
Skania is a Cambrian fossil arthropod. The type species, S. fragillis, is known from the Burgess Shale of British Columbia, Canada. A second possible species "S." sundbergi is known from the Kaili Formation of China, but its placement within the genus has been questioned.

Eurypterus is an extinct genus of eurypterid, a group of organisms commonly called "sea scorpions". The genus lived during the Silurian period, from around 432 to 418 million years ago. Eurypterus is by far the most well-studied and well-known eurypterid. Eurypterus fossil specimens probably represent more than 95% of all known eurypterid specimens.

Canadaspis is an extinct genus of bivalved Cambrian arthropod, known from North America and China. They are thought to have been benthic feeders that moved mainly by walking and possibly used its biramous appendages to stir mud in search of food. They have been placed within the Hymenocarina, which includes other bivalved Cambrian arthropods.

Waptia is an extinct genus of arthropod from the Middle Cambrian of North America. It grew to a length of 6.65 cm (3 in), and had a large bivalved carapace and a segmented body terminating into a pair of tail flaps. It was an active swimmer and likely a predator of soft-bodied prey. It is also one of the oldest animals with direct evidence of brood care. Waptia fieldensis is the only species classified under the genus Waptia, and is known from the Burgess Shale Lagerstätte of British Columbia, Canada. Specimens of Waptia are also known from the Spence Shale of Utah, United States.

Alkenopterus is a genus of prehistoric eurypterid classified as part of the family Onychopterellidae. The genus contains two species, A. brevitelson and A. burglahrensis, both from the Devonian of Germany.

Nanahughmilleria is a genus of eurypterid, an extinct group of aquatic arthropods. Fossils of Nanahughmilleria have been discovered in deposits of Devonian and Silurian age in the United States, Norway, Russia, England and Scotland, and have been referred to several different species.

Onychopterella is a genus of predatory eurypterid, an extinct group of aquatic arthropods. Fossils of Onychopterella have been discovered in deposits from the Late Ordovician to the Late Silurian. The genus contains three species: O. kokomoensis, the type species, from the Early Pridoli epoch of Indiana; O. pumilus, from the Early Llandovery epoch of Illinois, both from the United States; and O. augusti, from the Late Hirnantian to Early Rhuddanian stages of South Africa.
A number of assemblages bear fossil assemblages similar in character to that of the Burgess Shale. While many are also preserved in a similar fashion to the Burgess Shale, the term "Burgess Shale-type fauna" covers assemblages based on taxonomic criteria only.
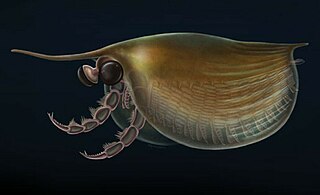
Isoxys is a genus of extinct bivalved Cambrian arthropod; the various species of which are thought to have been freely swimming predators. It had a pair of large spherical eyes, and two large frontal appendages used to grasp prey.

Radiodonta is an extinct order of stem-group arthropods that was successful worldwide during the Cambrian period. Radiodonts are distinguished by their distinctive frontal appendages, which are morphologically diverse and were used for a variety of functions. Radiodonts were among the earliest large predators, but they also included sediment sifters and filter feeders. Some of the most famous species of radiodonts are the Cambrian taxa Anomalocaris canadensis, Hurdia victoria, Peytoia nathorsti, Titanokorys gainesi, Cambroraster falcatus and Amplectobelua symbrachiata. The later surviving members include the subfamily Aegirocassisinae from the Early Ordovician of Morocco and the Early Devonian member Schinderhannes bartelsi from Germany.
This glossary describes the terms used in formal descriptions of spiders; where applicable these terms are used in describing other arachnids.

Progradungula otwayensis, commonly known as the Otway odd-clawed spider, is a species of cribellate spider endemic to the Great Otway National Park of Victoria, Australia. It is one of only three species in the gradungulid genus Progradungula.

Slimonidae is a family of eurypterids, an extinct group of aquatic arthropods. Slimonids were members of the superfamily Pterygotioidea and the family most closely related to the derived pterygotid eurypterids, which are famous for their cheliceral claws and great size. Many characteristics of the Slimonidae, such as their flattened and expanded telsons, support a close relationship between the two groups.

Strabops is a genus of strabopid, an extinct group of arthropods. Strabops is known from a single specimen from the Late Cambrian of the Potosi Dolomite, Missouri, collected by a former professor, Arthur Thacher. It is classified in the family Strabopidae of the monotypic order Strabopida, a group closely related to the aglaspidids with uncertain affinities. The generic name is composed by the Ancient Greek words στραβός, meaning "squinting", and ὄψῐς, meaning "face".

Paleomerus is a genus of strabopid, a group of extinct arthropods. It has been found in deposits from the Cambrian period. It is classified in the family Strabopidae of the monotypic order Strabopida. It contains two species, P. hamiltoni from Sweden and P. makowskii from Poland. The generic name is composed by the Ancient Greek words παλαιός (palaiós), meaning "ancient", and μέρος (méros), meaning "part".
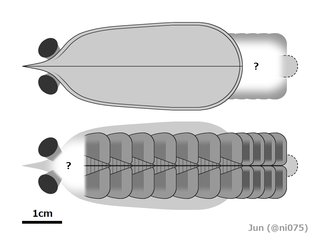
Erratus is an extinct genus of marine arthropod from the Cambrian of China. Its type and only species is Erratus sperare. Erratus is likely one of the most basal known arthropods, and its discovery has helped scientists understand the early evolution of arthropod trunk appendages. Some of the stem-arthropods like radiodonts did not have legs, instead they had flap like appendages that helped them swim. Erratus on the other hand had not only flaps but also a set of primitive legs. It also supported the theory that the gills of aquatic arthropods probably evolved into the wings and lungs of terrestrial arthropods later in the Paleozoic.

Oelandocaris is an extinct genus of stem-mandibulate, or possibly a megacheiran, within the family Oelandocarididae.

Rehbachiella is a genus of Cambrian crustacean comprising the only species Rehbachiella kinnekullensis. It is a possible branchiopod from the Orsten of Sweden.

Bredocaris admirabilis is a pancrustacean from the Cambrian Orsten.
Sandtorpia vestrogothiensis is a Cambrian arthropod from the Orsten of Sweden. It is known from a single specimen.
















