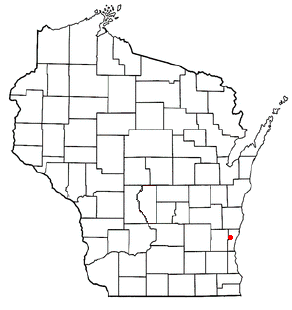
Saukville is a town in Ozaukee County, Wisconsin, United States. The Village of Saukville is located in the town's southeast quadrant. The population was 1,755 at the 2000 census.

Burns Bog is an ombrotrophic peat bog located in Delta, British Columbia, Canada. It is the largest raised peat bog and the largest undeveloped urban land mass on the West Coast of the Americas. Burns Bog was originally 4,000–4,900 hectares before development. Currently, only 3,500 hectares remain of the bog.

Big Bog State Recreation Area, a recent addition to the Minnesota state park system, is located on Minnesota State Highway 72, north of Waskish, Minnesota. It covers 9,459 acres (38.3 km2), primarily swamps, bogs, and upland "islands".

The Tannersville Cranberry Bog or Cranberry Swamp is a sphagnum bog on the Cranberry Creek in Tannersville, Pennsylvania. It is the southernmost boreal bog east of the Mississippi River, containing many black spruce and tamarack trees at the southern limit of their ranges. Technically, it can be classed as an acid fen, as it receives some groundwater flow. The site was designated a National Natural Landmark in December 1974. It was purchased by The Nature Conservancy and the Conservation and Research Foundation in 1957. Like many bogs, its terrain presents an image of solidity, but a liquid mass of decaying peat lies beneath a six-inch (152 mm) layer of sphagnum and a network of supporting tree roots. However, this bog may be viewed from a floating walkway.

Pinhook Bog is a unique bog in Indiana that has been designated a National Natural Landmark. It is part of Indiana Dunes National Park, an area that many citizens, scientists, and politicians fought hard to preserve. Its sister bog, Volo Bog, is located nearby. The bog contains a large variety of plants, including insect eating plants, tamarack trees, stands of blueberry bushes, and floating mats of sphagnum moss. Pinhook Bog is about 580 acres (2.3 km2), a quarter of which is a floating mat of sphagnum peat moss. A "moat" separates the bog from the uplands.

Cowles Bog is a 4,000-year-old wetland complex in Indiana Dunes National Park, near Chesterton, Indiana. It is named for Henry Chandler Cowles who did his pioneering work in ecology and ecological succession here. His work brought international attention to the area which led to efforts to preserve the Indiana Dunes. It was designated a National Natural Landmark in 1965. It contains bog, fen, marsh, wet meadow, swamp, and pond habitats.

Huntley Meadows Park, the largest park operated by the Fairfax County Park Authority, is located in the Hybla Valley area of Fairfax County, Virginia, south of the city of Alexandria. The park features a visitor center, a beaver-created wetland with boardwalk, wildlife observation platforms, and an interpretative trail system. The park is home to abundant wildlife and is known for attracting many birds, amphibians, and plants that are considered less common in the region. Secondary-growth forest, sprinkled with several small, native-grass and wildflower meadows surround much of the wetland habitat. The main bodies of water that flow through the park are Dogue Creek at the western border of the park, Barnyard Run, the source of the park's Central Wetland, and the headwaters of Little Hunting Creek.

Cors Caron is a raised bog in Ceredigion, Wales. Cors is the Welsh word for "bog". Cors Caron covers an area of approximately 349 hectares. Cors Caron represents the most intact surviving example of a raised bog landscape in the United Kingdom. About 44 different species groups inhabit the area including various land and aquatic plants, fish, insects, crustaceans, lichen, fungi, terrestrial mammals and birds.
Moss Lake Bog is an 84-acre (34 ha) site containing a 15-acre (6.1 ha) glacial kettle lake located in the town of Caneadea, New York, outside Houghton. Over time, sphagnum moss has grown over the open water, turning it into an acidic bog. It is managed by The Nature Conservancy as part of Moss Lake Preserve, and was declared a National Natural Landmark in 1973.
Wauconda Bog Nature Preserve is a tamarack bog nature preserve located in Wauconda Lake County, Illinois. It is a National Natural Landmark.

Hoosier Prairie is a unit of Indiana Dunes National Park in Lake County, Indiana. It began in the 1970s as wasteland that conservation organization found of a unique interest. From a core of 304 acres (123 ha), it has grown to 1,547 acres (626 ha) of important prairie habitat. The area was designated a National Natural Landmark in 1974 and a State Nature Preserve in 1977 The sandy soil creates a variety of habitats, from oak barrens, wet prairie, including sedge meadows and prairie marshes. More than 350 native species of vascular plants have been identified. A minimum of 43 species are uncommon in the State of Indiana.

The Cooperrider-Kent Bog State Nature Preserve is state nature preserve located mainly in Kent, Ohio. The preserve surrounds the Kent Bog, a remnant of the Wisconsin Glaciation. It is a true bog with acidic waters, and unique environmental conditions have enabled it to survive. The bog contains the largest stand of tamarack trees in the state of Ohio.

The Douglas-Hart Nature Center, located in Mattoon, Illinois, is a nature reserve that offers visitors different Illinois habitats, field programs, environmental educational classes, and volunteer opportunities for all ages.

Chiwaukee Prairie is a 485-acre (1.96 km2) prairie in Pleasant Prairie, Wisconsin managed by the Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources. It is located on Lake Michigan at the Illinois state line and includes grassy wetlands, wooded areas, and the Kenosha Sand Dunes at its northern tip. It is home to an abundance of wildlife. It was designated a Wisconsin State Natural Area in 1967 and a National Natural Landmark in 1973.

Grandma Lake Wetlands State Natural Area is a Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources-designated State Natural Area featuring the undeveloped, pristine 44-acre Grandma Lake, which lies in a depression formed during the last glacial period. The lake is ringed by a large, open sphagnum bog mat. The bog mat is surrounded by a coniferous swamp of tamarack and black spruce. The bog mat supports a plant community that is considered diverse and unusual, with several rare species present, including: bog arrow-grass, dragon's mouth orchid, livid sedge, small-headed bog sedge, as well as one of only a few known populations of bog rush in the State of Wisconsin. In 1991, the US Forest Service designated the site as a Research Natural Area. Also, the site is listed as one of Wisconsin's Wetland Gems, by the Wisconsin Wetlands Association.
Tamarack Swamp Natural Area is a boreal (non-glacial) bog in Sproul State Forest, in Clinton County, Pennsylvania, United States. It is named for the tamarack tree that is common in the surrounding wetland. The protected natural area consists of 267 acres within the larger Tamarack Swamp complex. Tamarack Swamp is considered an Important Bird Area by Audubon Pennsylvania, and was named as one of the top 100 birding sites in Pennsylvania by the Pennsylvania Game Commission.

The Alfred Bog is a domed peat bog in Eastern Ontario, Canada, about 7 kilometres (4.3 mi) south of Alfred and 70 kilometres (43 mi) east of Ottawa. The bog is considered the largest high-quality bog in Southern Ontario, and was designated by the Ontario Ministry of Natural Resources as a "Class 1 Wetland" and an "Area of Natural and Scientific Interest (ANSI)" in 1984. It is home to rare animal species and a healthy moose population.

Kiser Lake Wetlands State Nature Preserve, or simply Kiser Lake Wetlands, is a 51 acres (21 ha) nature reserve located in Johnson Township, Champaign County, Ohio, United States. It is located wholly within the Kiser Lake State Park, and operated by the Ohio Department of Natural Resources.

Wagner Natural Area is a provincially designated protected area in the Canadian province of Alberta, 8 kilometres (5.0 mi) west of Edmonton. It contains 130 hectares of land and predominantly comprises calcareous fens alongside marl ponds, wetland meadows, and forests of black spruce and tamarack. In 1987, it was designated as a Natural Area under the Wilderness Areas, Ecological Reserves, Natural Areas and Heritage Rangelands Act. Purchased by the Alberta provincial government in 1971, it is administered by the Wagner Natural Area Society (WNAS) and the Natural Resources Service of Alberta Environment. The most important feature of the area are the fens, which are now uncommon around Edmonton. The designation of the site as a natural area was primarily for the preservation of the fens. However one issue unresolved by the protective designation is that most of the groundwater reservoirs that feed the fens are outside of the Wagner Natural Area itself.