
The United Nations Security Council (UNSC) is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations (UN) and is charged with ensuring international peace and security, recommending the admission of new UN members to the General Assembly, and approving any changes to the UN Charter. Its powers as outlined in the United Nations Charter include establishing peacekeeping operations, enacting international sanctions, and authorizing military action. The UNSC is the only UN body with authority to issue resolutions that are binding on member states.

The member states of the United Nations comprise 193 sovereign states. The United Nations (UN) is the world's largest intergovernmental organization. All members have equal representation in the UN General Assembly.

A United Nations Security Council resolution (UNSCR) is a United Nations resolution adopted by the Security Council (UNSC), the United Nations (UN) 15-member body charged with "primary responsibility for the maintenance of international peace and security".
A United Nations General Assembly resolution is a decision or declaration voted on by all member states of the United Nations in the General Assembly.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 1706, adopted on August 31, 2006, after recalling previous resolutions on the situation in Sudan, including resolutions 1556 (2004), 1564 (2005), 1574 (2004), 1590 (2004), 1591 (2005), 1593 (2004), 1663 (2006), 1665 (2006) and 1679 (2006), the Council expanded the mandate of the United Nations Mission in the Sudan (UNMIS) to include deployments in Darfur to enforce the Darfur Peace Agreement.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 83, adopted on June 27, 1950, determined that the attack on the Republic of Korea by forces from North Korea constituted a breach of the peace. The Council called for an immediate cessation of hostilities and for the authorities in North Korea to withdraw their armed forces to the 38th parallel. They also noted the report by the United Nations Commission on Korea that stated North Korea's failure to comply with Security Council Resolution 82 and that urgent military measures were required to restore international peace and security.

The United Nations Security Council Resolution 84, adopted on July 7, 1950, was the United Nations Security Council resolution which authorized the formation of the United Nations Command to provide military support for South Korea, following a North Korean invasion and offensive at the outbreak of the Korean War.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 86, adopted on September 26, 1950, having found that the Republic of Indonesia was a peace-loving State which fulfilled the conditions laid down in Article 4 of the United Nations Charter, the Council recommended that the UN General Assembly admit the Republic of Indonesia to membership in the United Nations.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 1907, adopted on December 23, 2009, imposed an arms embargo on Eritrea, travel bans on its leaders, and froze the assets of some of the country's political and military officials after accusing the Eritrean government of aiding Al-Shabaab in Somalia and reportedly refusing to withdraw troops from its disputed border with Djibouti, following a conflict in 2008. The African Union and other organisations had been calling on the Security Council to sanction Eritrea for several months.

United Nations Security Council resolution 763, adopted without a vote on 6 July 1992, after examining the application of the Republic of Georgia for membership in the United Nations, the Council recommended to the General Assembly that Georgia be admitted.
United Nations Security Council resolution 1248, adopted without a vote on 25 June 1999, after examining the application of the Republic of Kiribati for membership in the United Nations, the Council recommended to the General Assembly that Kiribati be admitted, bringing total membership of the United Nations to 186.
United Nations Security Council resolution 1249, adopted on 25 June 1999, after examining the application of the Republic of Nauru for membership in the United Nations, the Council recommended to the General Assembly that Nauru be admitted, bringing total membership of the United Nations to 187.
United Nations Security Council resolution 1253, adopted without a vote on 28 July 1999, after examining the application of the Kingdom of Tonga for membership in the United Nations, the Council recommended to the General Assembly that Tonga be admitted, bringing total membership of the United Nations to 188.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1290 was adopted on 17 February 2000. Resolution 1290 examined Tuvalu's application to become the 189th member of the United Nations (UN). Tuvalu achieved independence in 1978 after over eighty years of British colonial rule. The country had struggled economically, and it took the 2000 sale of Tuvalu's Internet country code top-level domain .tv for the nation to be able to afford UN membership. Resolution 1290 was adopted unopposed, although China abstained due to concerns over Tuvalu's relationship with Taiwan.
United Nations Security Council Resolution 1922, adopted unanimously on May 12, 2010, after recalling resolutions 1769 (2007), 1778 (2007), 1834 (2008), 1861 (2009) and 1913 (2010), the Council noted that the situation in the region of Darfur in Sudan, Chad and the Central African Republic constituted a threat to international peace and security, and therefore extended the mandate of the United Nations Mission in the Central African Republic and Chad (MINURCAT) for a further two weeks until May 26, 2010, pending further discussions on its future.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 1978, adopted unanimously on April 27, 2011, after recalling all previous resolutions on the situation in Sudan, the Council extended the mandate of the United Nations Mission in Sudan (UNMIS) until July 9, 2011 and announced its intention to create a successor mission.
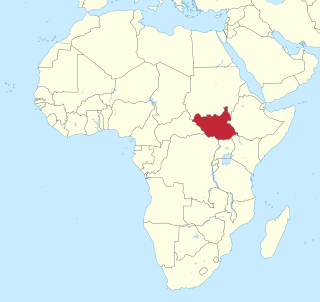
United Nations Security Council Resolution 1996, adopted unanimously on July 8, 2011, after welcoming the independence of South Sudan from Sudan, the Council established the United Nations Mission in the Republic of South Sudan (UNMISS) for an initial period of one year.
United Nations Security Council Resolution 1997, adopted unanimously on July 11, 2011, after recalling resolutions 1590 (2005), 1627 (2005), 1663 (2006), 1706 (2006), 1709 (2006), 1714 (2006), 1755 (2007), 1812 (2008), 1870 (2009), 1919 (2010) and 1978 (2011) on the situation in Sudan, the Council authorised the withdrawal of the United Nations Mission in Sudan (UNMIS) by August 31, 2011.
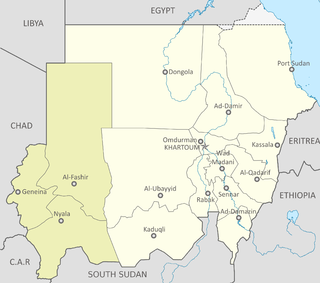
United Nations Security Council Resolution 2003, adopted unanimously on July 29, 2011, after reaffirming all previous resolutions and statements on the situation in Sudan, the Council extended the mandate of the African Union – United Nations Hybrid Operation in Darfur (UNAMID) for a further 12 months until July 31, 2012.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 2428 was adopted on 13 July 2018. According to the resolution, the Security Council voted to impose an arms embargo in South Sudan in addition to current sanctions until 31 May 2019.















