External links
| | This United Nations–related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
| | This article related to international law is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
The United Nations Standard Minimum Rules for the Administration of Juvenile Justice, often referred to as the Beijing Rules, is a resolution of the United Nations General Assembly regarding the treatment of juvenile prisoners and offenders in member nations.
In September 1980, the United Nations held its Sixth United Nations Congress on the Prevention of Crime and the Treatment of Offenders in Caracas, Venezuela. The UN had previously declared 1980 the "Year of the Child".
Dahn Batchelor, who holds a certificate in criminology and participant at that Congress, presented a paper about the need for a bill of rights for young offenders. The United States delegation supported the paper. Much drafting of the policy took place at a conference in Beijing, China. It was originally proposed as a Bill of Rights for Young Offenders, but was eventually renamed the United Nations Standard Minimum Rules on the Administration of Juvenile Justice.
The proposed draft was then discussed at length at the United Nations Seventh Congress on the Prevention of Crime and the Treatment of Offenders in Milan, Italy, in September 1985.
It was adopted on 29 November 1985 by the United Nations General Assembly.

The United Nations Convention on the Rights of the Child is an international human rights treaty which sets out the civil, political, economic, social, health and cultural rights of children. The convention defines a child as any human being under the age of eighteen, unless the age of majority is attained earlier under national legislation.
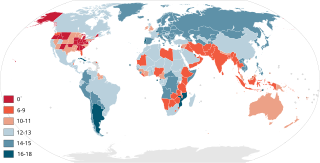
The age of criminal responsibility is the age below which a child is deemed incapable of having committed a criminal offence. In legal terms, it is referred to as a defence/defense of infancy, which is a form of defense known as an excuse so that defendants falling within the definition of an "infant" are excluded from criminal liability for their actions, if at the relevant time, they had not reached an age of criminal responsibility. After reaching the initial age, there may be levels of responsibility dictated by age and the type of offense committed.
Measure 11, also known as "One Strike You're Out", was a citizens' initiative passed in 1994 in the U.S. State of Oregon. This statutory enactment established mandatory minimum sentencing for several crimes. The measure was approved in the November 8, 1994 general election with 788,695 votes in favor, and 412,816 votes against.

Juvenile delinquency, also known as juvenile offending, is the act of participating in unlawful behavior as a minor or individual younger than the statutory age of majority. The term delinquent usually refers to juvenile delinquency, and is also generalised to refer to a young person who behaves an unacceptable way.

A juvenile court, also known as young offender's court or children's court, is a tribunal having special authority to pass judgements for crimes that are committed by children who have not attained the age of majority. In most modern legal systems, children who commit a crime are treated differently from legal adults that have committed the same offense.

The Juvenile Justice and Delinquency Prevention Act of 1974 (JJDPA) is a United States federal law providing formula grants to states that follow a series of federal protections on the care and treatment of youth in the juvenile justice and criminal justice systems.

The Juvenile Justice Act, 2000 is the primary legal framework for juvenile justice in India. The act provides for a special approach towards the prevention and treatment of juvenile delinquency and provides a framework for the protection, treatment and rehabilitation of children in the purview of the juvenile justice system. This law, brought in compliance of the 1989 UN Convention on the Rights of the Child (UNCRC), repealed the earlier Juvenile Justice Act of 1986 after India signed and ratified the UNCRC in 1992. In the wake of Delhi gang rape, the law suffered a nationwide criticism owing to its helplessness against crimes where juveniles get involved in heinous crimes like rape and murder. In 2015, responding to the public sentiment, both the houses of parliament in India further amended the bill that proposed adult-like treatment for juveniles aged 16–18 above accused of heinous crimes. The lower house, i.e. Lok Sabha passed the bill on 7 May 2015 and the upper house, i.e. Rajya Sabha on 22 December 2015. The bill was approved by President Pranab Mukherjee's assent on 31 December 2015.

The American juvenile justice system is the primary system used to handle minors who are convicted of criminal offenses. The system is composed of a federal and many separate state, territorial, and local jurisdictions, with states and the federal government sharing sovereign police power under the common authority of the United States Constitution. The juvenile justice system intervenes in delinquent behavior through police, court, and correctional involvement, with the goal of rehabilitation. Youth and their guardians can face a variety of consequences including probation, community service, youth court, youth incarceration and alternative schooling. The juvenile justice system, similar to the adult system, operates from a belief that intervening early in delinquent behavior will deter adolescents from engaging in criminal behavior as adults.

The United Nations Standard Minimum Rules for the Treatment of Prisoners were adopted by the United Nations General Assembly on 17 December 2015 after a five-year revision process. They are known as the Mandela Rules in honor of the former South African President, Nelson Mandela. The Mandela Rules are composed of 122 "rules". Not all are rules, but some are principles such as institutional equality and the philosophy of confinement.
Juvenile delinquency in the United States refers to crimes committed by children or young people, particularly those under the age of eighteen.
The Council of Europe have been organising Conferences of Ministers of Justice (MJU) on a regular basis since 1961. They constitute an important forum of exchange and coordination of legal policy at the pan-European level. They are one of the best known of the Council of Europe's Conferences of Specialised Ministers.

The United States incarcerates more of its youth than any other country in the world through the juvenile courts and the adult criminal justice system, which reflects the larger trends in incarceration practices in the United States. In 2010, approximately 70,800 juveniles were incarcerated in youth detention facilities alone. As of 2006, approximately 500,000 youth were brought to detention centers in a given year. This data does not reflect juveniles tried as adults. As of 2013, around 40% were incarcerated in privatized, for-profit facilities.
The International Penal and Penitentiary Foundation is an international organisation with quasi-governmental status. It promotes studies on crime-prevention and treatment of offenders, focussing on research, publications and teaching. It has been approved by the General Assembly of the United Nations and holds consultative status at the United Nations and the Council of Europe.

Criminal justice reform seeks to address structural issues in criminal justice systems such as racial profiling, police brutality, overcriminalization, mass incarceration, and recidivism. Reforms can take place at any point where the criminal justice system intervenes in citizens’ lives, including lawmaking, policing, sentencing and incarceration. Criminal justice reform can also address the collateral consequences of conviction, including disenfranchisement or lack of access to housing or employment, that may restrict the rights of individuals with criminal records.

The United Nations Congress on Crime Prevention and Criminal Justice is a United Nations (UN) sponsored congress on the topics of crime, crime prevention and criminal justice, held every five years. It is organized by the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC). Participants of the Congress include UN Member States and Observers, international organizations, non-governmental organization and individual experts.
Prisoners in New Zealand are afforded numerous, but not all, human rights. Criticisms by a United Nations report in 2014 highlighted various issues that constitute ill-treatment of prisoners, such as remand prisoners being routinely held on lock-down for 19 hours per day, an increasingly strict prison regime, and the mixing of adult and youth prisoners.
The Bangkok Rules, or formally, "The United Nations Rules for the Treatment of Women Prisoners and Non-custodial Measures for Women Offenders", is a set of 70 rules focused on the treatment of female offenders and prisoners adopted by the United Nations General Assembly on 22 December 2010. The Bangkok Rules, or the "70 Rules" as it is frequently known, is the first set of rules tailored to the treatment of women prisoners. It supplements existing international standards on the treatment of prisoners, particularly the Standard Minimum Rules for the Treatment of Prisoners, which applies to all prisoners regardless of gender.
The Islamic Republic of Iran signed the UN Convention on the Rights of the Child (CRC) in 1991 and ratified it in 1994. Upon ratification, Iran made the following reservation: "If the text of the Convention is or becomes incompatible with the domestic laws and Islamic standards at any time or in any case, the Government of the Islamic Republic shall not abide by it."

The Commission on Crime Prevention and Criminal Justice (CCPCJ) is a functional commission of the United Nations Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC) based in Vienna. The commission serves as the primary organ that guides the activities of the United Nations in the fields of crime prevention and criminal justice.
Asia Crime Prevention Foundation (ACPF) is a not-for-profit organization that works for peace and stability in Asia with the help of policies related to crime prevention in Asia. The organization was started in Tokyo in 1982 with the support of United Nations Asia and the Far East Institute for the Prevention of Crime and the Treatment of Offenders (UNAFEI). It was granted the special consultative status by the UN in 1991 and reclassified to same status in 2000.