

This is a list of territories which are directly administered, or once were, by the United Nations (UN). These are not to be confused with UN trust territories, which were run by a single country under a UN mandate.


This is a list of territories which are directly administered, or once were, by the United Nations (UN). These are not to be confused with UN trust territories, which were run by a single country under a UN mandate.
| Name | Location | Years | Today part of |
|---|---|---|---|
| United Nations Peacekeeping Force in Cyprus (UNFICYP) | United Nations Buffer Zone in Cyprus (UNBZC) | 1964–present | |
| United Nations Disengagement Observer Force (UNDOF) | UNDOF Zone on the Golan Heights | 1974–present | |
| United Nations Interim Administration Mission in Kosovo (UNMIK) | United Nations Administered Kosovo | 1999–present (only de jure since 2008) | (claimed by |
| Name | Location | Years | Today part of |
|---|---|---|---|
| United Nations Temporary Executive Authority (UNTEA) | Western New Guinea | 1962–1963 | |
| United Nations Transitional Authority in Cambodia (UNTAC) | Cambodia | 1992–1993 | |
| United Nations Transitional Administration for Eastern Slavonia, Baranja and Western Sirmium (UNTAES) | Eastern Slavonia, Baranja and Western Syrmia | 1996–1998 | |
| United Nations Transitional Administration in East Timor (UNTAET) | United Nations Administered East Timor | 1999–2002 |
A League of Nations mandate represented a legal status under international law for specific territories following World War I, involving the transfer of control from one nation to another. These mandates served as legal documents establishing the internationally agreed terms for administering the territory on behalf of the League of Nations. Combining elements of both a treaty and a constitution, these mandates contained minority rights clauses that provided for the rights of petition and adjudication by the Permanent Court of International Justice.

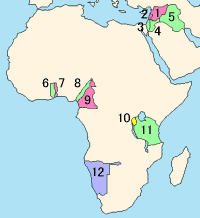
The Trust Territory of the Pacific Islands (TTPI) was a United Nations trust territory in Micronesia administered by the United States from 1947 to 1994. The Imperial Japanese South Seas Mandate had been seized by the US during the Pacific War, as Japan had administered the territory since the League of Nations gave Japan a mandate over the area from Imperial Germany after World War I. However, in the 1930s, Japan left the League of Nations and invaded additional lands. During World War II, military control of the islands was disputed, but by the war's end, the islands had come under the Allies' control. The Trust Territory of the Pacific was created to administer the islands as part of the United States while still under the auspices of the United Nations. Most of the island groups in the territory became independent states, with some degree of ties kept with the United States: the Federated States of Micronesia, Marshall Islands and Palau are today independent states in a Compact of Free Association with the US, while the Northern Mariana Islands remain under US jurisdiction, as an unincorporated territory and commonwealth.

The United Nations Trusteeship Council is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations, established to help ensure that trust territories were administered in the best interests of their inhabitants and of international peace and security.

The United Nations trust territories were the successors of the remaining League of Nations mandates, and came into being when the League of Nations ceased to exist in 1946. All the trust territories were administered through the United Nations Trusteeship Council and authorized to a single country. The concept is distinct from a territory temporarily and directly governed by the United Nations.

The history of the State of Palestine describes the creation and evolution of the State of Palestine in the West Bank and Gaza Strip. During the British mandate period, numerous plans of partition of Palestine were proposed but without the agreement of all parties. In 1947, the United Nations Partition Plan for Palestine was voted for. The leaders of the Jewish Agency for Palestine accepted parts of the plan, while Arab leaders refused it. This triggered the 1947–1949 Palestine war and led, in 1948, to the establishment of the state of Israel on a part of Mandate Palestine as the Mandate came to an end.

The occupied Palestinian territories, also referred to as the Occupied Palestinian Territory and the Palestinian territories, consist of the West Bank and the Gaza Strip—two regions of the former British Mandate for Palestine that have been occupied by Israel since the Six-Day War of 1967. These territories make up the State of Palestine, which was self-declared by the Palestine Liberation Organization in 1988 and is recognized by 146 out of 193 UN member states.

British Togoland, officially the Mandate Territory of Togoland and later officially the Trust Territory of Togoland, was a territory in West Africa under the administration of the United Kingdom, which subsequently entered a union with Ghana, part of which became its Volta Region. The territory was effectively formed in 1916 by the splitting of the German protectorate of Togoland into two territories, French Togoland and British Togoland, during the First World War. Initially, it was a League of Nations Class B mandate. In 1922, British Togoland was formally placed under British rule, and French Togoland, now Togo, was placed under French rule.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 478, adopted on 20 August 1980, is the last of seven UNSC resolutions condemning Israel's annexation of East Jerusalem. UNSC res 478 notes Israel's non-compliance with United Nations Security Council Resolution 476 and condemned Israel's 1980 Jerusalem Law which declared Jerusalem to be Israel's "complete and united" capital, as a violation of international law. The resolution states that the council will not recognize this law, and calls on member states to accept the decision of the council. This resolution also calls upon member states to withdraw their diplomatic missions from the city. The UNSC resolutions followed two General Assembly resolutions regarding Israel's actions in East Jerusalem.
The international law bearing on issues of Arab–Israeli conflict, which became a major arena of regional and international tension since the birth of Israel in 1948, resulting in several disputes between a number of Arab countries and Israel.
An international zone is any area not fully subject to the border control policies of the state in which it is located. There are several types of international zones ranging from special economic zones and sterile zones at ports of entry exempt from customs rules to concessions over which administration is ceded to one or more foreign states. International zones may also maintain distinct visa policies from the rest of the surrounding state.

The status of Jerusalem has been described as "one of the most intractable issues in the Israeli–Palestinian conflict" due to the long-running territorial dispute between Israel and the Palestinians, both of which claim it as their capital city. Part of this issue of sovereignty is tied to concerns over access to holy sites in the Abrahamic religions; the current religious environment in Jerusalem is upheld by the "Status Quo" of the former Ottoman Empire. As the Israeli–Palestinian peace process has primarily navigated the option of a two-state solution, one of the largest points of contention has been East Jerusalem, which was part of the Jordanian-annexed West Bank until the beginning of the Israeli occupation in 1967.

Corpus separatum was the internationalization proposal for Jerusalem and its surrounding area as part of the United Nations Partition Plan for Palestine. It was adopted by the United Nations General Assembly with a two-thirds majority in November 1947. According to the Partition Plan, the city of Jerusalem would be brought under international governance, conferring it a special status due to its shared importance for the Abrahamic religions. The legal base ("Statute") for this arrangement was to be reviewed after ten years and put to a referendum. The corpus separatum was again one of the main issues of the post-war Lausanne Conference of 1949, besides the borders of Israel and the question of the Palestinian right of return.
An international city is an autonomous or semi-autonomous city-state that is separate from the direct supervision of any single nation-state.
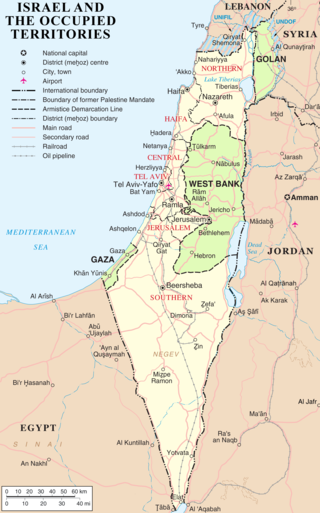
The modern borders of Israel exist as the result both of past wars and of diplomatic agreements between the State of Israel and its neighbours, as well as an effect of the agreements among colonial powers ruling in the region before Israel's creation. Only two of Israel's five total potential land borders are internationally recognized and uncontested, while the other three remain disputed; the majority of its border disputes are rooted in territorial changes that came about as a result of the 1967 Arab–Israeli War, which saw Israel occupy large swathes of territory from its rivals. Israel's two formally recognized and confirmed borders exist with Egypt and Jordan since the 1979 Egypt–Israel peace treaty and the 1994 Israel–Jordan peace treaty, while its borders with Syria, Lebanon and the Palestinian territories remain internationally defined as contested.

Marshall Islands–United States relations are bilateral relations between Marshall Islands and the United States.
The decolonisation of Oceania occurred after World War II when nations in Oceania achieved independence by transitioning from European colonial rule to full independence.

Mandatory Palestine was a geopolitical entity that existed between 1920 and 1948 in the region of Palestine under the terms of the League of Nations Mandate for Palestine.

The Israeli annexation of East Jerusalem, known to Israelis as the reunification of Jerusalem, refers to the Israeli occupation of East Jerusalem during the 1967 Six-Day War, and its annexation.