
Tektites are gravel-sized bodies composed of black, green, brown or grey natural glass formed from terrestrial debris ejected during meteorite impacts. The term was coined by Austrian geologist Franz Eduard Suess (1867–1941), son of Eduard Suess. They generally range in size from millimetres to centimetres. Millimetre-scale tektites are known as microtektites.

The Araguainha crater or Araguainha dome is an impact crater on the border of Mato Grosso and Goiás states, Brazil, between the villages of Araguainha and Ponte Branca. With a diameter of 40 kilometres (25 mi), it is the largest known impact crater in South America.

The Arkenu structures, also known as the Arkenu craters, are a pair of prominent circular geological structures in eastern Libya. The structures are approximately 10 kilometres (6.2 mi) and 6.8 kilometres (4.2 mi) in diameter, and lie about 70 kilometres (43 mi) west of Jabal Arkanu on the eastern margin of the al-Kufrah Basin.
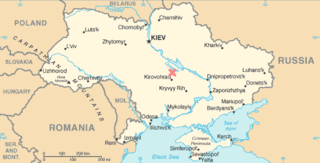
The Boltysh crater or Bovtyshka crater is a buried impact crater in the Kirovohrad Oblast of Ukraine, near the village of Bovtyshka. The crater is 24 kilometres (15 mi) in diameter and its age of 65.39 ± 0.14/0.16 million years, based on argon-argon dating techniques, less than 1 million years younger than Chicxulub crater in Mexico and the Cretaceous–Paleogene boundary. The Chicxulub impact is believed to have caused the mass extinction at the end of the Cretaceous period, which included the extinction of the non-avian dinosaurs. The Boltysh crater is currently thought to be unrelated to the Chicxulub impact, and to have not generated major global environmental effects.
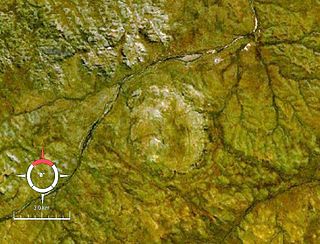
Foelsche is a partly buried impact structure, the eroded remnant of a former impact crater. It is situated about 85 km southeast of Borroloola in the Northern Territory, Australia, and named after the nearby Foelsche River. Although little of it is exposed at the surface, and no crater shaped topography is evident, the circular nature of the feature is obvious on aeromagnetic images, a factor that led to its discovery.

Gosses Bluff is thought to be the eroded remnant of an impact crater. Known as Tnorala to the Western Arrernte people of the surrounding region, it is located in the southern Northern Territory, near the centre of Australia, about 175 km (109 mi) west of Alice Springs and about 212 km (132 mi) to the northeast of Uluru. It was named by Ernest Giles in 1872 after Australian explorer William Gosse's brother Henry, who was a member of William's expedition.

Goyder is an impact structure, the eroded remnant of a former impact crater. It is situated in Arnhem Land in the Northern Territory, Australia, and was named after the nearby Goyder River. The impact occurred into Mesoproterozoic sedimentary rocks of the McArthur Basin. The deformed area is exposed at the surface and marked by a 3 km diameter ring of fractured and faulted sandstone, which is interpreted as the eroded relic of a central uplift ; the original crater rim, long since removed by erosion, being estimated at approximately 9–12 km diameter. Evidence for an impact origin includes the presence of shatter cones and shocked quartz in outcrops of deformed sandstone at the center of the site.
Obolon' crater Ukrainian: Оболонь is a 20 km (12 mi) diameter buried meteorite impact crater situated about 200 km (120 mi) southeast of Kyiv in Ukraine . The site has been drilled, which revealed the presence of shocked minerals and impact melt rock; the high chlorine content of the latter suggesting that the area was covered by shallow sea at the time of impact. One estimate puts the age at 169 ± 7 million years.

Ouarkziz is a meteorite impact crater in Algeria. It is 3.5 kilometers in diameter and the age is estimated to be less than 70 million years. The crater is exposed at the surface.

Riachão Ring is a meteorite impact crater in Brazil. It lies within the Parnaíba Basin. It is 4.5 kilometres (2.8 mi) in diameter and the age is estimated to be less than 200 million years. The crater is exposed at the surface.

Rochechouart impact structure or Rochechouart astrobleme is an impact structure in France. Erosion has over the millions of years has mostly destroyed its impact crater, the initial surface expression of the asteroid impact leaving highly deformed bedrock and fragments of the crater's floor as evidence of it.
Tookoonooka is a large meteorite impact crater (astrobleme) situated in South West Queensland, Australia. It lies deeply buried within Mesozoic sedimentary rocks of the Eromanga Basin and is not visible at the surface.

Vargeão Dome is a meteorite crater in Santa Catarina State, Brazil, straddling the municipalities of Vargeão, Faxinal dos Guedes, and Passos Maia.
Viewfield is an impact crater in Saskatchewan, Canada.

The Cumberland Gap is a pass in the eastern United States through the long ridge of the Cumberland Mountains, within the Appalachian Mountains and near the tripoint of Kentucky, Virginia, and Tennessee. At an elevation of 1,631 feet (497 m) above sea level, it is famous in American colonial history for its role as a key passageway through the lower central Appalachians.
In geology, a cryptoexplosion structure is an explosion of unknown cause. The term is now largely obsolete. It was once commonly used to describe sites where there was geological evidence of a large-scale explosion within the Earth's crust, but no definitive evidence for the cause such as normal volcanic rocks. These sites are usually circular with signs of anomalous rock deformation contrasting with the surrounding region, and often showing evidence that crustal material had been uplifted and/or blown outwards. The assumption was that some unusual form of volcanism, or a gas explosion originating within the crust, was the cause. The use of the term went away with the rise of the science of impact crater recognition in the late 20th century. Most structures described as cryptoexplosions turned out to be eroded impact craters, caused by the impact of meteorites. Today geologists discount former cryptoexplosion theories.

Vepriai is the largest town in Ukmergė district, Lithuania, situated south-west of Ukmergė with population of about 549 (2011). The capital of Vepriai elderate.

The Lac Wiyâshâkimî, also called the Clearwater Lakes in English and Allait Qasigialingat by the Inuit, are a pair of annular lakes on the Canadian Shield in Quebec, Canada, near Hudson Bay.
Amelia Creek crater is an impact structure, the eroded remnant of a former impact crater, located in the Davenport Range, Northern Territory, Australia. It lies within a low range of Paleoproterozoic sedimentary and volcanic rocks, which are extensively folded and faulted, thus making an eroded impact crater difficult to recognize. It was only discovered by the identification of shatter cones near its centre. The central shatter cone locality is surrounded by a 20 by 12 km area of anomalous deformation, the asymmetry being possibly related to very oblique impact, but may be at least partly due to the pre-existing structural complexity of the rocks. This deformed zone gives the best estimate for the original size of the crater. Impact took place after folding of the Paleoproterozoic rocks but before deposition of Neoproterozoic and Cambrian rocks which overlie them, thus constraining the impact event to the interval between about 1660 and 600 Ma.

















