| This article is part of a series about the |
| United Nations |
|---|
 |
| Charter |
| UN System |
| Funds, programmes, and other bodies |
| Specialized agencies |
| Membership |
| History |
| Resolutions |
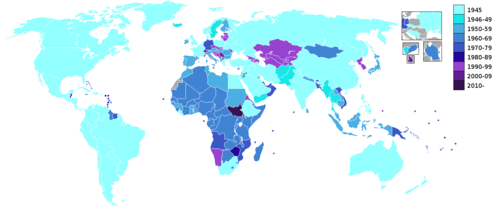
As of 25December2025, there are 193 member states in the United Nations (UN), each of which is a member of the United Nations General Assembly. [1]
Contents
The following is a list of United Nations member states arranged in chronological order according to their dates of admission (with the United Nations Security Council resolutions that recommended their admission and the United Nations General Assembly resolutions that admitted them, signified with SCR and GAR, respectively), [2] including former members. Members denoted with "→" changed their names, had their memberships in the UN continued by a successor state, merged with other members, or were dissolved.