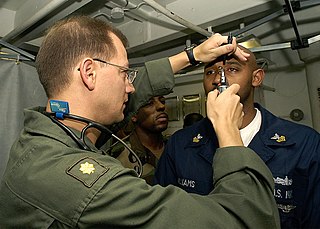
A flight surgeon is a military medical officer practicing in the clinical field of aviation medicine, which is also occasionally known as flight surgery.

United States astronaut badges are the various badges of the United States which are awarded to military and civilian personnel of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration, the various child departments of the Department of Defense, or a private space-faring entity, who have performed a spaceflight. The military versions are among the least-awarded qualification badges of the United States armed forces.
An aviator badge is an insignia used in most of the world's militaries to designate those who have received training and qualification in military aviation. Also known as a pilot's badge, or pilot wings, the aviator badge was first conceived to recognize the training that military aviators receive, as well as provide a means to outwardly differentiate between military pilots and the “foot soldiers” of the regular ground forces.
The Observer Badge is a military badge of the United States armed forces dating from the First World War. The badge was issued to co-pilots, navigators, and flight support personnel who had received a variation in the training required for the standard Pilot's Badge. The Observer Badge survived through the Second World War and into the 1950s, at which time the concept of an Observer Badge was phased out in favor of the modern Aircrew Badge and Navigator-Observer Badges. In addition to wings for Naval Aviators and Naval Flight Officers, the United States Navy still maintains an "Observer Badge" which is issued to flight-qualified mission specialists, such as a select number of meteorologists and intelligence officers in both the U.S. Navy and U.S. Marine Corps. The U.S. Air Force awards its USAF Observer Badge, which is identical to the USAF Navigator Badge, to Air Force officers who have qualified as NASA Space Shuttle Mission Specialists, have flown an actual mission aboard the shuttle and/or the International Space Station and who are otherwise not previously aeronautically rated as an Air Force pilot or navigator.
The Navigator Badge is a military qualification badge of the United States Air Force which was first created during the Second World War. The current USAF badge is designated by Air Force Instructions as the Navigator/Observer Badge and is issued to rated officers in both rating categories. In 2009, it was renamed as the Combat Systems Officer badge.
A naval flight officer (NFO) is a commissioned officer in the United States Navy or United States Marine Corps who specializes in airborne weapons and sensor systems. NFOs are not pilots (naval aviators), but they may perform many "co-pilot" or "mission specialist" functions, depending on the type of aircraft. Until 1966, their duties were performed by both commissioned officer and senior enlisted naval aviation observers (NAO).
The Flight Surgeon Badge is a military badge of the United States Armed Forces which has existed to designate Flight Surgeons since the Second World War.

Insignias and badges of the United States Navy are military badges issued by the United States Department of the Navy to naval service members who achieve certain qualifications and accomplishments while serving on both active and reserve duty in the United States Navy. Most naval aviation insignia are also permitted for wear on uniforms of the United States Marine Corps.

Badges of the United States Air Force are specific uniform insignia authorized by the United States Air Force that signify aeronautical ratings, special skills, career field qualifications, and serve as identification devices for personnel occupying certain assignments.
The Aircrew Badge, commonly known as Wings, is a qualification badge of the United States military that is awarded by all five branches of armed services to personnel who serve as aircrew members on board military aircraft. The badge is intended to recognize the training and qualifications required by aircrew of military aircraft. In order to qualify as an aircrew member and receive the Aircrew Badge, such personnel typically undergo advanced training in aircraft in-flight support roles.

Vance Air Force Base is a United States Air Force base located in southern Enid, Oklahoma, about 65 mi (105 km) north northwest of Oklahoma City. The base is named after local World War II hero and Medal of Honor recipient, Lieutenant Colonel Leon Robert Vance Jr.

A naval aviator is a commissioned officer or warrant officer qualified as a crewed aircraft pilot in the United States Navy or United States Marine Corps. United States Coast Guard crewed aircraft pilots are officially designated as "Coast Guard aviators", although they complete the same undergraduate flight training as Navy and Marine Corps crewed aircraft pilots, and are awarded the same aviation breast insignia.

A Weapon Systems Officer (WSO), nicknamed "Wizzo", is an air flight officer directly involved in all air operations and weapon systems of a military aircraft.

In the United States Armed Forces, the ranks of warrant officer and chief warrant officer are rated as officers above all non-commissioned officers, candidates, cadets, and midshipmen, but subordinate to the lowest officer grade of O‑1. This application differs from the Commonwealth of Nations and other militaries, where warrant officers are the most senior of the other ranks, equivalent to the U.S. Armed Forces grades of E‑8 and E‑9.

U.S. Air Force aeronautical ratings are military aviation skill standards established and awarded by the United States Air Force for commissioned officers participating in "regular and frequent flight", either aerially or in space, in performance of their duties. USAF aeronautical badges, commonly referred to as "wings" from their shape and their historical legacy, are awarded by the Air Force in recognition of degrees of achievement and experience. Officers earning these badges and maintaining their requirements are classified as rated officers and receive additional pay and allowances.

Strike Fighter Squadron 125 (VFA-125), also known as the "Rough Raiders", is a United States Navy strike fighter squadron based at Naval Air Station Lemoore, California. The "Rough Raiders" are a Fleet Replacement Squadron flying the F-35C Lightning II.

The Naval Air Training and Operating Procedures Standardization (NATOPS) program prescribes general flight and operating instructions and procedures applicable to the operation of all United States naval aircraft and related activities. The program issues policy and procedural guidance of the Chief of Naval Operations (CNO) and the Commandant of the Marine Corps (CMC) that is applicable to all United States Navy (USN) and United States Marine Corps (USMC) aviation personnel.

The Flying/Aviation Cadet Pilot Training Program was originally created by the U.S. Army to train its pilots. Originally created in 1907 by the U.S. Army Signal Corps, it expanded as the Army's air assets increased.
The US Navy had four programs for the training of naval aviators.

An officer is a person who holds a position of authority as a member of an armed force or uniformed service.


















