and in parts of Asia. They are still in service or even newly introduced in Hong Kong, Alexandria, Oranjestad, Blackpool, Birkenhead, Franschhoek, Auckland and Douglas, mostly as heritage or tourist trams.

The Portsdown and Horndean Light Railway was a tram service that ran initially from Cosham to Horndean in Hampshire, England.

The Rothesay tramway was a narrow gauge electric tramway on the Isle of Bute, Scotland. It opened in 1882 as a 4 ft gauge horse tramway, was converted to a 3 ft 6 in gauge electric tramway in 1902, and closed in 1936. It was the only public tramway to be built on a Scottish island.

Between 1901 and 1949 Manchester Corporation Tramways was the municipal operator of electric tram services in Manchester, England. At its peak in 1928, the organisation carried 328 million passengers on 953 trams, via 46 routes, along 292 miles (470 km) of track.
Trams operated in Edinburgh from 1871 to 1956, and resumed in 2014. The first systems were horse-drawn, while cable-haulage appeared in the city in 1888. Electric trams first ran on systems in neighbouring Musselburgh (1904) and Leith (1905), meeting the Edinburgh cable-trams at Joppa and Pilrig respectively. Electrification meant cable trams last ran in 1923, with through running now possible to Leith and as far east as Port Seton. The various systems were operated by different private and municipal entities over the years; the Edinburgh and Leith systems had been merged under Edinburgh Corporation by 1920, but it wasn't until 1928, after the partial closure of Musselburgh line, that all trams operating in Edinburgh were in the sole control of the corporation. The last electric trams ran in 1956, but electric trams returned in 2014 with the opening of Edinburgh Trams. Many of the trams from the horse/cable/first electric era were built in Shrubhill Works. Two trams have been preserved, a horse tram and an electric tram, built by Shrubhill in 1885 and 1948 respectively. A 1903 Dick Kerr cable-tram has also been purchased for preservation. Remnants of the cable-tram system can be seen in Waterloo Place and Henderson Row, and of the Musselburgh line at Morrison's Haven.

Northampton Corporation Tramways operated the tramway service in Northampton between 1901 and 1934.

Wolverhampton Corporation Tramways operated a tramway service in Wolverhampton between 1902 and 1928.

Nelson Corporation Tramways operated a tramway service in Nelson, Lancashire between 1903 and 1934.
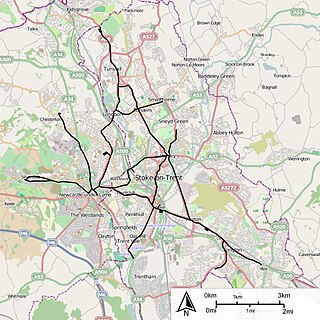
The Potteries Electric Traction Company operated a tramway service in The Potteries between 1899 and 1928.

The City of Carlisle Electric Tramways Company operated an electric tramway service in Carlisle between 1900 and 1931.

Wigan Corporation Tramways operated a tramway service in Wigan, England, between 1901 and 1931. The first tramway service in the town was run by the Wigan Tramways Company, whose horse trams began carrying passengers in 1880. They began replacing horses with steam tram locomotives from 1882, but the company failed in 1890 when a Receiver was appointed to manage it. The Wigan & District Tramways Company took over the system in 1893 and ran it until 1902. Meanwhile, Wigan Corporation were planning their own tramway system, obtaining an authorising Act of Parliament in 1893, and a second one in 1898. This enabled them to build electric tramways, and in 1902, they took over the lines of the Wigan & District Tramways Company.
At the peak of Britain’s first-generation tramways, it was possible to travel by tram all the way from Pier Head at Liverpool to the Pennines in Rochdale by tram.

Bath Tramways Company and its successors operated a 4 ft horse-drawn tramway service in Bath between 1880 and 1902. From 1903 until its closure in 1939 an expanded route carried electric trams operated by Bath Electric Tramways Company.

Bolton Corporation Tramways operated a tramway service in Bolton between 1899 and 1947.
At the peak of Britain’s first-generation tramways, it was possible to travel by tram all the way from Pier Head at Liverpool to the Pennines in Rochdale by tram.

Huddersfield Corporation Tramways operated a tramway service in Huddersfield, England, between 1883 and 1940. It initially used steam locomotives pulling unpowered tramcars, but as the system was expanded, a decision was taken to change to electric traction in 1900, and the first electric trams began operating in February 1901. The system was built to the unusual gauge of 4 ft 7+3⁄4 in, in the hope that coal wagon from neighbouring coal tramways, which used that gauge, could be moved around the system. This did not occur, but two coal trams were used to delivered coal to three mills.

The Trams in Mandalay were owned and operated by the Mandalay Electric Company, which was incorporated in London in October 1902 with a capital of £ 200,000.

The Great Grimsby Street Tramways Company was a tramway serving Grimsby and Cleethorpes in Lincolnshire, England. It was a subsidiary of The Provincial Tramways Company. They opened a horse tramway in 1881, running from the Wheatsheaf Inn in Bargate to the border with Cleethorpes, with a branch along Freeman Street, and extended the line into Cleethorpes in 1887. It followed the trend of many British systems, and was converted to an electric tramway in December 1901. Small extensions were made to the system at both ends, but the basic plan of the system remained the same throughout its life.

Stockport Corporation Tramways operated a tramway service in Stockport, England, between 1901 and 1951. It was preceded by a horse tramway from Levenshulme to Stockport, which opened in 1880, and was ultimately run by the Manchester Carriage and Tramways Company. A second independent horse tramway opened in 1890, running to Hazel Grove. In 1899 the Corporation bought the first line, electrified it, and leased it back to the operating company. Their powers to buy the Stockport and Hazel Grove Tramway, authorised by the same Act of Parliament, were not exercised until 1905.
















