Protein Wnt-8a is a protein that in humans is encoded by the WNT8A gene. [5] Wnt8a may be involved in the development of early embryos as well as germ cell tumors. [5]
Protein Wnt-8a is a protein that in humans is encoded by the WNT8A gene. [5] Wnt8a may be involved in the development of early embryos as well as germ cell tumors. [5]
The Wnt8a gene is part of the Wnt family of genes and plays a role in vertebrates in the process of axis patterning. Wnt8a encodes for 2 proteins, Wnt8a.1 and Wnt8a.2 via a complicated mechanism involving the coordination of signaling molecules to control up and down stream promoters. [6] Furthermore, Wnt8a has shown to play a role in neural crest induction via Wnt/𝜷-catenin signaling based on experiments using zebrafish as a model organism. Wnt8a among other Wnt genes influence the Wnt/𝜷-catenin signaling in neural crest development. 𝜷-catenin is degraded in the absence of a Wnt signaling, but upon the binding of a Wnt ligand with a frizzled receptor and Lrp5/6 the 𝜷-catenin signaling molecule is no longer degraded. Instead, it interacts with transcription factors that activate Wnt expression, of which, Wnt8 is crucial for neural crest development and other cell fates. In a study of morpholino based gene knockdown in zebrafish, knocking down Wnt8a resulted in the lack of expression of various other genes important for neural crest induction (pax3, sox10, and foxd3). It is unclear however, if the loss of these neural crest specifiers is a result of Wnt8a directly in the induction process or is a downstream consequence of disruptions in Wnt8a signaling earlier in development. [7] Regardless, the results of this study show Wnt8a as a key player in neural crest induction.
The Wnt signaling pathways are a group of signal transduction pathways which begin with proteins that pass signals into a cell through cell surface receptors. The name Wnt is a portmanteau created from the names Wingless and Int-1. Wnt signaling pathways use either nearby cell-cell communication (paracrine) or same-cell communication (autocrine). They are highly evolutionarily conserved in animals, which means they are similar across animal species from fruit flies to humans.

Zinc finger protein GLI2 also known as GLI family zinc finger 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GLI2 gene. The protein encoded by this gene is a transcription factor.
Catenin beta-1, also known as beta-catenin (β-catenin), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CTNNB1 gene.
In the field of developmental biology, regional differentiation is the process by which different areas are identified in the development of the early embryo. The process by which the cells become specified differs between organisms.
Cripto is an EGF-CFC or epidermal growth factor-CFC, which is encoded by the Cryptic family 1 gene. Cryptic family protein 1B is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CFC1B gene. Cryptic family protein 1B acts as a receptor for the TGF beta signaling pathway. It has been associated with the translation of an extracellular protein for this pathway. The extracellular protein which Cripto encodes plays a crucial role in the development of left and right division of symmetry.

Dickkopf-related protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DKK1 gene.

Protein Wnt-3a is a protein that in humans is encoded by the WNT3A gene.

ZIC3 is a member of the Zinc finger of the cerebellum (ZIC) protein family.

Zinc finger protein ZIC2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ZIC2 gene. ZIC2 is a member of the Zinc finger of the cerebellum (ZIC) protein family.

Tyrosine-protein kinase-like 7 also known as colon carcinoma kinase 4 (CCK4) is a receptor tyrosine kinase that in humans is encoded by the PTK7 gene.

B-cell CLL/lymphoma 9 protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the BCL9 gene.

Wnt7b is a signaling protein that plays a crucial role for many developmental processes including placental, lung, eye, dendrite, and bone formation along with kidney development. The primary role of Wnt7b is to establish the cortico-medullary axis of epithelial organization.

Homeobox protein GBX-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GBX2 gene.

CXXC-type zinc finger protein 5 is a protein that is encoded by the CXXC5 gene in humans.

Dishevelled (Dsh) is a family of proteins involved in canonical and non-canonical Wnt signalling pathways. Dsh is a cytoplasmic phosphoprotein that acts directly downstream of frizzled receptors. It takes its name from its initial discovery in flies, where a mutation in the dishevelled gene was observed to cause improper orientation of body and wing hairs. There are vertebrate homologs in zebrafish, Xenopus (Xdsh), mice and humans. Dsh relays complex Wnt signals in tissues and cells, in normal and abnormal contexts. It is thought to interact with the novel protein, SPATS1, when regulating the Wnt Signalling pathway.
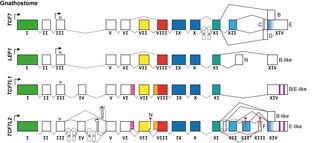
The TCF/LEF family is a group of genes that encode transcription factors which bind to DNA through a SOX-like high mobility group domain. They are involved in the Wnt signaling pathway, particularly during embryonic and stem-cell development, but also had been found to play a role in cancer and diabetes. TCF/LEF factors recruit the coactivator beta-catenin to enhancer elements of genes they target. They can also recruit members of the Groucho family of corepressors.

Retinal homeobox protein Rx also known as retina and anterior neural fold homeobox is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RAX gene. The RAX gene is located on chromosome 18 in humans, mice, and rats.

Protein Wnt-9b is a protein that in humans is encoded by the WNT9B gene.

SRY-box 17 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SOX17 gene.

ZIC5 is a member of the Zinc finger of the cerebellum (ZIC) protein family. ZIC5 is located on chromosome 13 in a divergently transcribed gene pair with the closely related gene ZIC2. It has been suggested that this tandem arrangement allows ZIC2 and ZIC5 to share regulatory elements and causes the two genes to have very similar expression patterns.