
Singer Corporation is an American manufacturer of consumer sewing machines, first established as I. M. Singer & Co. in 1851 by Isaac M. Singer with New York lawyer Edward C. Clark. Best known for its sewing machines, it was renamed Singer Manufacturing Company in 1865, then the Singer Company in 1963. It is based in La Vergne, Tennessee, near Nashville. Its first large factory for mass production was built in 1863 in Elizabeth, New Jersey.

A loom is a device used to weave cloth and tapestry. The basic purpose of any loom is to hold the warp threads under tension to facilitate the interweaving of the weft threads. The precise shape of the loom and its mechanics may vary, but the basic function is the same.

A sewing machine is a machine used to sew fabric and materials together with thread. Sewing machines were invented during the first Industrial Revolution to decrease the amount of manual sewing work performed in clothing companies. Since the invention of the first sewing machine, generally considered to have been the work of Englishman Thomas Saint in 1790, the sewing machine has greatly improved the efficiency and productivity of the clothing industry.
The White Motor Company was an American automobile, truck, bus and agricultural tractor manufacturer from 1900 until 1980. The company also produced bicycles, roller skates, automatic lathes, and sewing machines. Before World War II, the company was based in Cleveland, Ohio. White Diesel Engine Division in Springfield, Ohio, manufactured diesel engine generators, which powered U.S. military equipment and infrastructure, namely Army Nike and Air Force Bomarc launch complexes, and other guided missile installations and proving grounds, sections of SAGE and DEW Line stations, radars, Combat Direction Centers and other ground facilities of the U.S. aerospace defense ring, such as the Texas Towers.

A crank is an arm attached at a right angle to a rotating shaft by which circular motion is imparted to or received from the shaft. When combined with a connecting rod, it can be used to convert circular motion into reciprocating motion, or vice versa. The arm may be a bent portion of the shaft, or a separate arm or disk attached to it. Attached to the end of the crank by a pivot is a rod, usually called a connecting rod (conrod).
The Crypt of Civilization is an impenetrable airtight chamber, built between 1937 and 1940, at the Oglethorpe University in Brookhaven, Georgia. The 2,000-cubic-foot (57 m3) repository is meant not to be opened before 8113 CE and contains numerous artifacts and sound recordings that illustrate civilization and human development to the 20th century. Classic literature and religious texts were also deposited, as well as items showing the extent of scientific progress to 1939.

Lycoming Engines is a major American manufacturer of aircraft engines. With a factory in Williamsport, Pennsylvania, Lycoming produces a line of horizontally opposed, air-cooled, four, six and eight-cylinder engines including the only FAA-certified aerobatic and helicopter piston engines on the market.

The Graphophone was the name and trademark of an improved version of the phonograph. It was invented at the Volta Laboratory established by Alexander Graham Bell in Washington, D.C., United States.

The Merrow Sewing Machine Company, best known for inventing the overlock sewing machine, is a manufacturer of sewing machines. After the explosion of his gunpowder mill in 1837, in 1838 J.M. Merrow built a knitting mill on the same site. The company developed crocheting machines for its own use and by 1887 evolved to design, build and market sewing machines exclusively. During its early decades it was organized as a partnership under various names: established in 1838 as Joseph M. Merrow & Sons by J. Makens Merrow, then Pitkin, Merrow, & Co., renamed Merrow Manufacturing Co. in 1857, then Merrow and Millard in 1863, J.B. Merrow and Sons in 1870, and incorporated as The Merrow Manufacturing Company in 1893. Originally all of its manufacturing was done at facilities in Merrow, Connecticut, and then in Hartford, Connecticut, after 1894. The company is currently based in Fall River, Massachusetts.

Union Switch & Signal was an American company based in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, which focused on railway signaling equipment, systems and services. The company was acquired by Ansaldo STS in 1988, operating as a wholly-owned company until January 2009, when US&S was renamed "Ansaldo STS USA" to operate as a subsidiary of Ansaldo in the Americas and Asia.

The White Sewing Machine Company was a sewing machine company founded in 1858 in Templeton, Massachusetts, by Thomas H. White and based in Cleveland, Ohio, since 1866.
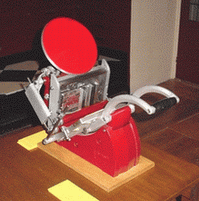
Adana Printing Machines were manufactured from 1922 to 1999 in Twickenham, England. Although most of the printing presses produced by Adana were aimed at hobby printers, they were frequently put to commercial use. Adanas are still to be found throughout the world in the hands of colleges, enthusiasts and professional printers. Caslon Limited manufactured machines after a takeover of the company in 1987.

Allen Benjamin Wilson (1823–1888) was an American inventor famous for designing, building and patenting some of the first successful sewing machines. He invented both the vibrating and the rotating shuttle designs which, in turns, dominated all home lockstitch sewing machines. With various partners in the 19th century he manufactured reliable sewing machines using the latter shuttle type.
The Singer Model 27 and later model 127 were a series of lockstitch sewing machines produced by the Singer Manufacturing Company from the 1880s to the 1960s.. They were Singer's first sewing machines to make use of "vibrating shuttle" technology. Millions were produced. They are all steel and cast iron, and were built before the advent of planned obsolescence, and so they were designed to be repaired rather than replaced. Consequently many remain today, some in collections and others still in service. In company literature they were called "the woman's faithful friend the world over".
A vibrating shuttle is a bobbin driver design used in home lockstitch sewing machines during the second half of the 19th century and the first half of the 20th century. It supplanted earlier transverse shuttle designs, but was itself supplanted by rotating shuttle designs.

The rotary hook or rotating hook is a bobbin driver design used in lockstitch sewing machines since the 19th century. It triumphed over competing designs because it can run at higher speeds with less vibration. Rotary hooks and oscillating shuttles are the two most common bobbin drivers in use today.

Throughout history, lockstitch sewing machines have used a variety of methods to drive their bobbins so as to create the lockstitch.

The White Sewing Machine was the first sewing machine from the White Sewing Machine Company. It used a vibrating shuttle bobbin driver design. For that reason, and to differentiate it from the later White Family Rotary that used a rotary hook design instead, it came to be known as the "White Vibrating Shuttle" or "White VS". In 1879 it cost USD50 to US$125 depending on which table or cabinet it was to be mounted in. The White VS continued in production, with improvements, until the early 1900s.
The Jones Sewing Machine Company was a British manufacturer of sewing machines founded in 1860 by William Jones and Thomas Chadwick under the name Chadwick and Jones that later become known as the Jones Sewing Machine Company.

The Singer Featherweight is a model series of lockstitch domestic sewing machines produced by the Singer Manufacturing Company from 1933 to 1968, significant among sewing machines for their continuing popularity, active use by quilters and high collector's value.















