
Enoplea (enopleans) is a class, which with the classes Secernentea and Chromadorea make up the phylum Nematoda in current taxonomy. The Enoplea are considered to be a more ancestral group than the Chromadorea, and researchers have referred to its members as the "ancestrally diverged nematodes", compared to the "more recently diverged nematodes" of Chromadorea.

Ascaris is a genus of parasitic nematode worms known as the "small intestinal roundworms", which is a type of parasitic worm. One species, Ascaris lumbricoides, affects humans and causes the disease ascariasis. Another species, Ascaris suum, typically infects pigs. Parascaris equorum, the equine roundworm, is also commonly called an "ascarid".
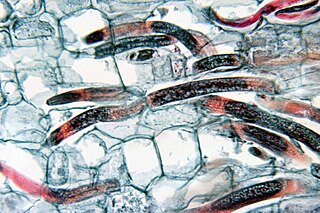
Radopholus similis is a species of nematode known commonly as the burrowing nematode. It is a parasite of plants, and it is a pest of many agricultural crops. It is an especially important pest of bananas and citrus, and it can be found on coconut, avocado, coffee, sugarcane, other grasses, and ornamentals. It is a migratory endoparasite of roots, causing lesions that form cankers. Infected plants experience malnutrition.

Meloidogyne incognita, also known as the "southern root-nematode" or "cotton root-knot nematode" is a plant-parasitic roundworm in the family Heteroderidae. This nematode is one of the four most common species worldwide and has numerous hosts. It typically incites large, usually irregular galls on roots as a result of parasitism.

Rotylenchulus reniformis, the reniform nematode, is a species of parasitic nematode of plants with a worldwide distribution in the tropical and subtropical regions.
Pratylenchus brachyurus is a plant parasitic nematode.
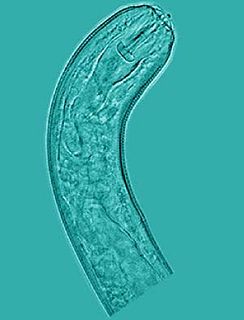
Pratylenchus zeae is a plant-pathogenic nematode found on potatoes, maize, cereal, tobacco, coffee, blackberry, and found most often on sugarcane.
Helicotylenchus multicinctus is a plant pathogenic nematode that affects primarily bananas and plantains. Nematodes of the genus Helicotylenchus are spiral nematodes and feed on a large variety of plant species.

Paratylenchus hamatus, the fig pin nematode, is a species of migratory plant endoparasites, that causes lesions on plant roots resulting in symptoms of chlorosis, wilting and ultimately yield losses. They move and feed on different parts of host tissue throughout their life cycle in order to find enough susceptible host tissue to survive and reproduce. A wide range of host plant species are susceptible to the fig pin nematode, including many valuable fruit and vegetable crops such as figs, carrots and celery. They are also commonly found associated with woody perennials in California. P. hamatus inhabits soils in both Europe and North America, and was originally isolated from fig in central California in 1950.
Xiphinema americanum, the American dagger nematode, is a species of plant pathogenic nematodes. It is one of many species that belongs to the genus Xiphinema. It was first described by N. A. Cobb in 1913, who found it on both sides of the United States on the roots of grass, corn, and citrus trees. Not only is Xiphinema americanum known to vector plant viruses, but also X. americanum has been referred to as "the most destructive plant parasitic nematode in America", and one of the four major nematode pests in the Southeastern United States.
Xiphinema diversicaudatum is an amphimictic ectoparasitic nematode species. This species has a characteristically long stylet capable of penetrating into a host’s vascular tissue. They have a wide host range with some of the extensively studied ones being strawberry, hops and raspberry, due to their economic importance. The direct root damage caused through penetration near the root tip and formation of galls is a secondary concern when compared with the damage caused by vectoring the arabis mosaic virus. The virus attaches to the interior cuticle lining and can be transferred from infected to uninfected root tissue as the nematode feeds and sheds. Management of this particular nematode relies on nematicides such as 1,3-Dichloropropene (Telone) at 40 gpa.or methyl bromide at 1000 lb/ac to control to 28 in deep.
Xiphinema index, the California dagger nematode, is a species of plant-parasitic nematodes.
Tylenchulus semipenetrans is a species of plant pathogenic nematodes and the causal agent of slow decline of citrus. T. semipenetrans is found in most citrus production areas and diverse soil textures worldwide. Their feeding strategy is semi-endoparasitic and has a very narrow host range among commonly grown crops. These nematodes are considered as major plant-parasitic nematode because they can cause 10-30% losses reported on citrus trees. They also parasitize other hosts such as olive, grape, persimmon and lilac. The citrus nematode was first discovered in California in 1913 by J.R. Hodges and was later described and named by Nathan Cobb that year.

Anguina agrostis is a plant pathogenic nematode.
Heterodera sacchari, the sugarcane cyst nematode, mitotic parthenogenic sedentary endoparasitic nematode. This plant-parasitic nematode infects the roots of sugarcane, and the female nematode eventually becomes a thick-walled cyst filled with eggs. Aboveground symptoms are species specific and are similar to those caused by other Heterodera species. Symptoms include: stunted and chlorotic plants, and reduced root growth. Seedlings may be killed in heavily infested soils.

Anguina is a genus of plant pathogenic nematodes.

Pratylenchus is a genus of nematodes known commonly as lesion nematodes. They are parasitic on plants and are responsible for root lesion disease on many taxa of host plants in temperate regions around the world. Lesion nematodes are migratory endoparasites that feed and reproduce in the root and move around, unlike the cyst or root-knot nematodes, which may stay in one place. They usually only feed on the cortex of the root. Species are distinguished primarily by the morphology of the stylets.
Globodera tabacum, commonly known as a tobacco cyst nematode, is a plant parasitic nematode that mainly infests the tobacco plant, but also plants in family Solanaceae.
Helicotylenchus is a genus of nematodes in the family Hoplolaimidae. They are known generally as spiral nematodes. They are found worldwide because they can live and survive in a wide range of habitats. They are among the most common parasitic nematodes of plants; found in corn, bananas, grass, soybeans.

Allantonematidae is a family of insect-parasitic nematodes from the order Tylenchida. Allantonematid nematodes infect a variety of insects including beetles, butterflies, flies, thrips, ants, and more. For instance, the nematode Howardula aoronymphium parasitizes mushroom-feeding fruit flies, Formicitylenchus oregonensis parasitizes carpenter ants, and Metaparasitylenchus hypothenemi parasitizes a pest of coffee beans, the coffee berry borer.










