
The Percidae are a family of ray-finned fish, part of the order Perciformes, which are found in fresh and brackish waters of the Northern Hemisphere. The majority are Nearctic, but there are also Palearctic species. The family contains more than 200 species in 11 genera. The perches and their relatives are in this family; well-known species include the walleye, sauger, ruffe, and three species of perch. However, small fish known as darters are also a part of this family.

The Squaliformes are an order of sharks that includes about 126 species in seven families.

The Carangidae are a family of ray-finned fish that includes the jacks, pompanos, jack mackerels, runners, trevallies, and scads. It is the largest of the six families included within the order Carangiformes. Some authorities classify it as the only family within that order but molecular and anatomical studies indicate that there is a close relationship between this family and the five former Perciform families which make up the Carangiformes.

Sander is a genus of predatory ray-finned fish in the family Percidae, which also includes the perches, ruffes, and darters. They are also known as "pike-perch" because of their resemblance to fish in the unrelated Esocidae (pike) family. They are the only genus in the monotypic tribe Luciopercini, which is one of two tribes in the subfamily Luciopercinae.

Pompanos are marine fish in the genus Trachinotus in the family Carangidae. Pompano may also refer to various other, similarly shaped members of the Carangidae, or the order Perciformes. Their appearance is of deep-bodied fishes, exhibiting strong lateral compression, with a rounded face and pronounced curve to the anterior portion of their dorsal profile. Their ventral profile is noticeably less curved by comparison, while their anterior profile is straight-edged, tapering sharply to a narrow caudal peduncle. Their dorsal and anal fins are typically sickle-shaped, with very long anterior rays and a succession of much shorter rays behind, with a similarly long & curved, deeply forked tail which has a narrow base. They are typically overall silvery in color, sometimes with dark or yellowish fins, and one or a few black markings on the side of their body. They are toothless and are relatively large fish, up to about 1.2 m (3.9 ft) long, although most species reach no more than half or two-thirds of that size. They are found worldwide in warmer seas, sometimes also entering brackish waters.

Notothenioidei is one of 19 suborders of the order Perciformes. The group is found mainly in Antarctic and Subantarctic waters, with some species ranging north to southern Australia and southern South America. Notothenioids constitute approximately 90% of the fish biomass in the continental shelf waters surrounding Antarctica.

Trichogaster is a genus of gouramis native to South Asia from Pakistan to Myanmar. It is the only genus in the monotypic subfamily Trichogastrinae as set out in the 5th Edition of Fishes of the World, although that book states that there are two genera, the other being Colisa which is treated as a synonym of Trichogaster by Fishbase and the Catalog of Fishes. Fishbase also places the genus in the Luciocephalinae. Species of this genus are very popular in the aquarium trade.

Haemulidae is a family of fishes in the order Perciformes known commonly as grunts. It is made up of the two subfamilies Haemulinae (grunters) and Plectorhynchinae (sweetlips), which in turn contain about 133 species in 19 genera. These fish are found in tropical fresh, brackish, and salt waters around the world. They are bottom-feeding predators, and named for the ability of Haemulinae to produce sound by grinding their teeth. They also engage in mutualistic relationship with cleaner gobies of genus Elacatinus, allowing them to feed on ectoparasites on their bodies.

Stichaeidae, the pricklebacks or shannies, are a family of marine ray-finned fishes in the suborder Zoarcoidei of the order Scorpaeniformes. Most species are found in the North Pacific Ocean with a few in the North Atlantic Ocean.
The Pseudotriakidae are a small family of ground sharks, belonging to the order Carcharhiniformes, containing the false catsharks and gollumsharks. It contains the only ground shark species that exhibit intrauterine oophagy, in which developing fetuses are nourished by eggs produced by their mother.

Jack mackerels or saurels are marine ray-finned fish in the genus Trachurus of the family Carangidae. The name of the genus derives from the Greek words trachys ("rough") and oura ("tail"). Some species, such as T. murphyi, are harvested in purse seine nets, and overfishing has sometimes occurred.

Dermatolepis is a genus of marine ray-finned fish, groupers from the subfamily Epinephelinae, part of the family Serranidae, which also includes the anthias and sea basses. They are found in the western Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans.

Gymnocephalus is a genus of ray-finned fishes from the family Percidae, which includes the perches, pike-perches and darters. They are from the Western Palearctic area, although one species, Gymnocephalus cernua has been accidentally introduced to the Great Lakes region where it is regarded as an invasive species. They have the common name "ruffe" and resemble the true perches in the genus Perca, but are usually smaller and have a different pattern.

Kuhlia xenura, the strange-tailed flagtail or Hawaii flagtail, is a species of ray-finned fish, a flagtail from the family Kuhliidae which is endemic to Hawaii, where it occurs in fresh, brackish, and marine waters. It can be found in tide pools, estuaries, and on reefs occurring over sand or rock.

An anchovy is a small, common forage fish of the family Engraulidae. Most species are found in marine waters, but several will enter brackish water, and some in South America are restricted to fresh water.

Bangana is a genus of fish in the family Cyprinidae, the carps and minnows. It is distributed across much of southern and eastern Asia. Species live mainly in the flowing waters of tropical and subtropical rivers.

Sebastiscus is a genus of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the subfamily Sebastinae part of the family Scorpaenidae. These fishes are native to the western Pacific Ocean. They are collectively called sea ruffes and resemble the rockfishes in the genus Sebastes, but are usually smaller and have a different pattern.
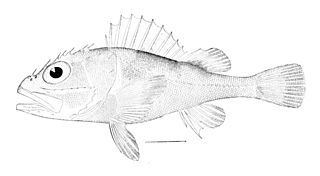
Trachyscorpia is a genus of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the subfamily Sebastinae, the rockfishes, part of the family Scorpaenidae. The species in this genus are found in the Atlantic, Indian and Pacific oceans.

Haemulinae is a subfamily of the Haemulidae and consists of the genera of that family which are regarded as being of New World origin, although they are now widespread. The subfamily is distinguished from the Plectorhynchinae by having a short dorsal fin which contains 13-16 soft rays, as opposed to the long dorsal fin with 17-26 soft rays of the subfamily Plectorhynchinae.

Rhonciscus is a genus of marine ray-finned fish, grunts belonging to the family Haemulidae. The species within the genus are found in the eastern Pacific and western Atlantic Ocean. It is not yet recognised by Fishbase but is by the Catalog of Fishes.



















