
The United Nations Organization Stabilization Mission in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, or MONUSCO, is a United Nations peacekeeping force in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC). A planned withdrawal from the country is currently on indefinite hold due to the unstable security situation.

Operation Artemis, formally European Union Force Democratic Republic of the Congo (EUFOR), was a short-term European Union-led UN-authorised military mission to the Democratic Republic of the Congo in 2003, during the Ituri conflict. ARTEMIS is considered the first military operation led by the EU, the first autonomous EU operation, the first rapid response mission of the EU, first operation outside Europe, first operation applying the principle of the framework nation and first example of "relay operation", conducted in cooperation between the EU and the United Nations. The deployment of EUFOR troops quickly decreased the conflict's intensity. It marked the first autonomous EU military mission outside Europe and an important milestone in development of the European Security and Defence Policy.
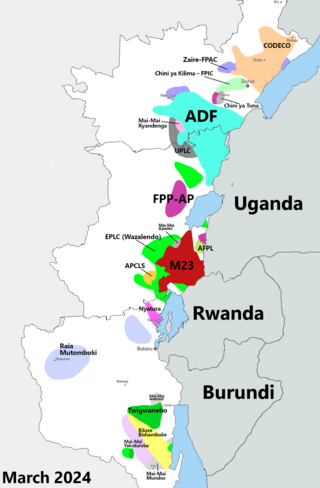
The Kivu conflict is an umbrella term for a series of protracted armed conflicts in the North Kivu and South Kivu provinces in the eastern Democratic Republic of the Congo which have occurred since the end of the Second Congo War. Including neighboring Ituri province, there are more than 120 different armed groups active in the eastern Democratic Republic of Congo. Currently, some of the most active rebel groups include the Allied Democratic Forces, the Cooperative for the Development of the Congo, the March 23 Movement, and many local Mai Mai militias. In addition to rebel groups and the governmental FARDC troops, a number of national and international organizations have intervened militarily in the conflict, including the United Nations force known as MONUSCO, and an East African Community regional force.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 1906, adopted unanimously on December 23, 2009, after reaffirming previous resolutions on the topic and noting the situation in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, the Council decided to extend the mandate of the United Nations Mission in the Democratic Republic of Congo (MONUC) until 31 May 2010. The resolution therefore allowed 21,000 police and domestic and international troops to remain the country.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 1925, adopted unanimously on May 28, 2010, after reaffirming previous resolutions on the situation in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, the Council extended the mandate of the United Nations Mission in the Democratic Republic of Congo (MONUC) until June 30, 2010, authorised a withdrawal of 2,000 troops and decided that from July 1, 2010, MONUC would be known as the United Nations Organization Stabilization Mission in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (MONUSCO) with a mandate until June 30, 2011.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1304, adopted unanimously on 16 June 2000, after recalling resolutions 1234 (1999), 1258 (1999), 1273 (1999), 1279 (1999), 1291 (1999) and 1296 (2000) on situation in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, the Council demanded the immediate withdrawal of Ugandan, Rwandan, Congolese opposition and other armed groups from Kisangani in the Democratic Republic of the Congo.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1332, adopted unanimously on 14 December 2000, after recalling resolutions 1234 (1999), 1258 (1999), 1265 (1999), 1273 (1999), 1279 (1999), 1291 (2000), 1296 (2000), 1304 (2000) and 1323 (2000) on situation in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, the Council extended the mandate of the United Nations Mission in the Democratic Republic of Congo (MONUC) until 15 June 2001.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1355, adopted unanimously on 15 June 2001, after recalling resolutions 1234 (1999), 1258 (1999), 1265 (1999), 1273 (1999), 1279 (1999), 1291 (2000), 1296 (2000), 1304 (2000), 1323 (2000), 1332 (2000) and 1341 (2001) on situation in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, the Council extended the mandate of the United Nations Mission in the Democratic Republic of Congo (MONUC) until 15 June 2002 subject to review every four months.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1445 was adopted unanimously on 4 December 2002. After recalling all previous resolutions on situation in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, the council expanded the military component of the United Nations Mission in the Democratic Republic of Congo (MONUC) to a level of 8,700 military personnel–up from 4,250–in two task forces.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1468, adopted unanimously on 20 March 2003, after recalling previous resolutions on the situation in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, the Council welcomed an agreement on the establishment of a transitional government and requested an increased presence of the United Nations Mission in the Democratic Republic of Congo (MONUC) in the Ituri region in the east of the country amid escalating violence.
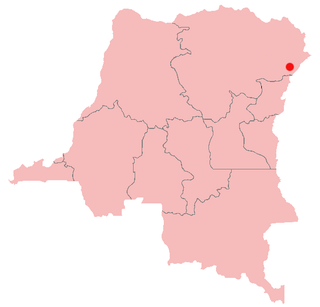
United Nations Security Council Resolution 1484, adopted unanimously on 30 May 2003, after recalling previous resolutions on the situation in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, the Council authorised Operation Artemis in Bunia, the capital of Ituri Province, amid the deteriorating security situation in the area.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1493, adopted unanimously on 28 July 2003, after recalling all resolutions on the situation in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, the council extended the mandate of the United Nations Mission in the Democratic Republic of Congo (MONUC) until 30 July 2004 and raised its troop level from 8,700 to 10,800.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1565, adopted unanimously on 1 October 2004 after recalling all previous resolutions on the situation in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, extended the mandate of the United Nations Mission in the Democratic Republic of Congo (MONUC) until 31 March 2005 and authorised an additional deployment of 5,900 troops and police. It reaffirmed the commitment to respect the “sovereignty, territorial integrity and political independence [sic]” of Congo and States in the region.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 1952, adopted unanimously on November 29, 2010, after recalling previous resolutions on the situation in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, including resolutions 1807 (2008), 1857 (2008) and 1896 (2009), the Council renewed an arms embargo and related targeted sanctions for a further period until November 30, 2011.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 1592, adopted unanimously on 30 March 2005, after recalling all previous resolutions on the situation in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, including Resolution 1565 (2004), the Council extended the mandate of the United Nations Mission in the Democratic Republic of Congo (MONUC) until 1 October 2005.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1635, adopted unanimously on 28 October 2005, after recalling all previous resolutions on the situation in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, including resolutions 1565 (2004), 1592 (2005), 1596 (2005), 1621 (2005) and 1628 (2005), the Council extended the mandate of the United Nations Mission in the Democratic Republic of Congo (MONUC) until 30 September 2006.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 1698, adopted unanimously on July 31, 2006, after recalling all previous resolutions concerning the situation in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, including resolutions 1493 (2003), 1533 (2004), 1552 (2004), 1565 (2004), 1592 (2005), 1596 (2005), 1616 (2005), 1649 (2005) and 1654 (2006), the Council renewed sanctions against the country until July 31, 2007.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 1711, adopted unanimously on September 29, 2006, after recalling all previous resolutions concerning the situation in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, including resolutions 1565 (2004), 1592 (2005), 1596 (2005), 1621 (2005), 1628 (2005), 1635 (2005), 1671 (2006) and 1693 (2006), and resolutions 1650 (2005), 1669 (2006), 1692 (2006) on the situation in Burundi and the African Great Lakes region, the Council extended the mandate of the United Nations Mission in the Democratic Republic of Congo (MONUC) until February 15, 2007.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 2078 was unanimously adopted on 28 November 2012.

The United Nations Force Intervention Brigade (FIB) is a military formation which constitutes part of the United Nations Organization Stabilization Mission in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (MONUSCO). It was authorized by the United Nations Security Council on 28 March 2013 through Resolution 2098. Although it is not the first instance in which the use of force was authorized by the UN, the Force Intervention Brigade is the first UN peacekeeping operation specifically tasked to carry out targeted offensive operations to "neutralize and disarm" groups considered a threat to state authority and civilian security. In this case, the main target was the M23 militia group, as well as other Congolese and foreign rebel groups. While such operations do not require the support of the Armed Forces of the Democratic Republic of the Congo (FARDC), the Force Intervention Brigade often acts in unison with the FARDC to disarm rebel groups.

















