
A mango is an edible stone fruit produced by the tropical tree Mangifera indica. It originated from the region between northwestern Myanmar, Bangladesh, and northeastern India. M. indica has been cultivated in South and Southeast Asia since ancient times resulting in two types of modern mango cultivars: the "Indian type" and the "Southeast Asian type". Other species in the genus Mangifera also produce edible fruits that are also called "mangoes", the majority of which are found in the Malesian ecoregion.
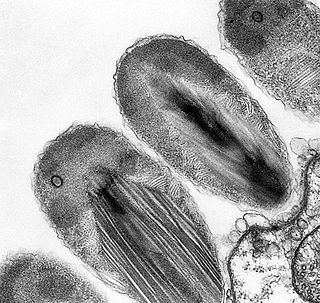
Verrucomicrobiota is a phylum of Gram-negative bacteria that contains only a few described species. The species identified have been isolated from fresh water, marine and soil environments and human faeces. A number of as-yet uncultivated species have been identified in association with eukaryotic hosts including extrusive explosive ectosymbionts of protists and endosymbionts of nematodes from genus Xiphinema, residing in their gametes.

Burong mangga is a Filipino side dish and concoction made by mixing sugar, salt, and water to mangoes that have previously been salted. The mixture of water and sugar should be boiled and cooled first, before pouring it over the salted mangoes. Some variants add chilis to the cooled sugar water mixture. Original "basic" burong mangga is made using a brine solution and pouring it over halved unripe or partially ripe mangoes. Mango cultivars commonly used for burong mangga include 'Carabao' mangoes and 'Pico' mangoes.
Xiphinema is a genus of ectoparasitic root nematodes commonly known as dagger nematodes. The genus is of economic importance on grape, strawberry, hops and a few other crops. Major species include X.americanum, X.diversicaudatum, X.index, X.italiae and X.pachtaicum. They can be easily recognized by their long bodies and stylets which are long enough to reach the vascular tissue of plants. Different members of the genus have been shown to induce moderate to large amounts of root damage through root penetration, which in some species results in the formation of galls. They are of agricultural concern because they are vectors of nepoviruses, transferring them during feeding. Efforts to study these nematodes in more detail have proved problematic in some species due to difficulties in maintaining populations in a greenhouse environment.
Xiphinema americanum, the American dagger nematode, is a species of plant pathogenic nematodes. It is one of many species that belongs to the genus Xiphinema. It was first described by N. A. Cobb in 1913, who found it on both sides of the United States on the roots of grass, corn, and citrus trees. Not only is Xiphinema americanum known to vector plant viruses, but also X. americanum has been referred to as "the most destructive plant parasitic nematode in America", and one of the four major nematode pests in the Southeastern United States.
Xiphinema diversicaudatum is an amphimictic ectoparasitic nematode species. This species has a characteristically long stylet capable of penetrating into a host's vascular tissue. They have a wide host range with some of the extensively studied ones being strawberry, hops and raspberry, due to their economic importance. The direct root damage caused through penetration near the root tip and formation of galls is a secondary concern when compared with the damage caused by vectoring the Arabis mosaic virus. The virus attaches to the interior cuticle lining and can be transferred from infected to uninfected root tissue as the nematode feeds and sheds. Management of this particular nematode relies on nematicides such as 1,3-Dichloropropene (Telone) at 40 gpa.or methyl bromide at 1000 lb/ac to control to 28 in deep.
Xiphinema index, the California dagger nematode, is a species of plant-parasitic nematodes.
Xiphinema insigne is a plant pathogenic nematode infecting tea. They are known to infect cacao trees.
Xiphinema rivesi is a plant pathogenic nematode infecting caneberries and fruit trees.
Xiphinema vuittenezi is a plant pathogenic nematode infecting apple and pear.
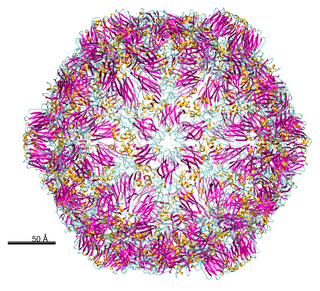
Grapevine fanleaf virus (GFLV) is a plant pathogenic virus of the family Secoviridae. It infects grapevines, causing chlorosis of the leaves and lowering the fruit quality. Because of its effect on grape yield, GFLV is a pathogen of commercial importance. It is transmitted via a nematode vector, Xiphinema index. This nematode acquires the virus through feeding on roots of an infected plant, and passes it on in the same manner.
Tomato ringspot virus (ToRSV) is a plant pathogenic virus of the family Secoviridae. It affects species of cucumber, tobacco, tomato, cowpea, among others. It causes ringspots in tobacco plants and raspberries, yellow bud mosaic in peaches, yellow vein in grapes, and stunted growth in gladiolus and Narcissus. Its range is in the temperate regions of North America, especially where its vector, Xiphinema americanum is present. Along with the adult and larval stages of this nematode, the virus is also spread by seed. This type of infection is more common in strawberries and soybeans than any other susceptible plant.

The 'Shan-e-Khuda' mango is a late-season mango cultivar grown in Pakistan, specifically the Multan and Rahim Yar Khan districts.

Mangifera indica, commonly known as mango, is a species of flowering plant in the family Anacardiaceae. It is a large fruit tree, capable of growing to a height of 30 metres. There are two distinct genetic populations in modern mangoes – the "Indian type" and the "Southeast Asian type".
Mango is a Lolo-Burmese language spoken by just under 50 people in Guangnan County, Yunnan, China.

Green mango chutney, also known as raw mango chutney, is an Indian chutney prepared from unripe mangoes. Ripe mangoes are sweet and are not used for chutneys as they are eaten raw. Green unripe mangoes are hard and sour, and they are cooked as chutneys. Mango chutneys are tangy in taste.
Carenum brevicolle is a species of ground beetle in the subfamily Scaritinae. It was described by Sloane in 1894.
Agonum brevicolle is a species of ground beetle in the family Carabidae. It is found in North America.

The Sindhri mango is a mango cultivar grown in Sindhri, a town in Sindh, and other areas of Sindh province in Pakistan. It is a large oval shaped mango which is extremely sweet and aromatic.







